|
Hydrochloride Salt
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Of Et3N Hydrochloride
Sample or samples may refer to: * Sample (graphics), an intersection of a color channel and a pixel * Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of something * Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal * Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set People * Sample (surname) * Samples (surname) Places * Sample, Kentucky, unincorporated community, United States * Sampleville, Ohio, unincorporated community, United States * Hugh W. and Sarah Sample House, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Iowa, United States Music * Sample (music), to reuse a portion of a sound recording in another recording, or the portion reused * "Sample" (Sakanaction song) * "Sample", a song by No-Man from ''Flowermix'' * The Samples, a band from Boulder, Colorado Other uses * USS ''Sample'' (FF-1048), a frigate in the U.S. Navy * The Sample, a defunct department store in Buffalo, New York, U.S. * SAMPLE history, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Salt
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Arrhenius acids. Brønsted and Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. The word ''acid'' is derived from the Latin , meaning 'sour'. An aqueous solution of an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acid An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...s, as originally proposed by Guillaume-François Rouelle, G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with Hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a wikt:saturated#Chemistry, saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscibility, miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Publishing, publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, Academic journal, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, Technology, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Pharmacopoeia
The ''European Pharmacopoeia'' (''Pharmacopoeia Europaea'', ''Ph. Eur.'') is a major regional pharmacopoeia which provides common quality standards throughout the pharmaceutical industry in Europe to control the quality of Pharmaceutical drug, medicines, and the substances used to Pharmaceutical manufacturing, manufacture them. It is a published collection of monographs which describe both the individual and general quality standards for ingredients, dosage forms, and methods of Pharmaceutical engineering, analysis for medicines. These standards apply to medicines for both Medicine, human and Veterinary medicine, veterinary use. Legal basis The ''European Pharmacopoeia'' has a Contract, legally binding character. It is used as an official reference to serve public health, and is part of the regulatory requirements for obtaining a Marketing Authorisation (MA) for a medicinal (human or veterinary) product. The quality standards of the European Pharmacopoeia apply throughout the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Base
In chemistry, a free base (freebase, free-base) is a term for the neutral form of an amine or other Lewis base. The term is used in the pharmaceutical industry in contrast to salt-based formulations like hydrochlorides. The amine is often an alkaloid, such as nicotine, cocaine, morphine, and ephedrine, or derivatives thereof. Colloquially, "free-basing" also means the treatment of salts or other formulations to convert them into the free base form, especially for recreational drugs. Properties Some alkaloids are more stable as ionic salts than as free base. The salts usually exhibit greater water solubility. Common counterions include chloride, bromide, sulfate, phosphate, nitrate, acetate, oxalate, citrate, and tartrate. Amine salts formed from the acid–base reaction with hydrochloric acid are known as hydrochlorides. For example, compare the free base hydroxylamine (NH2OH) with the salt hydroxylamine hydrochloride (NH3OH+ Cl−). Freebasing Cocaine hydrochloride ("p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
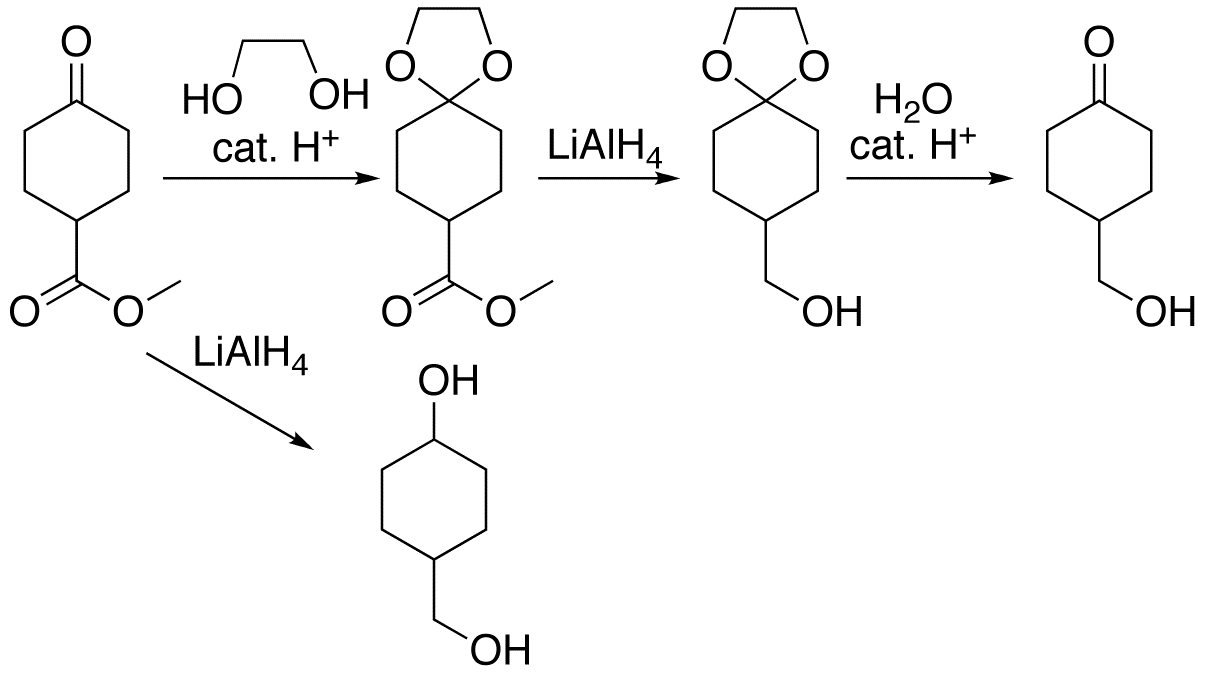
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the acetal, restoring the carbonyl. This step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride is the organic compound with the formula H3O2CCH2NH3l. A white, water-soluble solid, it is the hydrochloride of the methyl ester of the amino acid glycine. Synthesis and reactions Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride can be prepared by treatment of glycine with 2 equivalents of trimethylsilyl chloride Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound ( silyl halide), with the formula , often abbreviated or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely u ..., followed by the addition of methanol. Upon treatment with base, the salt converts to glycine methyl ester. Glycine methyl ester (and other esters of glycine) are not shelf-stable, tending to polymerize when stored at room temperature or convert to diketopiperazine. The hydrochloride is shelf-stable. References {{Reflist Methyl esters Amino acid derivatives Hydrochlorides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pronunciation of the word "chloride" is . Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Other examples of ionic chlorides include potassium chloride (), calcium chloride (), and ammonium chloride (). Examples of covalent chlorides include methyl chloride (), carbon tetrachloride (), sulfuryl chloride (), and monochloramine (). Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger than a chlorine atom (diameter 99 pm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |