|
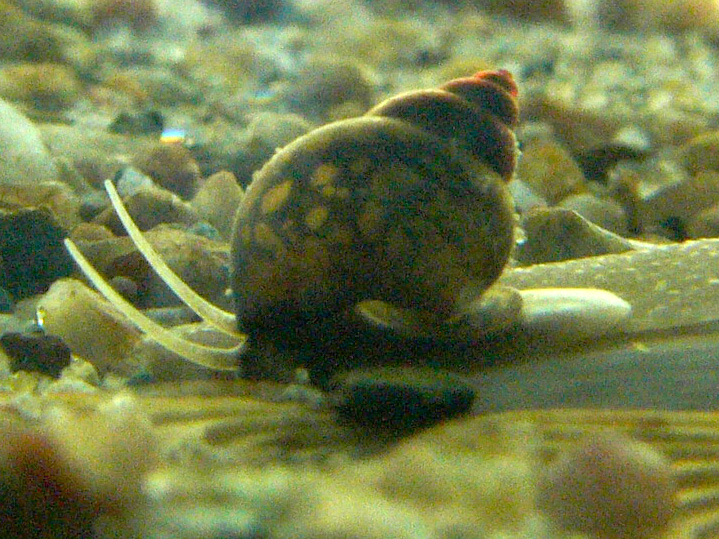
Hydrobioides Nassa
''Hydrobioides nassa'' is a species of a freshwater snail with an operculum, aquatic prosobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Bithyniidae. This species occurs in Laos, Myanmar and Thailand Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa .... ''Hydrobioides nassa'' lives in freshwater rivers, lakes and ponds. References Bithyniidae Gastropods described in 1865 {{Bithyniidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Theobald
William Theobald (1829 – 31 March 1908) was a malacologist and naturalist on the staff of the Geological Survey of India serving in Burma, then a part of British India. Biography Very little is known of Theobald's early life. Theobald was referred to in official documents as "William Theobald, Junior". He arrived in Calcutta on the ship ''Hindostan'' via the Suez in March 1847 and worked as a volunteer in the coal exploration of the upper Damodar and Son valleys under David Williams. During this time Joseph Hooker visited him and they spent time together. Later Theobald became an assistant to John McClelland who took over the exploration from David Williams. He went to Burma in 1855 as a staff of the Geological Survey of India and took over the ''Pegu survey''. He returned Bengal on completion of the survey in 1873 to be appointed Deputy Superintendent of Bengal in 1876.Mabberley DJ (1985). "William Theobald (1829-1908): Unwitting Reformer of Botanical Nomenclature?". ''Taxon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Annandale
Thomas Nelson Annandale Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire, CIE Royal Society of Edinburgh, FRSE (15 June 1876, in Edinburgh – 10 April 1924, in Calcutta) was a British zoology, zoologist, entomologist, anthropology, anthropologist, and Herpetology, herpetologist. He was the founding director of the Zoological Survey of India. Life The eldest son of Thomas Annandale, the regius professor of Regius Chair of Clinical Surgery, clinical surgery at the University of Edinburgh. His maternal grandfather was a publisher, William Nelson. Thomas was educated at Rugby School, Balliol College, Oxford where he studied under Ray Lankester and Edward Burnett Tylor, E. B. Tylor (doing better in anthropology than zoology), and at the University of Edinburgh where he studied anthropology, receiving a D.Sc. (1905). As a student he made visits to Iceland and the Faeroe Islands. In 1899 he travelled with Herbert C. Robinson as part of the Skeat Expedition to the northern part of the Malay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryant Walker
Bryant Walker (1856–1936) was an American malacologist who specialized in the non-marine Mollusca. He mainly studied the freshwater mollusks of the USA, in particular those of Michigan. He published many papers on the Unionida, an order of freshwater mussels. Taxa Walker named numerous taxa of freshwater gastropods and bivalves Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consis ..., including: Gastropods *'' Neoplanorbis carinatus'' Walker, 1908 *†'' Neoplanorbis smithi'' Walker, 1908 Publications A partial list of his publications*Ortmann, A.E., and B. Walker 1912. A new North American naiad. Nautilus 25(9):97-100 + 1 plate. *Ortmann, A.E., and B. Walker 1922. A new genus and species of American naiades. Nautilus 36(1):1-6 + 1 plate. *Ortmann, A.E., and B. Walker. 1922. On the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Snail
Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks that live in fresh water. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs to major rivers. The great majority of freshwater gastropods have a gastropod shell, shell, with very few exceptions. Some groups of snails that live in freshwater Respiratory system, respire using gills, whereas Pulmonata, other groups need to reach the surface to breathe air. In addition, some are amphibious and have both gills and a lung (e.g. ''Ampullariidae''). Most feed on algae, but many are detritivores and some are Filter feeding, filter feeders. Freshwater snails are indirectly among the deadliest animals to humans, as they carry parasitic worms that cause schistosomiasis, a disease estimated to kill between 10,000 and 200,000 people annually. There are thousands of known species, and at least 33–38 independent Lineage (evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operculum (gastropod)
An operculum (; ) is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor that exists in many (but not all) groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails, including the Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc. The operculum is attached to the upper surface of the foot and in its most complete state, it serves as a sort of "trapdoor" to close the aperture (mollusc), aperture of the shell when the soft parts of the animal are retracted. The shape of the operculum varies greatly from one family of gastropods to another. It is fairly often circular, or more or less oval in shape. In species where the operculum fits snugly, its outline corresponds exactly to the shape of the aperture (mollusc), aperture of the shell and it serves to seal the entrance of the shell. Many families have opercula that are reduced in size, and which are not capable of closing the shell aperture. Opercula have sometimes been modifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respiratory system, respiratory organ (biology), organs called gills, cutaneous respiration, through the skin or enteral respiration, across enteral mucosae, although some are evolution, evolved from terrestrial ancestors that re-adaptation, adapted to aquatic environments (e.g. marine reptiles and marine mammals), in which case they actually use lungs to breathing, breathe air and are essentially apnea, holding their breath when living in water. Some species of gastropod mollusc, such as the Elysia chlorotica, eastern emerald sea slug, are even capable of kleptoplastic photosynthesis via endosymbiosis with ingested yellow-green algae. Almost all aquatic animals reproduce in water, either oviparously or viviparously, and many species routinely fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosobranch
Prosobranchia was a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Class (biology), subclass of sea snails, land snails and freshwater snails. This taxon of gastropods dates back to the 1920s. It has however been proven to be polyphyly, polyphyletic (consisting of more than one lineage (evolution), lineage of descent). Generally speaking in biology Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is required to reflect phylogeny, in other words the classification of a group must reflect its evolutionary descent, as far as that is known, so the taxon Prosobranchia is no longer considered suitable to be used. One can still encounter this subclass used as if it is still valid in many texts and websites. Although Prosobranchia is no longer generally accepted as a taxon by people who study living Mollusca, still the term prosobranch is legitimately used as an anatomically descriptive adjective or noun, and the taxon Prosobranchia is still sometimes used by paleontologists. ''Prosobranch'' means ''gills in front'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and sea slug, slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda is a diverse and highly successful class of mollusks within the phylum Mollusca. It contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Furongian, Late Cambrian. , 721 family (taxonomy), families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently neontology, extant living fossil, with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater and even terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known extant i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bithyniidae
Bithyniidae is a family of small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2015). Bithyniidae Gray, 1857. In: MolluscaBase (2015). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=182697 on 2016-02-28 Their minute shell is often colored. They are characterized by a calcareous operculum, a lobe on the upper surface of the neck. The ctenidium, the respiratory gill-comb, is very broad. They have a ciliary feeding habit. The kidney has a large extension towards the mantle. Genera Genera in the family Bithyniidae include: * '' Alocinna'' Annandale & Prashad, 1919 * ''Bithynia'' Leach, 1818 - type genusGlöer P. (2002). ''Die Süßwassergastropoden Nord- und Mitteleuropas''. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands, ConchBooks, Hackenheim, 326 pp., . Reference for subgenera of genus ''Bithynia''. ** Subgenus ''Bithynia'' Leach, 1818 ** Subgenus '' Codiella'' Locard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Non-marine Molluscs Of Thailand
The non-marine mollusks of Thailand are a part of the molluscan fauna of Thailand (the wildlife of Thailand). A number of species of non-marine mollusks are found in the wild in Thailand. There is known at least 23 families, 57 genera and 125 species of land gastropods from Eastern Thailand.Dumrongrojwattana P., Matchacheep S., Kharmkhaew A., Pimubol T., Phookitsana S., Wongtanapanya A. (PDF file created 22 December 2006). "Pre-checklist of non-marine mollusks from Eastern Thailand. (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Basommatophora; Systellomatophora; Stylommatophora)". 7 pp., pages unnumberedPDF. There is known at least 8 species of freshwater gastropods and at least 2 species of freshwater bivalves from the Sakaeo Province in the Eastern Thailand. Boon-ngam P., Sriyarun J., Tanamai S. & Dumrongrojwattana P. (PDF file created 12 January 2010). "การศึกษาเบืองต้ นความหลากชนิดของหอยทากบก และหอยนํ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |