|
Hydrofluorocarbon
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are synthetic organic compounds that contain fluorine and hydrogen atoms, and are the most common type of organofluorine compounds. Most are gases at room temperature and pressure. They are frequently used in air conditioning and as refrigerants; R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) is one of the most commonly used HFC refrigerants. In order to aid the recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer, HFCs were adopted to replace the more potent chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) such as R-12, which were phased out from use by the Montreal Protocol, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) such as R-21 which are presently being phased out. HFCs are also used in insulating foams, aerosol propellants, as solvents and for fire protection. HFCs may not harm the ozone layer as much as the compounds they replace, but they still contribute to global warming – with some like trifluoromethane (CHF3 or R-23) having 11,700 times the warming potential of carbon dioxide. HFC atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
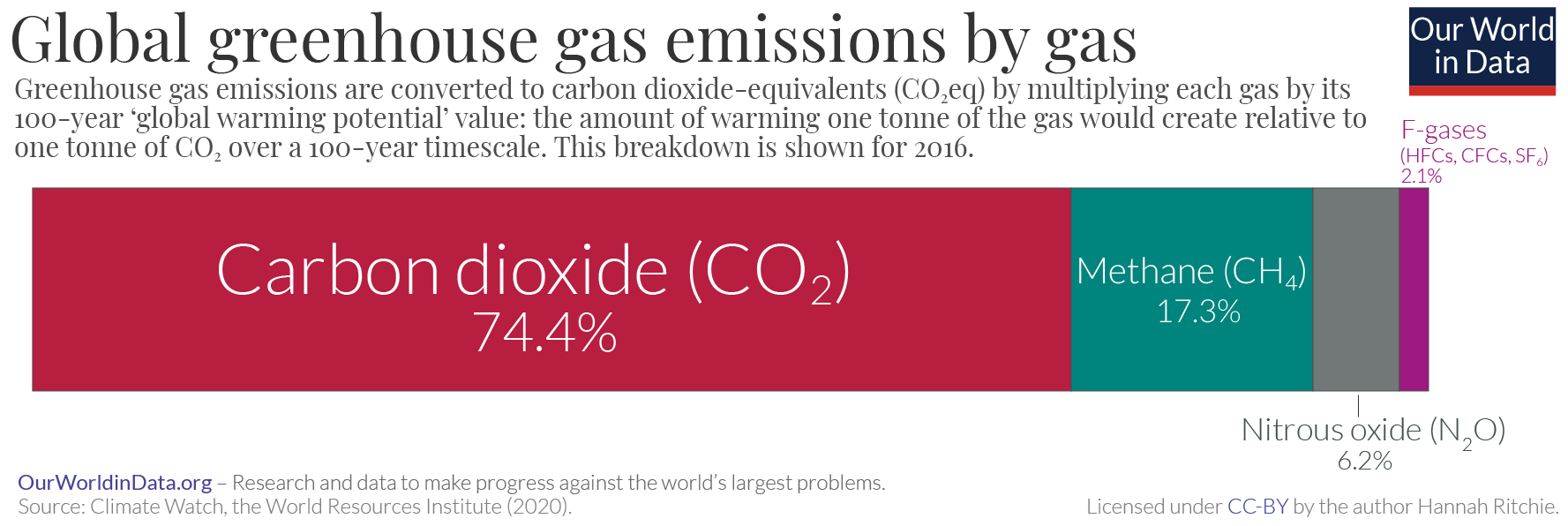
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. The most common example of a CFC is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12). R-12, also commonly called Freon, is used as a refrigerant. Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), gaseous fire suppression systems, and solvents. As a result of CFCs contributing to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) including R-410A, R-134a and 2,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene, R-1234yf. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbons in CFCs bond with tetrahe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. The most common example of a CFC is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12). R-12, also commonly called Freon, is used as a refrigerant. Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), gaseous fire suppression systems, and solvents. As a result of CFCs contributing to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) including R-410A, R-134a and R-1234yf. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbons in CFCs bond with tetrahedral symmetry. Because the fluorine and chlorine atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or through other methods, such as passive cooling and ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners but use a reversing valve, allowing them to both heat and cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used in vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming increasingly common in cool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorine
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from Lipophobicity, oil and hydrophobe, water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/mol). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kigali Amendment
The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol is an international agreement to gradually reduce the consumption and production of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). It is a legally binding agreement designed to create rights and obligations in international law. The Montreal Protocol was originally created to preserve and restore the ozone layer; participating countries agreed to phase out chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), gases that had been causing ozone depletion. HFCs do not contain chlorine, so they do not cause ozone depletion, and therefore have been replacing CFCs under the Protocol. However, HFCs are powerful greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change, so this amendment adds HFCs to the list of chemicals that countries promise to phase down. , 163 states and the European Union have ratified the Kigali Amendment. Background Many industrial products, including refrigerant, refrigerants and other cooling services, use HFCs. Originally, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoromethane
Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is made of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. The name stems from the fact that it is methane (CH4) with a fluorine atom substituted for one of the hydrogen atoms. It is used in semiconductor manufacturing processes as an etching gas in plasma etch reactors. Fluoromethane (originally called "fluorohydrate of methylene") became the first organofluorine compound to be discovered when it was synthesized by French chemists Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot in 1835 by distilling dimethyl sulfate with potassium fluoride. Composition The compound is the lowest mass member of the hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) family, compounds which contain only hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon. These compounds are related to the chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), but since they do not contain chlorine, are not destructive to the ozone l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol on Substances That Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force on 1 January 1989. Since then, it has undergone several amendments and adjustments, with revisions agreed to in 1990 (London), 1992 (Copenhagen), 1995 (Vienna), 1997 (Montreal), 1999 (Beijing), 2007 (Montreal), 2016 (Kigali) and 2018 (Quito). As a result of the international agreement, the ozone hole over Antarctica is slowly recovering. Climate projections indicate that the ozone layer will return to 1980 levels between 2040 (across much of the world) and 2066 (over Antarctica). Due to its widespread adoption and implementation, it has been hailed as an example of successful international co-operation. Former United Nations (UN) Secretary-General Kofi Annan stated that "perhaps the single most succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is a concept used to quantify a change to the balance of energy flowing through a planetary atmosphere. Various factors contribute to this change in energy balance, such as concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols, and changes in surface albedo and solar irradiance. In more technical terms, it is defined as "the change in the net, downward minus upward, radiative flux (expressed in W/m2) due to a change in an external driver of climate change." These external drivers are distinguished from feedbacks and variability that are internal to the climate system, and that further influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the top of the stratosphere. It is quantified in units of watts per square meter, and often summarized as an average over the total surface area of the globe. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerants
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated because of their toxicity and flammability, as well as the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and the contribution of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a direct expansion (DX) circulating system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside or vice versa. These can be air conditioner cooling only systems, cooling & heating reverse DX systems, or heat pump and heating only DX cycles. Refrigerants are controlled substances that are classified by several international safety regulations and, depending on their classification, may only be handled by qualified engineers due to extreme pressure, temperature, flammability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-134a
1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane (also known as norflurane ( INN), R-134a, Klea 134a, Freon 134a, Forane 134a, Genetron 134a, Green Gas, Florasol 134a, Suva 134a, HFA-134a, or HFC-134a) is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and haloalkane refrigerant with thermodynamic properties similar to R-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane) but with insignificant ozone depletion potential and a lower 100-year global warming potential (1,430, compared to R-12's GWP of 10,900). It has the formula CFCHF and a boiling point of −26.3 °C (−15.34 °F) at atmospheric pressure. R-134a cylinders are colored light blue. A phaseout and transition to HFO-1234yf and other refrigerants, with GWPs similar to CO2, began in 2012 within the automotive market. Uses 1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane is a non-flammable gas used primarily as a "high-temperature" refrigerant for domestic refrigeration and automobile air conditioners. These devices began using 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane in the early 1990s as a replacement for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |