|
Hydrogen Silsesquioxane
200px, thumbnail, Hydrogen silsesquioxane (R = H). Hydrogen silsesquioxane(s) (HSQ, H-SiOx, THn, H-resin) are inorganic compounds with the empirical formula SiO3/2sub>n. The cubic H8Si8O12 (TH8) is used as the visual representation for HSQ. TH8, TH10, TH12, and TH14 have been characterized by elemental analysis, gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy ( GC-MS), IR spectroscopy, and NMR spectroscopy. High purity semiconductor-grade HSQ has been investigated as a negative resist in photolithography and electron-beam (e-beam) lithography. HSQ is commonly delivered in methyl isobutyl ketone ( MIBK) and can be used to form 0.01–2 μm films on substrates/wafers. When exposed to electrons or extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV), HSQ cross-links via hydrogen evolution concomitant with Si-O bond crosslinking. Recently, the possibility of crosslinking HSQ using ultrashort laser pulses through multiphoton absorption and its application to 3D printing of silica glass Fused quart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silsesquioxane T8 Cube
220x220px, thumbnail, A cubic silsesquioxane. A silsesquioxane is an organosilicon compound with the chemical formula SiO3/2sub>n (R = H, alkyl, aryl, alkenyl or alkoxyl.). Silsesquioxanes are colorless solids that adopt cage-like or polymeric structures with Si-O-Si linkages and tetrahedral Si vertices. Silsesquioxanes are members of polyoctahedral silsesquioxanes ("POSS"), which have attracted attention as preceramic polymer precursors to ceramic materials and nanocomposites. Diverse substituents (R) can be attached to the Si centers. The molecules are unusual because they feature an inorganic silicate core and an organic exterior. The silica core confers rigidity and thermal stability. Structure Silsesquioxanes are known in molecular form as well as polymers. The 6-, 8-, 10-, and 12-Si cages are sometimes labeled T6 T8, T10, and T12, respectively (T = tetrahedral vertex). The T8 cages, the most widely studied members, have the formula SiO3/2sub>8, or equivalently R8Si8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
Extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL, also known simply as EUV) is a technology used in the semiconductor industry for manufacturing integrated circuits (ICs). It is a type of photolithography that uses 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light from a laser-pulsed tin (Sn) plasma to create intricate patterns on semiconductor substrates. , ASML Holding is the only company that produces and sells EUV systems for chip production, targeting 5 nanometer (nm) and 3 nm process nodes. The EUV wavelengths that are used in EUVL are near 13.5 nanometers (nm), using a laser-pulsed tin (Sn) droplet plasma to produce a pattern by using a reflective photomask to expose a substrate covered by photoresist. Tin ions in the ionic states from Sn IX to Sn XIV give photon emission spectral peaks around 13.5 nm from 4p64d''n'' – 4p54d''n''+1 + 4d''n''−14f ionic state transitions. History and economic impact In the 1960s, visible light was used for the production of integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fused Quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses, such as soda-lime glass, lead glass, or borosilicate glass, in which other ingredients are added which change the glasses' optical and physical properties, such as lowering the melt temperature, the spectral transmission range, or the mechanical strength. Fused quartz, therefore, has high working and melting temperatures, making it difficult to form and less desirable for most common applications, but is much stronger, more chemically resistant, and exhibits lower thermal expansion, making it more suitable for many specialized uses such as lighting and scientific applications. The terms ''fused quartz'' and ''fused silica'' are used interchangeably but can refer to different manufacturing techniques, resulting in different trace impurities. However fused quartz, being in the glassy s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiphoton Lithography
Multiphoton lithography (also known as direct laser lithography or direct laser writing) is similar to standard photolithography techniques; structuring is accomplished by illuminating negative-tone or positive-tone photoresists via light of a well-defined wavelength. The main difference is the avoidance of photomasks. Instead, two-photon absorption is utilized to induce a change in the solubility of the resist for appropriate developers. Hence, multiphoton lithography is a technique for creating small features in a photosensitive material, without the use of excimer lasers or photomasks. This method relies on a multi-photon absorption process in a material that is transparent at the wavelength of the laser used for creating the pattern. By scanning and properly modulating the laser, a chemical change (usually polymerization) occurs at the focal spot of the laser and can be controlled to create an arbitrary three-dimensional pattern. This method has been used for rapid prototyping o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrashort Pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators. Amplification of ultrashort pulses almost always requires the technique of chirped pulse amplification, in order to avoid damage to the gain medium of the amplifier. They are characterized by a high peak intensity (or more correctly, irradiance) that usually leads to nonlinear interactions in various materials, including air. These processes are studied in the field of nonlinear optics. In the specialized literature, "ultrashort" refers to the femtosecond (fs) and picosecond (ps) range, although such pulses no longer hold the record for the shortest pulses artificially generated. Indeed, x-ray pulses with durations on the attosecond time scale have been reported. The 1999 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
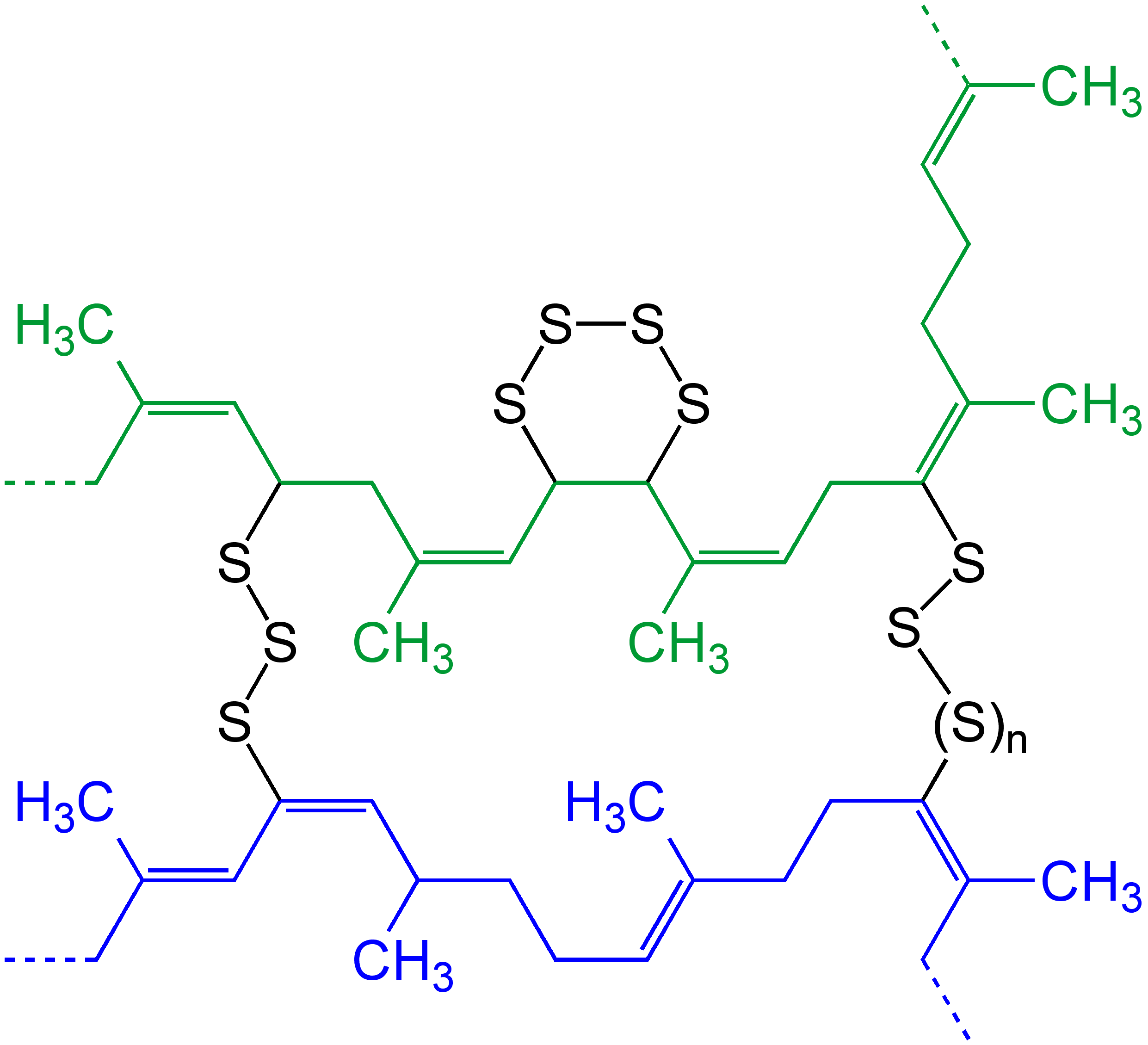
Crosslink
In chemistry and biology, a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. Synthetic polymers : 260px, left, Chemical reactions associated with crosslinking of drying oils, the process that produces curing'' refers to the crosslinking of thermosetting">linoleum. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) is a chemical reaction that yields H2. The conversion of protons to H2 requires reducing equivalents and usually a catalyst. In nature, HER is catalyzed by hydrogenase enzymes which rely on iron- and nickel-based catalysts. Commercial electrolyzers typically employ supported nickel-based catalysts. HER in electrolysis HER is a key reaction which occurs in the electrolysis of water for the production of hydrogen for both industrial energy applications, as well as small-scale laboratory research. Due to the abundance of water on Earth, hydrogen production poses a potentially scalable process for fuel generation. This is an alternative to steam methane reforming for hydrogen production, which has significant greenhouse gas emissions, and as such scientists are looking to improve and scale up electrolysis processes that have fewer emissions. Electrolysis mechanism In acidic conditions, the hydrogen evolution reaction follows the formula: : In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isobutyl Ketone
Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK, 4-methylpentan-2-one) is an organic compound with the structural formula, condensed chemical formula (CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH3. This ketone is a colourless liquid that is used as a solvent for gums, resins, paints, varnishes, lacquers, and nitrocellulose. Production At laboratory scale, MIBK can be produced via a three-step process using acetone as the starting material. Self-condensation, a type of aldol reaction, produces diacetone alcohol, which readily dehydration (chemistry), dehydrates to give 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one (commonly, mesityl oxide). Mesityl oxide is then hydrogenation, hydrogenated to give MIBK. : Industrially, these three steps are combined. Acetone is treated with a strongly acidic, palladium catalyst-doped Ion-exchange resin, cation exchange resin under medium pressure of hydrogen. Several million kilograms are produced annually.Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elemental Analysis
Elemental analysis is a process where a sample of some material (e.g., soil, waste or drinking water, bodily fluids, minerals, chemical compounds) is analyzed for its elemental and sometimes isotopic composition. Elemental analysis can be qualitative (determining what elements are present), and it can be quantitative (determining how much of each is present). Elemental analysis falls within the ambit of analytical chemistry, the instruments involved in deciphering the chemical nature of our world. History Antoine Lavoisier is regarded as the inventor of elemental analysis as a quantitative, experimental tool to assess the chemical composition of a compound. At the time, elemental analysis was based on the gravimetric determination of specific absorbent materials before and after selective adsorption of the combustion gases. Today fully automated systems based on thermal conductivity or infrared spectroscopy detection of the combustion gases, or other spectroscopic methods are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isobutyl Ketone
Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK, 4-methylpentan-2-one) is an organic compound with the structural formula, condensed chemical formula (CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH3. This ketone is a colourless liquid that is used as a solvent for gums, resins, paints, varnishes, lacquers, and nitrocellulose. Production At laboratory scale, MIBK can be produced via a three-step process using acetone as the starting material. Self-condensation, a type of aldol reaction, produces diacetone alcohol, which readily dehydration (chemistry), dehydrates to give 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one (commonly, mesityl oxide). Mesityl oxide is then hydrogenation, hydrogenated to give MIBK. : Industrially, these three steps are combined. Acetone is treated with a strongly acidic, palladium catalyst-doped Ion-exchange resin, cation exchange resin under medium pressure of hydrogen. Several million kilograms are produced annually.Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron-beam Lithography
Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography or EBL) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (exposing). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (developing). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by Etching (microfabrication), etching. The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 Nanometre, nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution but low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of Semiconductor device, semiconductor devices, and research and development. Systems Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |