|
I1 Receptor
Imidazoline receptors are the primary receptor (biochemistry), receptors on which clonidine and other 2-Imidazoline, imidazolines act. There are three main classes of imidazoline receptor: I1 is involved in inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system to lower blood pressure, I2 has as yet uncertain functions but is implicated in several psychiatric conditions, and I3 regulates insulin secretion. Classes As of 2017, there are three known subtypes of imidazoline receptors: I1, I2, and I3. I1 receptor The I1 receptor appears to be a G protein-coupled receptor that is localized on the plasma membrane. It may be coupled to Phospholipase A2, PLA2 signalling and thus prostaglandin synthesis. In addition, activation inhibits the sodium-hydrogen antiporter and enzymes of catecholamine synthesis are induced, suggesting that the I1 receptor may belong to the neurocytokine receptor family, since its signaling pathways are similar to those of interleukins. It is found in the neurons of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and Signal_transduction, transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses, such as a change in the electrophysiology, electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptor, GABA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand (biochemistry), ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Cell surface receptors, also known as transmembrane receptors, include ligand-gated ion channels, G prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamines
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS 45041-90
RS may refer to: Businesses and organizations * RS Group, entertainment & media company in Thailand * RS Group plc, British electronics & industrial distributor in England with brands including RS Components and RS Americas, Inc * RS Infotainment, Indian film production and distribution company * RS Productions, defunct Australian television and radio production company * Relief Society, an official auxiliary of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) * République solidaire, a French political party * Roberval and Saguenay Railway (reporting mark RS) * Russian Party (Serbia) (''Ruska stranka''), a political party in Serbia Sport * RS Sailing, an international designer and builder of sailboats and dinghies * Queens Park Rangers F.C., a professional football club from Shepherd's Bush, London, commonly nicknamed 'The Rs' Places * Republic of Serbia (ISO 3166-1 code RS), country * Republic of Slovenia, country * Republika Srpska, one of the two political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CR-4056
CR-4056 is an analgesic drug candidate with a novel mechanism of action, acting as a ligand for the imidazoline receptor I2. It showed promising results in animal studies against various types of neuropathic pain, and has reached Phase II human clinical trials as a potential treatment for pain associated with osteoarthritis. See also * List of investigational analgesics This is a list of investigational analgesics, or analgesics that are currently under development for clinical use but are not yet approved. ''Chemical/generic names are listed first, with developmental code names, synonyms, and brand names in par ... References Analgesics Imidazoline receptor modulators {{analgesic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moxonidine
Moxonidine (INN) is a new-generation alpha-2/imidazoline receptor agonist antihypertensive drug licensed for the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. It may have a role when thiazides, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers are not appropriate or have failed to control blood pressure. In addition, it demonstrates favourable effects on parameters of the insulin resistance syndrome, apparently independent of blood pressure reduction. It is also a growth hormone releaser. It is manufactured by Solvay Pharmaceuticals (acquired by Abbott in 2009) under the brand name Physiotens and Moxon. Mechanism of action Moxonidine is a selective agonist at the imidazoline receptor subtype 1 (I1). This receptor subtype is found in both the rostral ventro-lateral pressor and ventromedial depressor areas of the medulla oblongata. Moxonidine therefore causes a decrease in sympathetic nervous system activity and, therefore, a decrease in blood pressure. Compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGN 192403
AGN may refer to: * Active galactic nucleus * Acute glomerulonephritis * Agutaynen language * Allergan Allergan plc is an American, Irish-domiciled pharmaceutical company that acquires, develops, manufactures and markets brand name drugs and medical devices in the areas of medical aesthetics, eye care, central nervous system, and gastroenterology. ... (stock symbol AGN) * Angoon Seaplane Base, Angoon, Alaska, United States * (''General National Archive'') {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
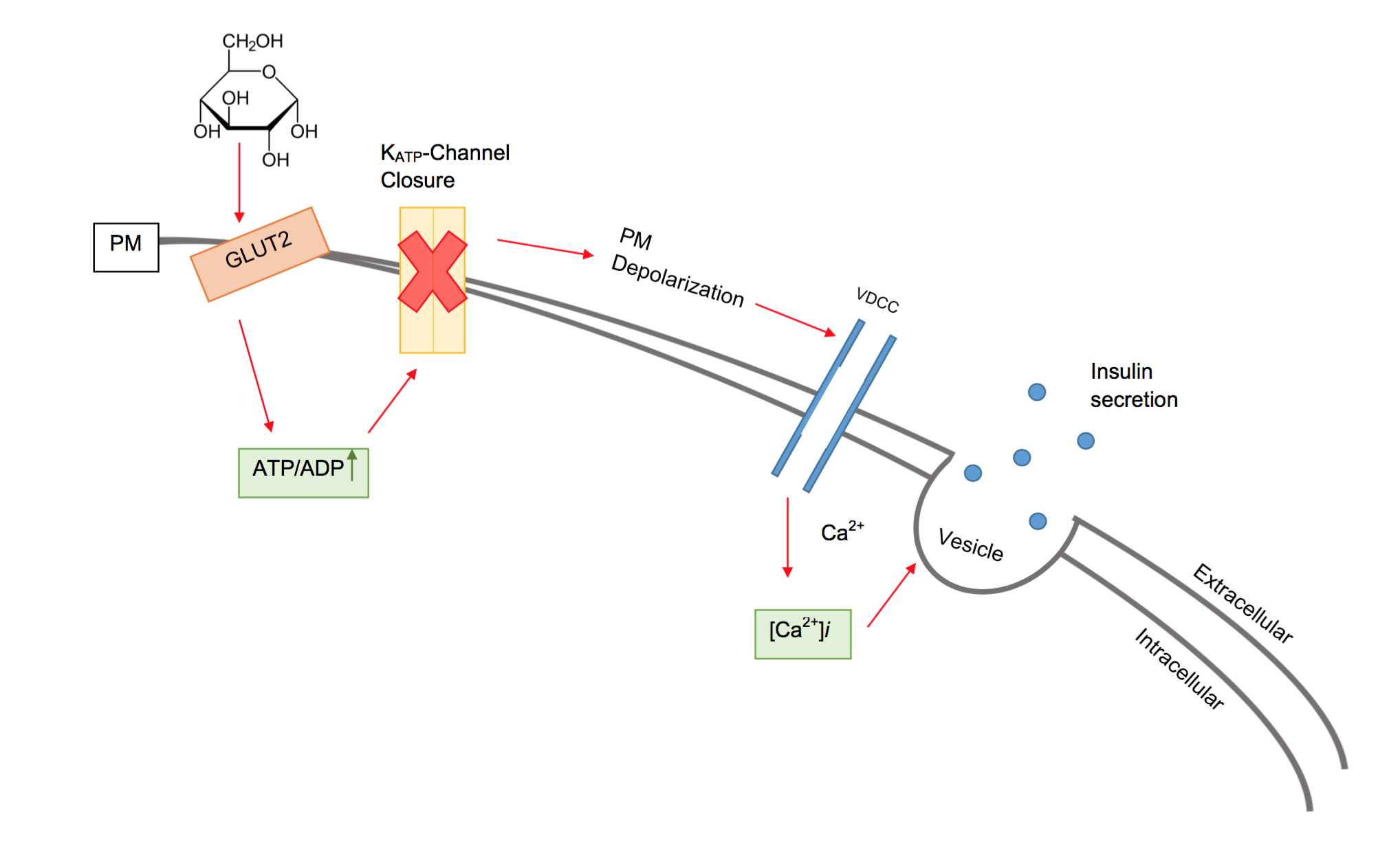
ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel
An ATP-sensitive potassium channel (or KATP channel) is a type of potassium channel that is gated by intracellular nucleotides, ATP and ADP. ATP-sensitive potassium channels are composed of Kir6.x-type subunits and sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits, along with additional components. KATP channels are widely distributed in plasma membranes; however some may also be found on subcellular membranes. These latter classes of KATP channels can be classified as being either sarcolemmal ("sarcKATP"), mitochondrial ("mitoKATP"), or nuclear ("nucKATP"). Discovery and structure KATP channels were first identified in cardiac myocytes by Akinori Noma in Japan. Glucose-regulated KATP channel activity was found in pancreatic beta cells by Frances Ashcroft at the University of Oxford. The closure of KATP channels leads to increased insulin secretion in beta cells and reduces glucagon secretion in alpha cells. SarcKATP are composed of eight protein subunits ( octamer). Four of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe hypothermia, there may be hallucinations and paradoxical undressing, in which a person removes their clothing, as well as an increased risk of the heart stopping. Hypothermia has two main types of causes. It classically occurs from exposure to cold weather and cold water immersion. It may also occur from any condition that decreases heat production or increases heat loss. Commonly, this includes alcohol intoxication but may also include low blood sugar, anorexia and advanced age. Body temperature is usually maintained near a constant level of through thermoregulation. Efforts to increase body temperature involve shivering, increased voluntary activity, and putting on warmer clothing. Hypothermia may be diagnosed based on either a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include headaches, Abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and Depression (mood), depression. People with fibromyalgia can also experience insomnia and extreme sensitivity. The causes of fibromyalgia are unknown, with several pathophysiologies proposed. People with fibromyalgia are sometimes accused of imagining their symptoms. Fibromyalgia was first recognised in the 1950s, and defined in 1990, with updated criteria in 2011, 2016, and 2019. Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2 to 4% of the population. Women are affected more than men. Rates appear similar across areas of the world and among varied cultures. Symptoms of fibromyalgia are persistent in most patients. The treatment of fibromyalgia is Symptomatic treatment, symptomatic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |