|
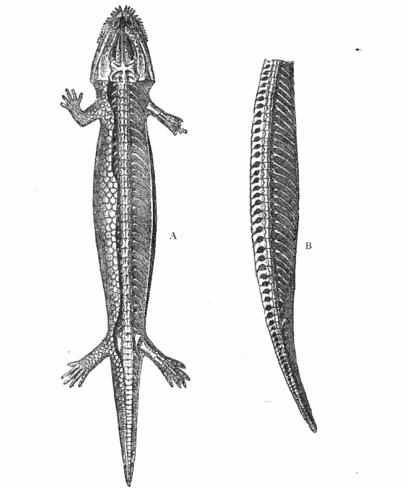
Hyloplesion
''Hyloplesion'' is an extinct genus of microbrachomorph microsaur. It is the type and only genus within the family Hyloplesiontidae. Fossils have been found from the Czech Republic near the towns of Plzeň, Nýřany, and Třemošná, and date back to the Middle Pennsylvanian. The type species is ''H. longicostatum'', named in 1883. Two species belonging to different genera, ''Seeleya pusilla'' and ''Orthocosta microscopica'', have been synonymized with ''H. longicostatum'' and are thought to represent very immature individuals. Description ''Hyloplesion'' was about as large as a medium-sized salamander, with the length of known specimens ranging from 17-77mm. The skull is triangular in shape. Unlike many other microsaurs, the palate of ''Hyloplesion'' contains large vacuities, or openings. The fifth maxillary tooth is enlarged and resembles a canine. The skull of ''Hyloplesion'' superficially resembles that of the unrelated romeriid reptile '' Romeria'' in lateral view d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsauria
Microsauria is an Extinction, extinct, possibly polyphyletic Order (biology), order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the Evolutionary grade, grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria. The microsaurs all had short tails and small legs, but were otherwise quite varied in form. The group included lizard-like animals that were relatively well-adapted to living on dry land, burrowing forms, and others that, like the modern axolotl, retained their gills into adult life, and so presumably never left the water. Their skeleton was heavily ossified, and their development was likely gradual with no metamorphosis. Distribution Microsaur remains have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsaur
Microsauria is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria. The microsaurs all had short tails and small legs, but were otherwise quite varied in form. The group included lizard-like animals that were relatively well-adapted to living on dry land, burrowing forms, and others that, like the modern axolotl, retained their gills into adult life, and so presumably never left the water. Their skeleton was heavily ossified, and their development was likely gradual with no metamorphosis. Distribution Microsaur remains have been found from Europe and North America in Late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Permian Period, Ma. It is the fifth and penultimate period of the Paleozoic era and the fifth period of the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon. In North America, the Carboniferous is often treated as two separate geological periods, the earlier Mississippian (geology), Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin ("coal") and ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern "system" names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare (geologist), William Conybeare and William Phillips (geologist), William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. Carboniferous is the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleofaunal Database initiative, which operated from August 1998 through August 2000. From 2000 to 2015, PBDB received funding from the National Science Foundation. PBDB also received support form the Australian Research Council. From 2000 to 2010 it was housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, a cross-disciplinary research center within the University of California, Santa Barbara. It is currently housed at University of Wisconsin-Madison and overseen by an international committee of major data contributors. The Paleobiology Database works closely with the Neotoma Paleoecology Database, which has a similar intellectual history, but has focused on the Quaternary (with an emphasis on the late Pleistocene and Holoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral-line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines play an important role in schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. Early in the evolution of fish, some of the sensory organs of the lateral line were modified to function as the electroreceptors called ampullae of Lorenzini. The lateral line system is ancient and basal to the vertebrate clade, as it is found in fishes that diverged over 400 million years ago. Function The lateral line system allows the detection of movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the water surrounding an animal. It plays an essential role in orientation, predation, and fish sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tridactyly
In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits (fingers and toes) on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. The term is derived from the Greek word () meaning "finger." Sometimes the suffix "-dactylia" is used. The derived adjectives end with "-dactyl" or "-dactylous." As a normal feature Pentadactyly Pentadactyly (from Greek "five") is the condition of having five digits on each limb. It is traditionally believed that all living tetrapods are descended from an ancestor with a pentadactyl limb, although many species have now lost or transformed some or all of their digits by the process of evolution. However, this viewpoint was challenged by Stephen Jay Gould in his 1991 essay "Eight (or Fewer) Little Piggies," where he pointed out polydactyly in early tetrapods and described the specializations of digit reduction. Despite the individual variations listed below, the relationship is to the original five-digit model. In reptiles, the limbs are pentadact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manus (anatomy)
The manus (Latin for '' hand'', plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the forelimb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits ( phalanges). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions. It can be represented by the hand of primates, the lower front limb of hoofed animals or the forepaw and is represented in the wing of birds, bats and prehistoric flying reptiles ( pterosaurs), the flipper of marine mammals and the 'paddle' of extinct marine reptile Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...s, such as plesiosaurs and ichthyosaurs. In cephalopods, the ''manus'' is the end, broader part of a tentacle, and its suckers are often larger and arrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbrachis
''Microbrachis'' is an extinct genus of microsaurian tetrapod from the Carboniferous Kladno Formation of the Czech Republic. Description ''Microbrachis'' was an elongated, salamander-like creature, about long, with over 40 vertebrae instead of the average 15–26 in its living relatives. It had minute limbs, and probably swam using fish-like lateral body movements. ''Microbrachis'' probably fed on fresh water plankton such as shrimp. ''Microbrachis'' was pedomorphic, retaining its larval gills in adulthood. Similar traits are found in the extant axolotl The axolotl (; from ) (''Ambystoma mexicanum'') is a neoteny, paedomorphic salamander, one that Sexual maturity, matures without undergoing metamorphosis into the terrestrial adult form; adults remain Aquatic animal, fully aquatic with obvio .... References Further reading * Andrew R. Milner, "The Tetrapod Assemblage from Nýrany, Czechoslovakia", in Systematics Association Special Volume No.15, "The Terrestri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapulocoracoid
The scapulocoracoid is the unit of the pectoral girdle that contains the coracoid and scapula. The coracoid itself is a beak-shaped bone that is commonly found in most vertebrates with a few exceptions. The scapula is commonly known as the ''shoulder blade''. The humerus is linked to the body via the scapula, and the clavicle is connected to the sternum via the scapula as well. Theria Theria ( or ; ) is a scientific classification, subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the Placentalia, placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-lay ...n mammals lack a scapulocoracoid. References * Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution by Kenneth V. Kardong. Page 325. Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Bone
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets. Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today, many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographical features and political boundaries, many atlases often feature geopolitical, social, religious, and economic statistics. They also have information about the map and places in it. Etymology The use of the word "atlas" in a geographical context dates from 1595 when the German-Flemish geographer Gerardus Mercator published ("Atlas or cosmographical meditations upon the creation of the universe and the universe as created"). This title provides Mercator's definition of the word as a description of the creation and form of the whole universe, not simply as a collection of maps. The volume that was published posthumously one year af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Bone
The parietal bones ( ) are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint known as a cranial suture, form the sides and roof of the neurocranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin ''paries'' (''-ietis''), wall. Surfaces External The external surface [Fig. 1] is convex, smooth, and marked near the center by an eminence, the parietal eminence (''tuber parietale''), which indicates the point where ossification commenced. Crossing the middle of the bone in an arched direction are two curved lines, the superior and inferior temporal lines; the former gives attachment to the temporal fascia, and the latter indicates the upper limit of the muscular origin of the temporal muscle. Above these lines the bone is covered by a tough layer of fibrous tissue – the epicranial aponeurosis; below them it forms part of the temporal fossa, and affords attachment to the temporal mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |