|
Hydrogenated MDI
Hydrogenated MDI (H12MDI or 4,4′-diisocyanato dicyclohexylmethane) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is a water white liquid at room temperature and is manufactured in relatively small quantities. It is also known as 4,4'-methylenedi(cyclohexyl isocyanate) or methylene bis(4-cyclohexylisocyanate) and has the formula CH2 C6H10)NCOsub>2. Manufacture The product is manufactured by hydrogenation of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate. It may also be manufactured by phosgenation of 4,4-Diaminodicyclohexylmethane. Uses Aliphatic diisocyanates are not used in the production of polyurethane foam as the cost is too high and foam is very much a commodity. It is used in special applications for polyurethane, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation from ultraviolet light. There are also multiple patents where prepolymers based on it are used in golf ball production. It is available comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C−N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomers
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and Elasticity (physics), elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with ''Synthetic rubber, rubber'', although the latter is preferred when referring to Vulcanization, vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several Chemical elements, elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable Segmental motion, molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. Rubber-like solids with elastic properties are called elastomers. Polymer chains are held together in these materials by relatively weak molecule, intermolecular bonds, which permit the polymers to stretch in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomers
A monomer ( ; ''wikt:mono-, mono-'', "one" + ''wikt:-mer, -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can chemical reaction, react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. By type: * natural vs synthetic, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively * polar vs nonpolar, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively * cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively By type of polymer they form: * those that participate in condensation polymerization * those that participate in addition polymerization Differing stoichiometry causes each class to create its respective form of polymer. : The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a polymer#Monomers and repeat units, homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanates
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C−N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isophorone Diisocyanate
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an Aliphatic compound, aliphatic diisocyanate. It is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for (with hexamethylene diisocyanate) only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. Aliphatic diisocyanates are used, not in the production of polyurethane foam, but in special applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to Abrasion (mechanical), abrasion and degradation from Ultraviolet, ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft. Properties Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) stands out as a cycloaliphatic diisocyanate distinguished by its two reactive isocyanate groups, exhibiting differences in reactivity between primary and secondary NCO groups. This unique property ensures high selectivity in reacting with hydroxyl-bearing compounds. This distinctive attrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene Diisocyanate
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is produced on a large scale, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI. Approximately 1.4 billion kilograms were produced in 2000. All isomers of TDI are colorless, although commercial samples can appear yellow. Synthesis 2,4-TDI is prepared in three steps from toluene via dinitrotoluene and 2,4-diaminotoluene (TDA). Finally, the TDA is subjected to ''phosgenation'', i.e., treatment with phosgene to form TDI. This final step produces HCl as a byproduct and is a major source of industrial hydrochloric acid. : Distillation of the raw TDI mixture produces an 80:20 mixture of 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI, known as TDI (80 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is an aromaticity, aromatic diisocyanate. Three isomers are common, varying by the positions of the isocyanate groups around the rings: 2,2′-MDI, 2,4′-MDI, and 4,4′-MDI. The 4,4′ isomer is most widely used, and is also known as 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate. This isomer is also known as Pure MDI. MDI reacts with polyols in the manufacture of polyurethane. It is the most produced diisocyanate, accounting for 61.3% of the global market in the year 2000. Production Total world production of MDI and polymeric MDI is over 7.5 million tonnes per year (in 2017). As of 2019, the largest producer was Wanhua Chemical Group. Other major producers are Covestro, BASF, Dow Chemical Company, Dow, Huntsman Corporation, Huntsman, Tosoh Corporation, Tosoh, Kumho Mitsui Chemicals. All major producers of MDI are members of the International Isocyanate Institute, whose aim is the promotion of the safe handling of MDI and Toluene diisocyanate, TDI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)6(NCO)2. It is classified as an diisocyanate. It is a colorless liquid. It has sometimes been called HMDI but this not usually done to avoid confusion with Hydrogenated MDI. Synthesis Compared to other commercial diisocyanates, HDI is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for (with isophorone diisocyanate) only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. It is produced by phosgenation of hexamethylene diamine. Applications Aliphatic diisocyanates are used in specialty applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation by ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft and vessels. HDI is also sold oligomerized as the trimer or biuret which are used in automotive refinish coatings. Although more viscous in these forms, it reduces the volatility and toxicity. At least 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane Dispersion
Polyurethane dispersion, or PUD, is understood to be a polyurethane polymer resin dispersed in water, rather than a solvent, although some cosolvent may be used. Its manufacture involves the synthesis of polyurethanes having carboxylic acid functionality or nonionic hydrophiles like PEG (polyethylene glycol) incorporated into, or pendant from, the polymer backbone. Two component polyurethane dispersions are also available. Background There has been a general trend towards converting existing resin systems to waterborne resins, for ease of use and environmental considerations. Particularly, their development was driven by increased demand for solventless systems since the manufacture of coatings and adhesives entailed the increasing release of solvents into the atmosphere from numerous sources. Using VOC exempt solvents is not a panacea as they have their own weaknesses. The problem has always been that polyurethanes in water are not stable, reacting to produce a urea and carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylol Propionic Acid
Dimethylolpropionic acid (DMPA) is a chemical compound that has the full IUPAC name of 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid and is an organic compound with one carboxyl and two hydroxy groups. It has the CAS Registry Number of 4767-03-7. Properties DMPA is an odorless free flowing white crystalline solid and essentially non-toxic. DMPA has two different functional groups hydroxyl and carboxylic acid so the molecule can be used for a wide variety of syntheses. In addition to reaction with other chemicals, DMPA can also react with itself to produce esters via esterification, as one example. Uses One key use of DMPA is in the field of coatings and adhesives. It is used as a modifier in the production of anionic Polyurethane dispersions. Solvent soluble binders/resins for coatings can be converted into an aqueous binder with the use of this material. In this case it is reacted with a suitable diisocyanate such as isophorone diisocyanate or TMXDI usually along with other polyols t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henkel
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, commonly known as Henkel, is a German multinational chemical and consumer goods company headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. Founded in 1876, the DAX company is organized into two globally operating business units (Consumer Brands, Adhesive Technologies) and is known for brands such as Loctite, Persil, Fa, Pritt, Dial and Purex. In the fiscal year 2024, Henkel reported sales of around 21.6 billion euros and an operating profit of 2.831 billion euros. Henkel holds 47,150 employees with more than 80% working outside of Germany. History The company was founded in 1876 in Aachen as Henkel & Cie by Friedrich Karl Henkel and two other partners who were owners of a factory producing sodium silicate. They marketed his first product, "Universalwaschmittel", a universal detergent based on sodium silicate. In 1878, Henkel bought out the two partners, and the first German brand-name detergent appeared: Henkel's Bleich-Soda. Made from sodium silicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
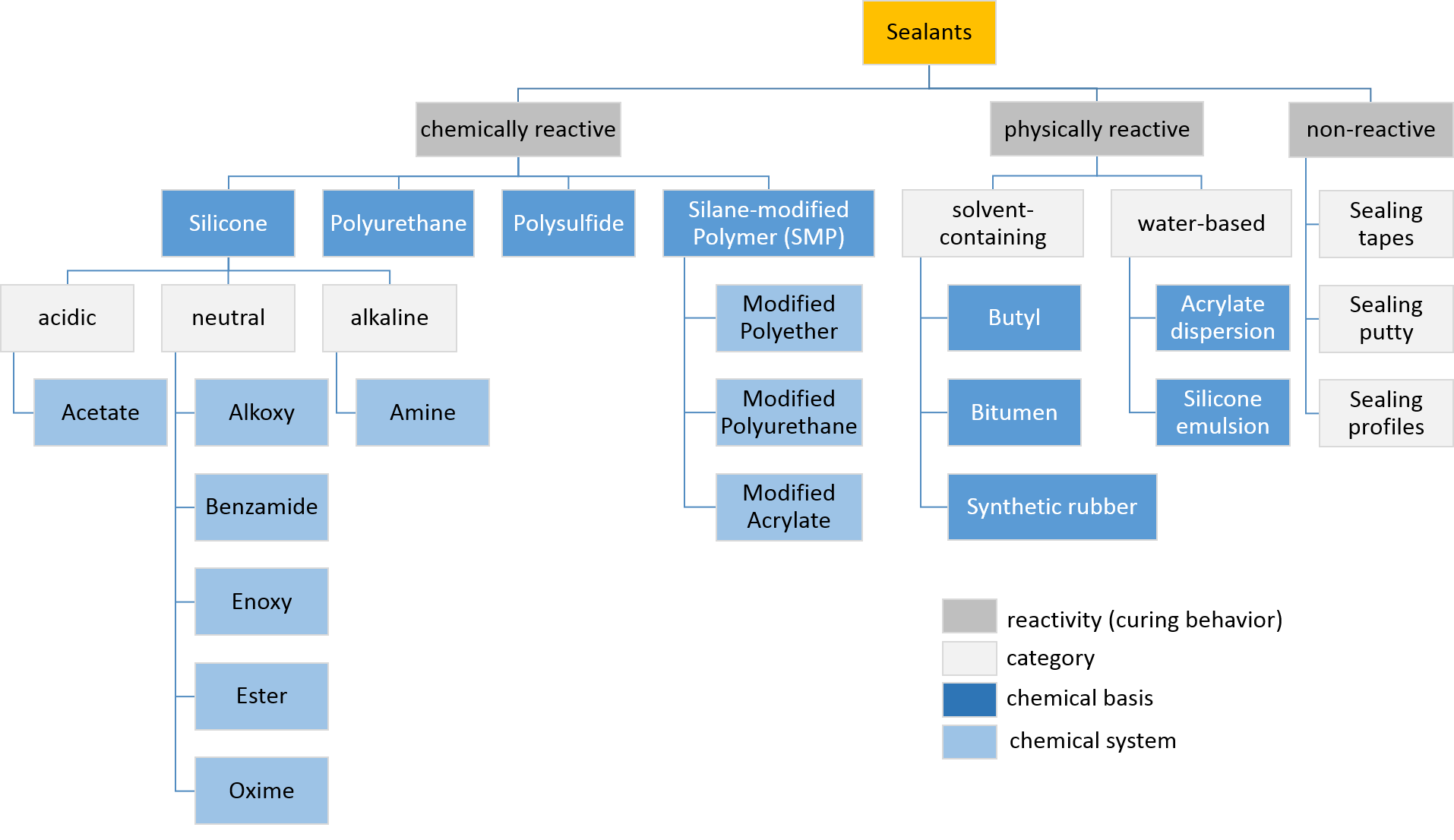
Sealants
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with ''caulk'' (especially if acrylic latex or polyurethane based) and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission. Sealants may be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, permanent or temporary. Sealants are not adhesives but some have adhesive qualities and are called ''adhesive-sealants'' or ''structural sealants''. History Sealants were first used in prehistory in the broadest sense as mud, grass and reeds to seal dwellings from the weather such as the daub in wattle and daub and thatching. Natural sealants and adhesive-sealants included plant resins such as pine pitch and birch pitch, bitumen, wax, tar, natural gum, clay (mud) mortar, lime mortar, lead, blood and egg. In the 17th century glazing putty was first used to seal window glass made with linseed oil and chalk, later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |