|
Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle
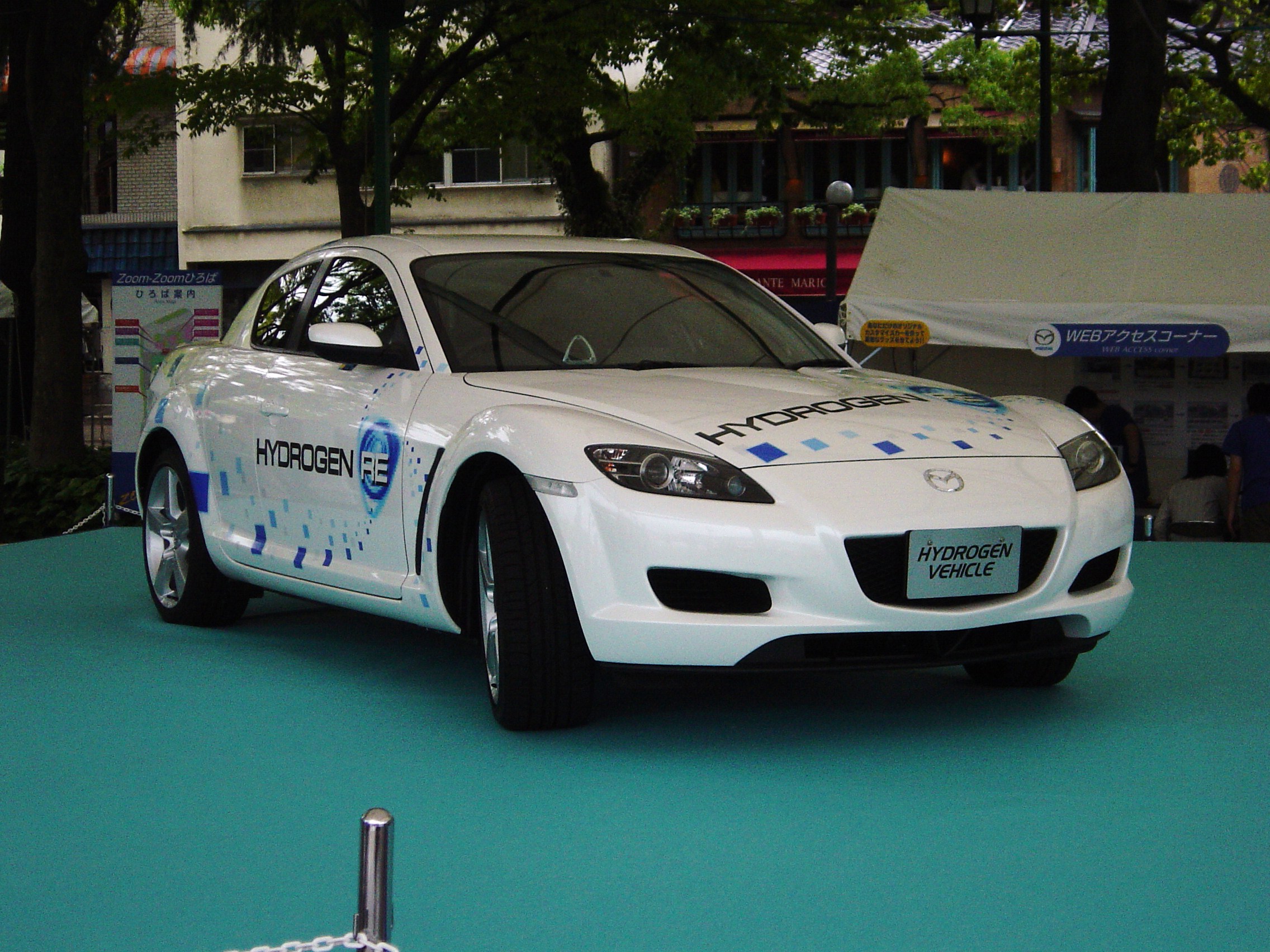
A hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicle (HICEV) is a type of hydrogen vehicle using an internal combustion engine that burns hydrogen fuel. Hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles are different from hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (which utilize hydrogen electrochemically rather than through oxidative combustion). Instead, the hydrogen internal combustion engine is simply a engine tuning, modified version of the traditional petrol engine, gasoline-powered internal combustion engine. The absence of carbon means that no is produced, which eliminates the main greenhouse gas emission of a conventional petroleum engine. As pure hydrogen does not contain carbon, there are no carbon-based pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO) or hydrocarbons (HC), nor is there any carbon dioxide () in the exhaust. As hydrogen combustion occurs in an atmosphere containing nitrogen and oxygen, however, it can produce NOx, oxides of nitrogen known as . In this respect, the combustion process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of a fuel injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines. All compression-ignition engines (e.g. diesel engines), and many spark-ignition engines (i.e. petrol (gasoline) engines, such as Otto or Wankel), use fuel injection of one kind or another. Mass-produced diesel engines for passenger cars (such as the Mercedes-Benz OM 138) became available in the late 1930s and early 1940s, being the first fuel-injected engines for passenger car use. In passenger car petrol engines, fuel injection was introduced in the early 1950s and gradually gained prevalence until it had largely replaced carburetors by the early 1990s. The primary difference between carburetion and fuel injection is that fuel injection atomizes the fuel through a small nozzle under high pressure, while carburetion relies on suction crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW Hydrogen 7
The BMW Hydrogen 7 is a limited production hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicle built from 2005–2007 by German automobile manufacturer BMW. The car is based on BMW’s traditional petrol-powered BMW 7 Series (E65) line of vehicles, and more specifically the 760Li. It uses the same 6-litre V-12 motor as does the 760i and 760Li; however, it has been modified to also allow for the combustion of hydrogen as well as petrol, making it a bivalent engine. Production Only 100 total vehicles were produced to put their technology to the test. BMW said it chose public figures such as politicians, media figures, businessmen and big names in the entertainment industry such as 2007 Academy Award-winning director Florian Henckel von Donnersmarck and the chairman of Sixt AG, Erich Sixt, because “they would be ideal ambassadors” for hydrogen fuel and could help spread awareness of the need for such technologies. Use of hydrogen technology The BMW Hydrogen 7 burns hydrogen in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Water Electrolysis
Alkaline water electrolysis is a type of electrolysis that is characterized by having two electrodes operating in a liquid alkaline electrolyte. Commonly, a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 25-40 wt% is used. These electrodes are separated by a diaphragm, separating the product gases and transporting the hydroxide ions (OH−) from one electrode to the other. A recent comparison showed that state-of-the-art nickel based water electrolysers with alkaline electrolytes lead to competitive or even better efficiencies than acidic polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis with platinum group metal based electrocatalysts. The technology has a long history in the chemical industry. The first large-scale demand for hydrogen emerged in late 19th century for lighter-than-air aircraft, and before the advent of steam reforming in the 1930s, the technique was competitive. Hydrogen-based technologies have evolved significantly since the initial discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Vehicle
A solar electric vehicle is an electric vehicle powered completely or significantly by direct solar energy. Usually, photovoltaic (PV) cells contained in solar panels convert the sun's energy directly into electric energy. A concentrated solar vehicle uses stored solar energy to run a heat engine, such as Rankine, Stirling or Brayton cycle, of the piston and crank type directly powering the vehicle or free-piston linear generator (FPLG)powering a hybrid electric car system. The term "solar vehicle" usually implies that solar energy is used to power all or part of a vehicle's propulsion. Solar power may also be used to provide power for communications or controls or other auxiliary functions. Solar vehicles are not sold as practical day-to-day transportation devices at present, but are primarily demonstration vehicles and engineering exercises, often sponsored by government agencies. However, indirectly solar-charged vehicles are widespread and solar boats are available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
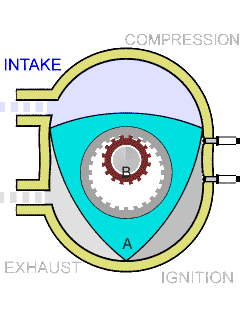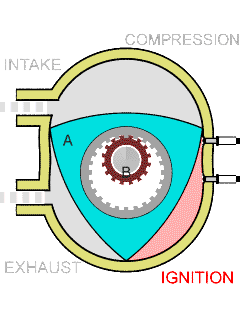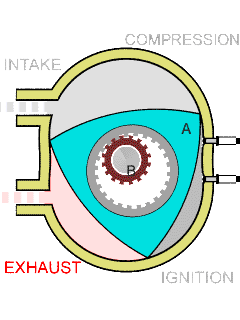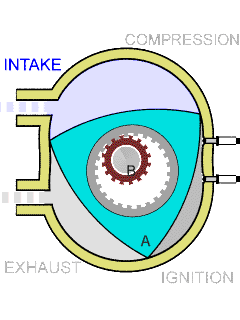
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric (mechanism), eccentric Pistonless rotary engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, followed by a commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing around a fixed gear. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, rotating the shaft via a Cam (mechanism), cam. In its basic gasoline-fuelled form, the Wankel engine has lower thermal efficiency and higher exhaust emissions relative to the Four-stroke engine, four-stroke reciprocating engine. This thermal inefficiency has restricted the Wankel engine to limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, many disadvantages have mainly been overcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo City University
, often called or TCU for short, is a private university focused on engineering, environmental and information sciences, located in Setagaya, Tokyo, Japan. The university has four campuses, the Setagaya campus close to the Tama River at Oyamadai, Setagaya, Tokyo being the main campus. The other three campuses are the Yokohama campus, located in Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama, the Ōzenji campus, located in Asao-ku, Kawasaki and the Todoroki campus, located in Setagaya, Tokyo. Gotoh Educational Corporation The Gotoh Educational Corporation manages the Tokyo City University Group. Dating its origins to 1939 and the establishment of the Toyoko Girls Commercial School, the educational corporation was founded by Keita Gotō a leading industrialist and founder of the Tokyu Group of companies. Incorporating the former facilities of Musashi Institute of Technology (founded in 1929), the university was reorganized and renamed Tokyo City University in 2009. The wider Tokyo City University Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippomobile (car)
The Hippomobile is an early, three wheeled automobile invented by Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir in France in 1863 which carried its own internal combustion engine. It was based on his 1860 invention, the Lenoir gas engine. History In 1863, the Hippomobile, with a coal gas fueled, one-cylinder internal combustion engine, made a test drive from Paris, France Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ... to Joinville-le-Pont, which covered around eleven miles in less than three hours, which was a fair achievement at the time. See also * History of the internal combustion engine * Motorized wagons * Timeline of transportation technology References External links ''Engine Maturity, Efficiency, and Potential Improvements'' US Dept of Energy, Washington, page 7 1860s cars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne Lenoir
Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir, also known as Jean J. Lenoir (12 January 1822 – 4 August 1900), was a Belgian-French engineer who invented the internal combustion engine in 1858. Prior designs for such engines were patented as early as 1807 (De Rivaz engine) and 1854 (Barsanti–Matteucci engine). He was born in Mussy-la-Ville (then in Luxembourg, part of the Belgian Luxembourg (Belgium), Province of Luxembourg since 1839). In 1838, he immigrated to France, taking up residence in Paris, where he developed an interest in electroplating. His interest in the subject led him to make several electrical inventions, including an improved electric telegraph. Lenoir engine By 1859, Lenoir's experimentation with electricity led him to develop the first internal combustion engine which burned a mixture of coal gas and air ignited by a "jumping sparks" ignition system by Induction coil, Ruhmkorff coil, and which he patented in 1860. The engine was a steam engine converted to burn gaseous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyhydrogen
Oxyhydrogen is a mixture of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. This gaseous mixture is used for torches to process refractory materials and was the first gaseous mixture used for welding. Theoretically, a ratio of 2:1 hydrogen:oxygen is enough to achieve maximum efficiency; in practice a ratio 4:1 or 5:1 is needed to avoid an oxidizing flame. This mixture may also be referred to as ' (Scandinavian and German '; ), although some authors define knallgas to be a generic term for the mixture of fuel with the precise amount of oxygen required for complete combustion, thus 2:1 oxyhydrogen would be called "hydrogen-knallgas". "Brown's gas" and HHO are terms for oxyhydrogen originating in pseudoscience, although is preferred due to meaning . Properties Oxyhydrogen will combust when brought to its autoignition temperature. For the stoichiometric mixture in air, at normal atmospheric pressure, autoignition occurs at about 570 °C (1065 °F). The minimum energy requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |