|
Hype Cycle
The Gartner hype cycle is a graphical presentation developed, used and branded by the American research and advisory firm Gartner to represent the maturity, adoption, and social application of specific technologies. The hype cycle framework was introduced in 1995 by Gartner analyst Jackie Fenn to provide a graphical and conceptual presentation of the maturity of emerging technologies through five phases. History Gartner's hype cycle framework was introduced in 1995 by analyst Jackie Fenn, who had joined the firm the year before. In her research reports, Fenn identified common patterns related to the maturity of emerging technologies. Fenn referred to this familiar progression as a "hype cycle" and created a graph depicting its ups and downs with each distinct stage given a title, starting with Technology trigger and ending with Plateau of productivity. The chart was included in a one-off research report, but it was popular with other Gartner analysts and clients and the "Hype Cyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondratiev Wave
In economics, Kondratiev waves (also called supercycles, great surges, long waves, K-waves or the long economic cycle) are hypothesized cycle-like phenomena in the modern world economy. The phenomenon is closely connected with the technology life cycle. It is stated that the period of a wave ranges from forty to sixty years, the cycles consist of alternating intervals of high sectoral growth and intervals of relatively slow growth.See, e.g. Long wave theory is not accepted by most academic economists. Among economists who accept it, there is a lack of agreement about both the cause of the waves and the start and end years of particular waves. Among critics of the theory, the consensus is that it involves recognizing patterns that may not exist (apophenia). History of concept The Soviet economist Nikolai Kondratiev (also written Kondratieff or Kondratyev) was the first to bring these observations to international attention in his book ''The Long Waves in Economic Life'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
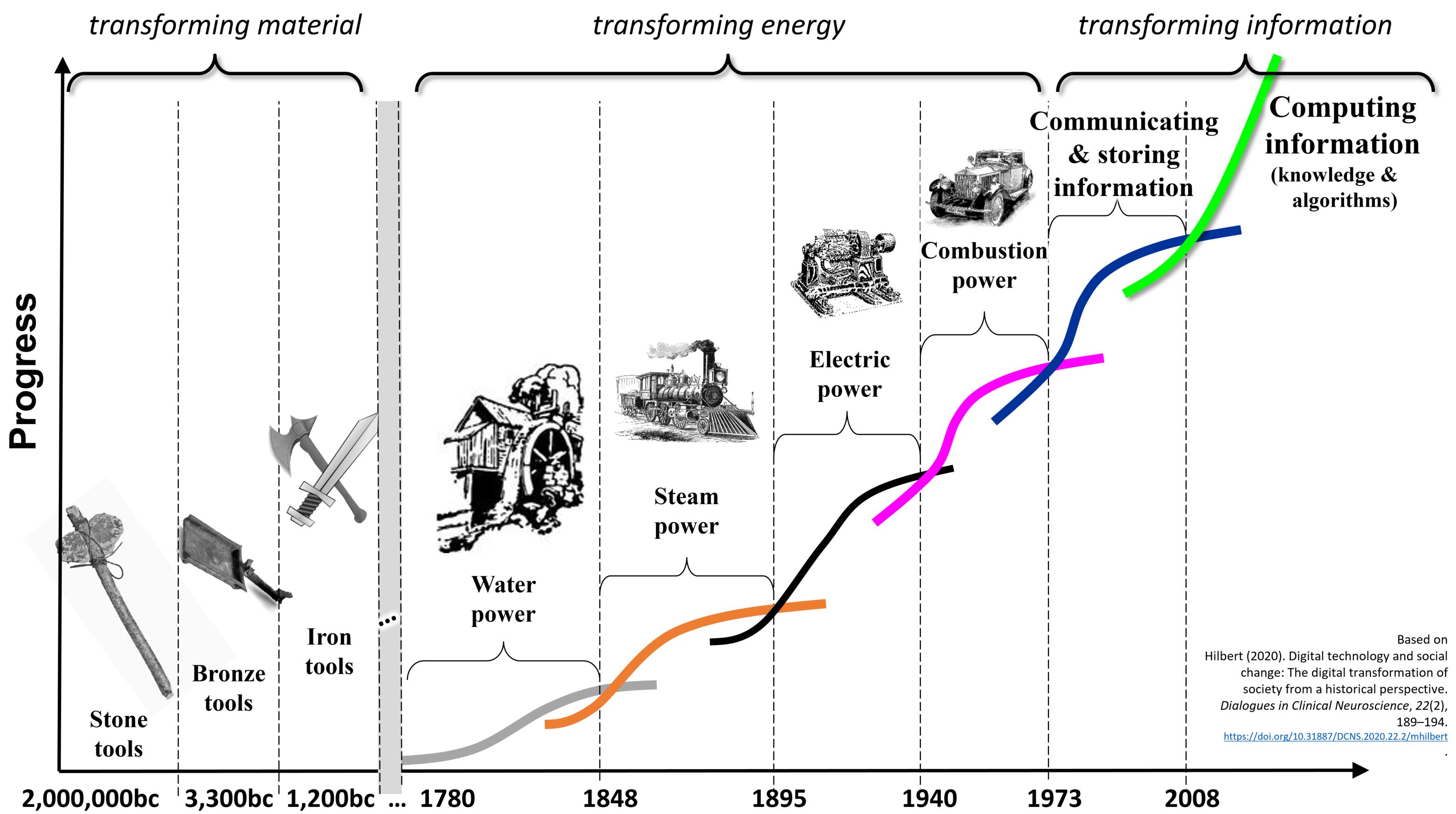
Technological Change
Technological change (TC) or technological development is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of innovations, diffusion of technology or business process, processes.From ''The New Palgrave Dictionary otechnical change by S. Metcalfe. •biased and biased technological change by Peter L. Rousseau. •skill-biased technical change by Giovanni L. Violante. In essence, technological change covers the invention of technologies (including processes) and their commercialization or release as open source via research and development (producing emerging technologies), the continual improvement process, continual improvement of technologies (in which they often become less expensive), and the diffusion of technologies throughout industry or society (which sometimes involves disruptive innovation, disruption and technological convergence, convergence). In short, technological change is based on both better and more technology. Modeling technological chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of Culture
The sociology of culture, and the related cultural sociology, concerns the systematic analysis of culture, usually understood as the ensemble of symbolic codes used by a member of a society, as it is manifested in the society. For Georg Simmel, culture referred to "the cultivation of individuals through the agency of external forms which have been objectified in the course of history". Culture in the sociological field is analyzed as the ways of thinking and describing, acting, and the material objects that together shape a group of people's way of life. Contemporary sociologists' approach to culture is often divided between a "sociology of culture" and "cultural sociology"—the terms are similar, though not interchangeable. The ''sociology of culture'' is an older concept, and considers some topics and objects as more or less "cultural" than others. By way of contrast, Jeffrey C. Alexander introduced the term ''cultural sociology'', an approach that sees all, or most, socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology Studies
Science and technology studies (STS) or science, technology, and society is an interdisciplinary field that examines the creation, development, and consequences of science and technology in their historical, cultural, and social contexts. History Like most interdisciplinary fields of study, STS emerged from the confluence of a variety of disciplines and disciplinary subfields, all of which had developed an interest—typically, during the 1960s or 1970s—in viewing science and technology as socially embedded enterprises. The key disciplinary components of STS took shape independently, beginning in the 1960s, and developed in isolation from each other well into the 1980s, although Ludwik Fleck's (1935) monograph ''Genesis and Development of a Scientific Fact'' anticipated many of STS's key themes. In the 1970s Elting E. Morison founded the STS program at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), which served as a model. By 2011, 111 STS research centers and academic prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Lifecycle Management
In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design, and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises. History The inspiration for the burgeoning business process now known as PLM came from American Motors Corporation (AMC). The automaker was looking for a way to speed up its product development process to compete better against its larger competitors in 1985, according to François Castaing, Vice President for Product Engineering and Development. AMC focused its R&D efforts on extending the product lifecycle of its flagship products, particularly Jeeps, because it lacked the "massive budgets of General Motors, Ford, and foreign competitors." After introducing its compact Jeep Cherokee (X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Development
New product development (NPD) or product development in business and engineering covers the complete process of launching a new product to the market. Product development also includes the renewal of an existing product and introducing a product into a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design. New product development is the realization of a market opportunity by making a product available for purchase. The products developed by an commercial organisation provide the means to generate income. Many technology-intensive organisations exploit technological innovation in a rapidly changing consumer market. A product can be a tangible asset or intangible. A service or user experience is intangible. In law, sometimes services and other processes are distinguished from "products". NPD requires an understanding of customer needs and wants, the competitive environment, and the nature of the market. Cost, time, and quality are the main variables that drive customer needs. Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity, realizing or redistributing value (economics), value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies. Innovation often takes place through the development of more-effective product (business), products, processes, Service (economics), services, technologies, art works or business models that innovators make available to Market (economics), markets, governments and society. Innovation is related to, but not the same as, ''invention'': innovation is more apt to involve the practical implementation of an invention (i.e. new / improved ability) to make a meaningful impact in a market or society, and not all innovations requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation Economics
Innovation economics is a growing field of economic theory and applied/ experimental economics that emphasizes innovation and entrepreneurship. It comprises both the application of any type of innovations, especially technological but not only, into economic use. In classical economics, this is the application of customer new technology into economic use; it could also refer to the field of innovation and experimental economics that refers the new economic science developments that may be considered innovative. In his 1942 book '' Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy'', economist Joseph Schumpeter introduced the notion of an innovation economy. He argued that evolving institutions, entrepreneurs, and technological changes were at the heart of economic growth; however, it is only in the early 21st century that "innovation economy", grounded in Schumpeter's ideas, became a mainstream concept. Historical origins Joseph Schumpeter was one of the first and most important scholars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (Molecular diffusion, particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunning–Kruger Effect
The Dunning–Kruger effect is a cognitive bias in which people with limited competence in a particular domain overestimate their abilities. It was first described by the psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger in 1999. Some researchers also include the opposite effect for high performers: their tendency to underestimate their skills. In popular culture, the Dunning–Kruger effect is often misunderstood as a claim about general overconfidence of people with low intelligence instead of specific overconfidence of people unskilled at a particular task. Numerous similar studies have been done. The Dunning–Kruger effect is usually measured by comparing self-assessment with objective performance. For example, participants may take a quiz and estimate their performance afterward, which is then compared to their actual results. The original study focused on logical reasoning, grammar, and social skills. Other studies have been conducted across a wide range of tasks. They in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Response
In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, a transient response is the response of a system to a change from an equilibrium or a steady state. The transient response is not necessarily tied to abrupt events but to any event that affects the equilibrium of the system. The impulse response and step response are transient responses to a specific input (an impulse and a step, respectively). In electrical engineering specifically, the transient response is the circuit’s temporary response that will die out with time. It is followed by the steady state response, which is the behavior of the circuit a long time after an external excitation is applied. Damping The response can be classified as one of three types of damping that describes the output in relation to the steady-state response. ;Underdamped :An underdamped response is one that oscillates within a decaying envelope. The more underdamped the system, the more oscillations and longer it takes to reach steady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |