|
IFNB1
Interferon beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IFNB1'' gene. The natural and recombinant protein Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be foun ... forms have antiviral, antibacterial, and anticancer properties. Interferon beta 1a (tradenames: Avonex and Rebif) and Interferon beta 1b (tradenames: Betaseron/Betaferon) are used as drugs. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-9-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant Protein
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining at least two fragments from two different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, and differ only in the nucleotide sequence within that identical overall structure. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, like the mythical chimera. R-DNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA may be joined to bact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
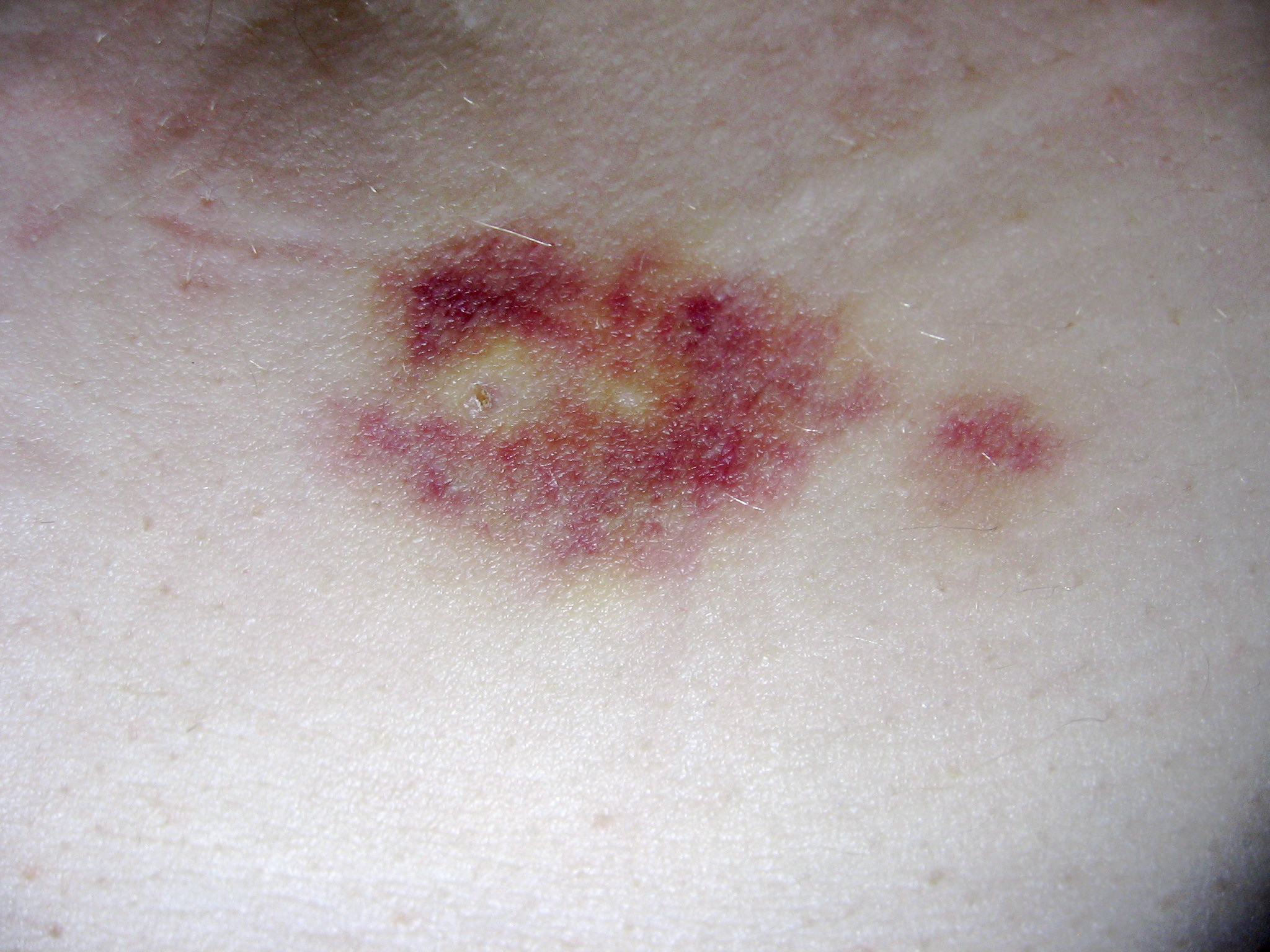
Interferon Beta 1a
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified '' E. coli''. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses. Interferon beta has not been shown to slow the advance of disability. Interferons are not a cure for MS (there is no known cure); the claim is that interferons may slow the progress of the disease if started early and continued for the duration of the disease. Medical uses Clinically isolated syndrome The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), that is, a single attack of a single symptom. During a CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive of demyelination which should be included in the spectrum of MS phenotypes. Treatment with interferons after an initial att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |