|
IFNAR2
Interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IFNAR2'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane protein that forms one of the two chains of a receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Binding and activation of the receptor stimulates Janus protein kinases, which in turn phosphorylate several proteins, including STAT1 and STAT2. Multiple transcript variants encoding at least two different isoforms have been found for this gene. Interactions IFNAR2 has been shown to interact with: * GNB2L1 Receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1), also known as guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-2-like 1 (GNB2L1), is a 35 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the RACK1 gene. Function RACK1 was originally isolated and identified ..., * IFNA2, * STAT1, and * STAT2. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Cytokine receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon-alpha/beta Receptor
The interferon-α/β receptor (IFNAR) is a virtually ubiquitous membrane receptor which binds endogenous type I interferon (IFN) cytokines. Endogenous human type I IFNs include many subtypes, such as interferons-α, -β, -ε, -κ, -ω, and -ζ. Function Activation of various innate immune signaling pathways ( TLR3, TLR4, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, cGAS, RIG-I, MDA-5) leads to the rapid induction of type I IFNs due to their (mostly) intronless gene structure. The regulatory elements upstream of type I IFN genes differ, allowing differential transcription of type I IFNs in response to stimuli. In particular, IFNβ contains a κB regulatory site, whereas IFNα subtypes do not. Production of specific type I IFNs is usually limited to a small number of type I IFN subtypes. Once secreted, type I IFNs signal through IFNAR in a paracrine and autocrine manner. IFNAR is a heteromeric cell surface receptor composed of two subunits, referred to as the low affinity subunit, IFNAR1, and the hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT2
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAT2'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. This protein is critical to the biological response of type I interferons (IFNs). STAT2 sequence identity between mouse and human is only 68%. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. In response to IFN, this protein forms a complex with STAT1 and IFN regulatory factor family protein p48 ( IRF9) and form ISGF-3 (IFN-stimulated gene factor-3), in which this protein acts as a transactivator, but lacks the ability to bind DNA directly. ISGF-3 proceeds the activation of genes via the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE). ISRE-driven genes include Ly-6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT1
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT1'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function All STAT molecules are phosphorylated by receptor associated kinases, that causes activation, dimerization by forming homo- or heterodimers and finally translocate to nucleus to work as transcription factors. Specifically STAT1 can be activated by several ligands such as Interferon alpha (IFNα), Interferon gamma (IFNγ), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), Interleukin 6 (IL-6), or IL-27. Type I interferons (IFN-α, IFN-ß) bind to receptors, cause signaling via kinases, phosphorylate and activate the Jak kinases TYK2 and JAK1 and also STAT1 and STAT2. STAT molecules form dimers and bind to ISGF3G/IRF-9, which is Interferon stimulated gene factor 3 complex with Interferon regulatory Factor 9. This allows STAT1 to enter the nucleus. STAT1 has a key role in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNB2L1
Receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1), also known as guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-2-like 1 (GNB2L1), is a 35 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the RACK1 gene. Function RACK1 was originally isolated and identified as an intracellular protein receptor for protein kinase C, noting the significant homology to the beta subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins. Later studies established RACK1, and its yeast homolog Asc1, as a core ribosomal protein of the eukaryotic small (40S) ribosomal subunit. Much of the function of Asc1/RACK1 appears to result from its position on the 'head' of the 40S ribosomal subunit. Asc1/RACK1 participates in several aspects of eukaryotic translation and ribosome quality control Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to for ..., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFNA2
Interferon alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IFNA2'' gene. Protein family Human interferon alpha-2 (IFNα2) is a cytokine belonging to the family of type I IFNs. IFNα2 is a protein secreted by cells infected by a virus and acting on other cells to inhibit viral infection. The first description of IFNs as a cellular agent interfering with viral replication was made by Alick Isaacs and Jean Lindenmann in 1957. The history of this finding was recently reviewed. There are 3 types of IFNs: Interferon type I, Interferon type II and Interferon type III. The type II IFN, also called IFNγ, is produced by specific cells of the immune system. Unlike type I and type III IFNs, IFNγ has only a modest role in directly restricting viral infections. Type I and type III IFNs act similarly. However, the action of type III IFNs, also known as IFNλ, is limited to epithelial cells while type I IFNs act on all body's cells. Type I IFNs form a family of several proteins: in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
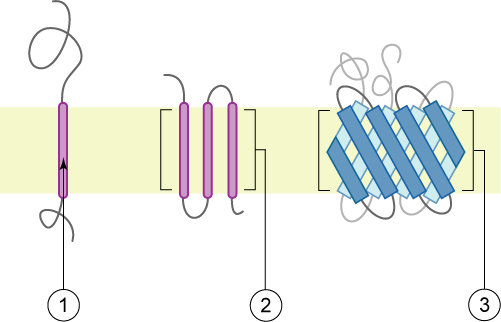
Type I Membrane Protein
A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome. Topology-based classification Bitopic proteins are classified into 4 types, depending on their transmembrane topology and location of the transmembrane he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Protein Kinase
Janus kinase (JAK) is a family of intracellular, non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transduce cytokine-mediated signals via the JAK-STAT pathway. They were initially named "just another kinase" 1 and 2 (since they were just two of many discoveries in a PCR-based screen of kinases), but were ultimately published as "Janus kinase". The name is taken from the two-faced Roman god of beginnings, endings and duality, Janus, because the JAKs possess two near-identical phosphate-transferring domains. One domain exhibits the kinase activity, while the other negatively regulates the kinase activity of the first. Family The four JAK family members are: * Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) * Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) * Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) * Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) Transgenic mice that do not express JAK1 have defective responses to some cytokines, such as interferon-gamma. JAK1 and JAK2 are involved in type II interferon (interferon-gamma) signalling, whereas JAK1 and TYK2 are involved in type I inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |