|
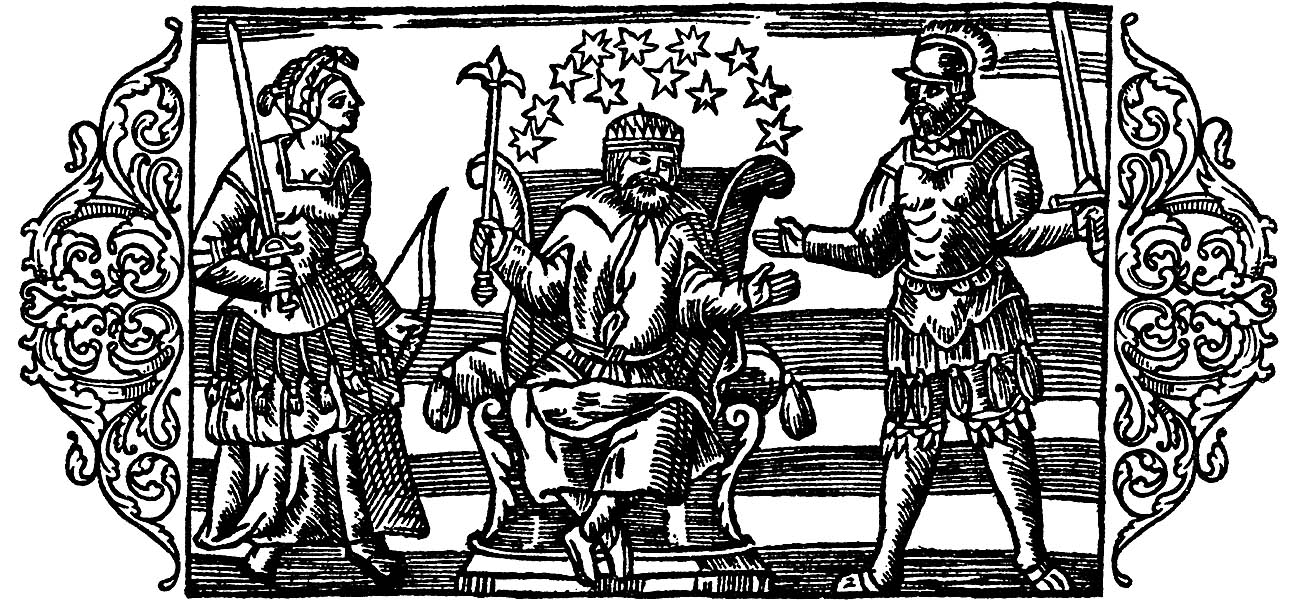
Hödekin
(spelled Hödeken, , and , etc.) is a kobold ( house spirit) of German folklore. The name is a diminutive meaning "Little Hat", and refers to the hat he wears, explained as being a '' pileus'' a felt hat of certain shapes. He famously haunted the castle of Bishop Bernard (Bernhardus), Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim, Lower Saxony, and in some versions, inhabited Winzenburg, a county the spirit helped the bishopric to obtain. Although Hütchen did not initiate harm, he was murderously vindictive and dismembered a kitchen boy who had habitually of insulted him and poured kitchen filth upon him. When the cook (who hadn't controlled the misbehaving boy) griped, the sprite tainted the meat for the bishop with toad blood and venom; the cook remained unfazed, and got pushed down the heights into a ditch to die. There was a man who during his absence entrusted his wife jokingly to the Hütchen, and the sprite chased off all the men calling on the adulterous wife. He also helped an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobold
A kobold (; ''kobolt'', ''kobolde'', cobold) is a general or generic name for the household spirit (''hausgeist'') in German folklore. It may invisibly make noises (i.e., be a poltergeist), or helpfully perform kitchen chores or stable work. But it can be a prankster as well. It may expect a bribe or offering of milk, etc. for its efforts or good behaviour. When mistreated (cf. fig. right), its reprisal can be utterly cruel. A () meaning "little hat" is one subtype; this and other kobold sprites are known for its pointy red cap, such as the ''niss'' (cognate of Nisse (folklore), nisse of Norway) or ''puk'' (cognate of Puck (folklore), puck fairy) which are attested in Northern Germany, alongside ''drak'', a dragon-type name, as the sprite is sometimes said to appear as a shaft of fire, with what looks like a head. There is also the combined form Nis Puk. A house sprite Hinzelmann is a shape-shifter assuming many forms, such as a feather or animals. The name supposedly refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Folklore
German folklore is the folk tradition which has developed in Germany over a number of centuries. Seeing as Germany was divided into numerous polities for most of its history, this term might both refer to the folklore of Germany proper and of all German-speaking countries, this wider definition including folklore of Austria and Liechtenstein as well as the German-speaking parts of Switzerland, Luxembourg, Belgium, and Italy. Characteristics It shares many characteristics with Nordic folklore and English folklore due to their origins in a common Germanic mythology. It reflects a similar mix of influences: a pre-Christian pantheon and other beings equivalent to those of Norse mythology; magical characters (sometimes recognizably pre-Christian) associated with Christian festivals, and various regional 'character' stories. As in Scandinavia, when belief in the old gods disappeared, remnants of the mythos persisted: There are: * Frau Holle or Perchta, a "supernatural" patron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Bechstein - Deutsches Sagenbuch 236a-(detail)huetchen
Ludwig may refer to: People and fictional characters * Ludwig (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Ludwig (surname), including a list of people * Ludwig von Koopa, a character in Mario (the game) Arts and entertainment * "Ludwig", a 1967 song by Al Hirt * ''Ludwig'' (film), a 1973 film by Luchino Visconti about Ludwig II of Bavaria * '' Ludwig: Requiem for a Virgin King'', a 1972 film by Hans-Jürgen Syberberg about Ludwig II of Bavaria * ''Ludwig'' (1977 TV series), a 1977 animated children's series * ''Ludwig'' (2024 TV series), a 2024 television comedy drama series Other uses * Ludwig (crater), a small lunar impact crater just beyond the eastern limb of the Moon * Ludwig, Missouri, an unincorporated community in the United States * Ludwig Canal, an abandoned canal in southern Germany * Ludwig Drums, an American manufacturer of musical instruments * ''Ludwig'' (ship), a steamer that sank in 1861 after a collision with the '' Stadt Zürich'' S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Praetorius (writer)
Johannes Praetorius (latinization of Hans Schultz; also called Praetorius Zeitlingensis to differentiate him from others with the same pen name; October 22, 1630, Zethlingen – October 25, 1680, Leipzig) was a German writer and historian. Praetorius attended school in Salzwedel and at the Gymnasium in Halle (Saale), then enrolled at the University of Leipzig, where he studied the natural sciences and obtained the Magister degree in 1653. He remained affiliated with the university until his death, studying texts at the Paulinum (University of Leipzig), Paulinum. Praetorius occasionally gave lectures, but spent the bulk of his time writing and compiling literary works, including compendia of fairy tales and legends. He is well known for collecting folk tales of the Rübezahl. Works * ''Daemonologia Rubinzalii … Ein ausführlicher Bericht von … dem Rübezahl.'' Leipzig 1662. * ''Catastrophe Muhammetica: Oder das Endliche Valet, und Schändliche Nativität des gantzen und nun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woden
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Empire's partial occupation of Germania ( BCE), the Migration Period (4th–6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th–11th centuries CE). Consequently, Odin has hundreds of names and titles. Several of these stem from the reconstructed Proto-Germanic theonym ''Wōðanaz'', meaning "lord of frenzy" or "leader of the possessed", which may relate to the god's strong association with poetry. Most mythological stories about Odin survive from the 13th-century ''Prose Edda'' and an earlier collection of Old Norse poems, the ''Poetic Edda'', along with other Old Norse items like ''Ynglinga saga''. The ''Prose Edda'' and other sources depict Odin as the head of the pantheon, sometimes called the Æsir, and bearing a spear and a ring. Wider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Empire's partial occupation of Germania ( BCE), the Migration Period (4th–6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th–11th centuries CE). Consequently, Odin has hundreds of names and titles. Several of these stem from the reconstructed Proto-Germanic theonym ''Wōðanaz'', meaning "lord of frenzy" or "leader of the possessed", which may relate to the god's strong association with poetry. Most mythological stories about Odin survive from the 13th-century ''Prose Edda'' and an earlier collection of Old Norse poems, the ''Poetic Edda'', along with other Old Norse items like '' Ynglinga saga''. The ''Prose Edda'' and other sources depict Odin as the head of the pantheon, sometimes called the Æsir, and bearing a spear and a ring. Wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headgear
Headgear, headwear, or headdress is any element of clothing which is worn on one's Human head, head, including hats, helmets, turbans and many other types. Headgear is worn for many purposes, including protective clothing, protection against the elements, decorative, decoration, or for religious or cultural reasons, including social conventions. Purposes Protection or defence Headgear may be worn for protective clothing, protection against cold (such as the Canadian tuque), heat, rain and other Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, glare, sunburn, sunstroke, dust, contaminants, etc. Helmets are worn for protection in battle or against impact, for instance when riding bicycles or motor vehicles. Fashion Headgear can be an article of fashion, usually hats, caps or hood (headgear), hoods. The formal man's black silk top hat was formerly an indispensable portion of the suit, and women's hats have, over the years, attained a fantastic number of shapes ranging from immense c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Sagen
''Deutsche Sagen'' ("German Legends") is a publication by the Brothers Grimm, appearing in two volumes in 1816 and 1818. The collection includes 579 short summaries of German folk tales and legends (where " German" refers not just to German-speaking Europe generally but includes early Germanic history as well). ''Deutsche Sagen'' followed the 1812 publication of '' Kinder- und Hausmärchen'' (known in English as ''Grimms' Fairy Tales''). It never gained the wide popular appeal and influence of the latter, although it did influence the scholarly study of folk narrative. The first volume contains 362 short tales, provided in short summary with a source. The source is in some cases "oral", with the region where it was collected (as in no. 1, ''Die drei Bergleute im Kuttenberg'' "the three miners in Kuttenberg", marked "oral" from Hessen), in other cases with a reference to the tale's previous publication (as in no. 362, ''Die drei Alten'' "The three old men", attributed to "Schmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxon Dialect
Low German is a West Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian and English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard High German, which is based on High German dialects. Low German evolved from Old Saxon (Old Low German), which is most closely related to Old Frisian and Old English (Anglo-Saxon). The Low German dialects s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Letzner
Johannes Letzner (29 November 1531 – 16 February 1613) was a Renaissance-era German Protestant priest and historian of Lower Saxony, in particular of Brunswick-Lüneburg. Letzner studied briefly at Wittenberg University in 1550–1551 before moving to Uslar as cantor and school master, and later as vicar to Parensen (1553) Langenholtensen (1564), Lüthorst (1583), Iber (1589) and finally to Strodthagen where he retired in 1610 and died three years later. Letzner's works were widely perused in 18th-century historiography of Germany, but they are now considered highly unreliable. His magnum opus was going to be a "Great Chronicle of Brunswick-Lüneburg" ("Große Braunschweig-Lüneburg-Göttingensche Chronika") in eight volumes, on which he worked during 36 years of his life. This work was never printed in full, but the fifteen works Letzner published in print during his lifetime can be seen as portions of this work. ''Conradus Fontanus'' is one of the purport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hochstift
In the Holy Roman Empire, the German language, German term (plural: ) referred to the territory ruled by a bishop as a prince (i.e. prince-bishop), as opposed to his diocese, generally much larger and over which he exercised only spiritual authority. The terms prince-bishopric (, or simply ) and ecclesiastical principality are synonymous with . and referred respectively to the territory (prince-archbishopric) ruled by a prince-archbishop and an elector-archbishop while referred to the territory ruled by an imperial abbot or abbess, or a Prince-abbot, princely abbot or abbess. was also often used to refer to any type of ecclesiastical principality. Names ''Das Stift'' [plural: ''die Stifte'' or, in some regions, ''die Stifter'']/''het sticht'' [in Dutch] (literally, the "donation"), denotes in its original meaning the donated or else acquired fund of estates whose revenues are taken to maintain a College (canon law), college and the pertaining church (''Stiftskirche'', i.e. c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zur Geschichte Der Religion Und Philosophie In Deutschland
''Zur Geschichte der Religion und Philosophie in Deutschland'' (''On the History of Religion and Philosophy in Germany'') is a three-part essay by Heinrich Heine, each part referred to as a "book". He wrote them in exile in Paris in 1833/34. They were initially published in French, titled ''De l'Allemagne depuis Luther'' (Germany after Luther), in the magazine '' Revue des deux Mondes'' in 1834. The first publication in German was as part of ''Der Salon. Zweiter Band'' the same year. Heine hoped for a revolution in Germany and looked at a history of emancipation in that country, beginning with the Reformation and followed by the philosophy of Kant and Hegel, among others. History Heinrich Heine wrote the essay in exile in Paris in 1833/34, following the French July Revolution of 1830 and the German Hambach Festival of 1832. As it was being completed, Heine's German text was successively translated into French. The French text was published in three parts as ''De l'Allemagne de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |