|
Hypodermic
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug administration, it is one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps. It is commonly used with a syringe, a hand-operated device with a plunger, to inject substances into the body (e.g., saline solution, solutions containing various drugs or liquid medicines) or extract fluids from the body (e.g., blood). Large-bore hypodermic intervention is especially useful in catastrophic blood loss or treating shock. A hypodermic needle is used for rapid delivery of liquids, or when the injected substance cannot be ingested, either because it would not be absorbed (as with insulin), or because it would harm the liver. It is also useful to deliver certain medications that cannot be delivered orally due to vomiting. There are many possible routes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
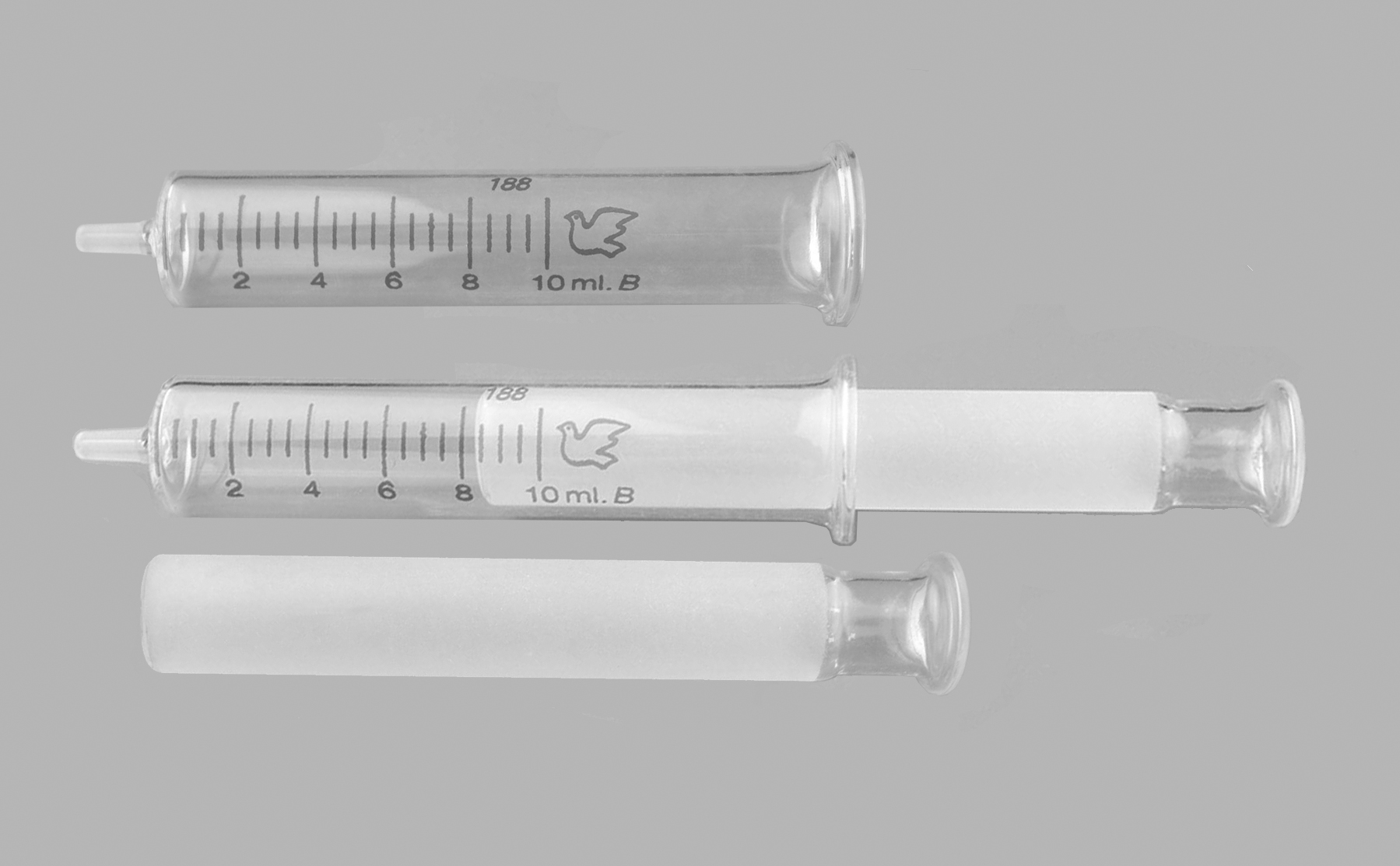
Syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle or tubing to direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are frequently used in clinical medicine to administer injections, infuse intravenous therapy into the bloodstream, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and draw/measure liquids. There are also prefilled syringes (disposable syringes marketed with liquid inside). The word "syringe" is derived from the Greek σῦριγξ ('' syrinx'', meaning "Pan flute", "tube"). Medical syringes Medical syringes include disposable and safety syringes, injectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringe And Hypodermic
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle or tubing to direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are frequently used in clinical medicine to administer injections, infuse intravenous therapy into the bloodstream, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and draw/measure liquids. There are also prefilled syringes (disposable syringes marketed with liquid inside). The word "syringe" is derived from the Greek σῦριγξ (''syrinx'', meaning "Pan flute", "tube"). Medical syringes Medical syringes include disposable and safety syringes, injection pens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Rynd
Francis Rynd (1801 – 19 July 1861) was an Irish physician known for inventing the hypodermic needle used in syringes. Early life Rynd was born in Dublin, Ireland, in 1801 to James Rynd and his third wife Hester Fleetwood. Rynd attended medical school at Trinity College Dublin, where he was reputed to be a "wayward" student, known for his busy social life and love of fox hunting. Career Rynd worked at the Meath Hospital in Dublin. At the Meath Hospital he trained under surgeon Sir Philip Crampton. Rynd became a member of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland in 1830. In 1836 he took a surgical post in the Meath Hospital working alongside William Stokes and Robert James Graves. Dr Rynd, who had a lucrative private practice, also served as medical superintendent of the Mountjoy Prison. Rynd was a member of the exclusive Kildare Street Club. Hypodermic needle In a 12 March 1845 article in the Dublin Medical Press, Rynd outlined how he had injected painkillers into a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water per os, by mouth. It may also be used to administer pharmaceutical drug, medications or other medical therapy such as blood transfusion, blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection (medicine)
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in UK English, or a "jag" in Scottish English and Scots) is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle) and a syringe. An injection is considered a form of parenteral drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injections, as well as less common injections such as epidural, intraperitoneal, intraosseous, intracardiac, intraarticular, and intracavernous injections. Injections are among the most common health care procedures, with at least 16 billion administered in developing and transitional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which is processed chemically to produce heroin and other synthetic opioids for medicinal use and for the illegal drug trade. Opium's main psychoactive alkaloids, primarily morphine, act on μ-opioid receptors, causing analgesia and addiction with long-term use leading to tolerance, dependence, and increased cancer risk. The latex also contains the closely related opiates codeine and thebaine, and non-analgesic alkaloids such as papaverine and noscapine. The traditional, labor-intensive method of obtaining the latex is to scratch ("score") the immature seed pods (fruits) by hand; the latex leaks out and dries to a sticky yellowish residue that is later scraped off and dehydrated. The English word for opium is loan word, borrowed fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS (; – ) was an English architect, astronomer, mathematician and physicist who was one of the most highly acclaimed architects in the history of England. Known for his work in the English Baroque style, he was accorded responsibility for rebuilding 52 churches in the City of London after the Great Fire in 1666, including what is regarded as his masterpiece, St Paul's Cathedral, on Ludgate Hill, completed in 1710. The principal creative responsibility for a number of the churches is now more commonly attributed to others in his office, especially Nicholas Hawksmoor. Other notable buildings by Wren include the Royal Hospital Chelsea, the Old Royal Naval College, Greenwich, and the south front of Hampton Court Palace. Educated in Latin and Aristotelian physics at the University of Oxford, Wren was a founder of the Royal Society and served as its president from 1680 to 1682. His scientific work was highly regarded by Isaac Newton and Blaise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science & Medicine
''Social Science & Medicine'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering social science research that is relevant to health. The disciplines covered by the journal include anthropology, economics, geography, psychology, social epidemiology, social policy, sociology, medicine, and health care practice, policy, and organization. The journal was established in 1967 and is published by Elsevier. History ''Social Science & Medicine'' () was published quarterly from 1967 to 1977 by Pergamon Press and was then split into: * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part A: Medical Psychology & Medical Sociology'' () * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part B: Medical Anthropology'' () * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part C: Medical Economics'' () * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part D: Medical Geography'' () * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part E: Medical Psychology'' () * ''Social Science & Medicine. Part F: Medical & Social Ethics'' () In 1982, Parts A-F were merged back into one journal. It was publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biology)
In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungus, or animal) lives. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock (its substrate) can be itself a substrate for an animal that lives on top of the algae. Inert substrates are used as growing support materials in the hydroponic cultivation of plants. In biology substrates are often activated by the nanoscopic process of substrate presentation. In agriculture and horticulture * Cellulose substrate * Expanded clay aggregate (LECA) * Rock wool * Potting soil * Soil In animal biotechnology Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture are the same as described for plant cell, tissue and organ culture (In Vitro Culture Techniques: The Biotechnological Principles). Desirable requirements are (i) air conditioning of a room, (ii) hot room with temperature recorder, (iii) microsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. The ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The epics depict man's struggle, the ''Odyssey'' especially so, as Odysseus perseveres through the punishment of the gods. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language that shows a mixture of features of the Ionic Greek, Ionic and Aeolic Greek, Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |