|
Hydraulic Gradient
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a measurement related to liquid pressure (normalized by specific weight) and the liquid elevation above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22, eq.3.2a. It is usually measured as an equivalent liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance (or bottom) of a piezometer. In an aquifer, it can be calculated from the depth to water in a piezometric well (a specialized water well), and given information of the piezometer's elevation and screen depth. Hydraulic head can similarly be measured in a column of water using a standpipe piezometer by measuring the height of the water surface in the tube relative to a common datum. The hydraulic head can be used to determine a ''hydraulic gradient'' between two or more points. Definition In fluid dynamics, the ''head'' at some point in an incompressible (constant density) flow is equal to the height of a static column of fluid whose pressure at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a measurement related to liquid pressure (normalized by specific weight) and the liquid elevation above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22, eq.3.2a. It is usually measured as an equivalent liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance (or bottom) of a piezometer. In an aquifer, it can be calculated from the depth to water in a piezometric well (a specialized water well), and given information of the piezometer's elevation and screen depth. Hydraulic head can similarly be measured in a column of water using a standpipe piezometer by measuring the height of the water surface in the tube relative to a common datum. The hydraulic head can be used to determine a ''hydraulic gradient'' between two or more points. Definition In fluid dynamics, the ''head'' at some point in an incompressible (constant density) flow is equal to the height of a static column of fluid whose pressure at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Pump
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the Energy transformation, conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or Volute (pump), volute chamber (casing), from which it exits. Common uses include water, sewage, agriculture, petroleum, and petrochemical pumping. Centrifugal pumps are often chosen for their high flow rate capabilities, abrasive solution compatibility, mixing potential, as well as their relatively simple engineering. A centrifugal fan is commonly used to implement an Air handler, air handling unit or vacuum cleaner. The reverse function of the centrifugal pump is a water turbine converting potential energy of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to per mille, ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a state function, thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag (physics), drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry. At a fixed point on the surface, the magnitude of gravity of Earth, Earth's gravity results from combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation. At different points on Earth's surface, the free fall acceleration ranges from , depending on altitude, latitude, and longitude. A conventional standard gravity, standard value is defined exactly as 9.80665 m/s² (about 32.1740 ft/s²). Locations of significant variation from this value are known as gravity anomaly, gravity anomalies. This does not take into account other effects, such as buoyancy or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound-force
The pound of force or pound-force (symbol: lbf, sometimes lbf,) is a unit of force used in some systems of measurement, including English Engineering units and the foot–pound–second system. Pound-force should not be confused with pound-mass (lb), often simply called "pound", which is a unit of mass; nor should these be confused with foot-pound (ft⋅lbf), a unit of energy, or pound-foot (lbf⋅ft), a unit of torque. Definitions The pound-force is equal to the gravitational force exerted on a mass of one avoirdupois pound on the surface of Earth. Since the 18th century, the unit has been used in low-precision measurements, for which small changes in Earth's gravity (which varies from equator to pole by up to half a percent) can safely be neglected. The 20th century, however, brought the need for a more precise definition, requiring a standardized value for acceleration due to gravity. Product of avoirdupois pound and standard gravity The pound-force is the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Weight
Unit may refer to: General measurement * Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law **International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system **English units, historical units of measurement used in England up to 1824 ** Unit of length Science and technology Physical sciences * Natural unit, a physical unit of measurement * Geological unit or rock unit, a volume of identifiable rock or ice * Astronomical unit, a unit of length roughly between the Earth and the Sun Chemistry and medicine * Equivalent (chemistry), a unit of measurement used in chemistry and biology * Unit, a vessel or section of a chemical plant * Blood unit, a measurement in blood transfusion * Enzyme unit, a measurement of active enzyme in a sample * International unit, a unit of measurement for nutrients and drugs Mathematics * Unit number, the number 1 * Unit, identity element * Unit (ring theory), an element that is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the International System of Units (SI) system, the base unit for length is the metre. Length is commonly understood to mean the most extended size, dimension of a fixed object. However, this is not always the case and may depend on the position the object is in. Various terms for the length of a fixed object are used, and these include height, which is vertical length or vertical extent, width, breadth, and depth. ''Height'' is used when there is a base from which vertical measurements can be taken. ''Width'' and ''breadth'' usually refer to a shorter dimension than ''length''. ''Depth'' is used for the measure of a third dimension. Length is the measure of one spatial dimension, whereas area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
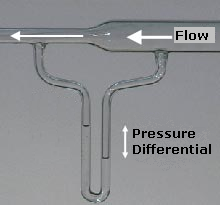
Bernoulli's Principle
Bernoulli's principle is a key concept in fluid dynamics that relates pressure, speed and height. For example, for a fluid flowing horizontally Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure, pressure The principle is named after the Swiss mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in his book ''Hydrodynamica'' in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler in 1752 who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form. Bernoulli's principle can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy. This states that, in a steady flow, the sum of all forms of energy in a fluid is the same at all points that are free of viscous forces. This requires that the sum of kinetic energy, potential energy and internal energy remains constant. Thus an increase in the speed of the fluid—implying an increase in its kinetic energy—occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy of an object or system due to the body's position relative to other objects, or the configuration of its particles. The energy is equal to the work done against any restoring forces, such as gravity or those in a spring. The term ''potential energy'' was introduced by the 19th-century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine, although it has links to the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of Potentiality and Actuality, ''potentiality''. Common types of potential energy include gravitational potential energy, the elastic potential energy of a deformed spring, and the electric potential energy of an electric charge and an electric field. The unit for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (symbol J). Potential energy is associated with forces that act on a body in a way that the total Work (physics), work done by these forces on the body depends only on the initial and final positions of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
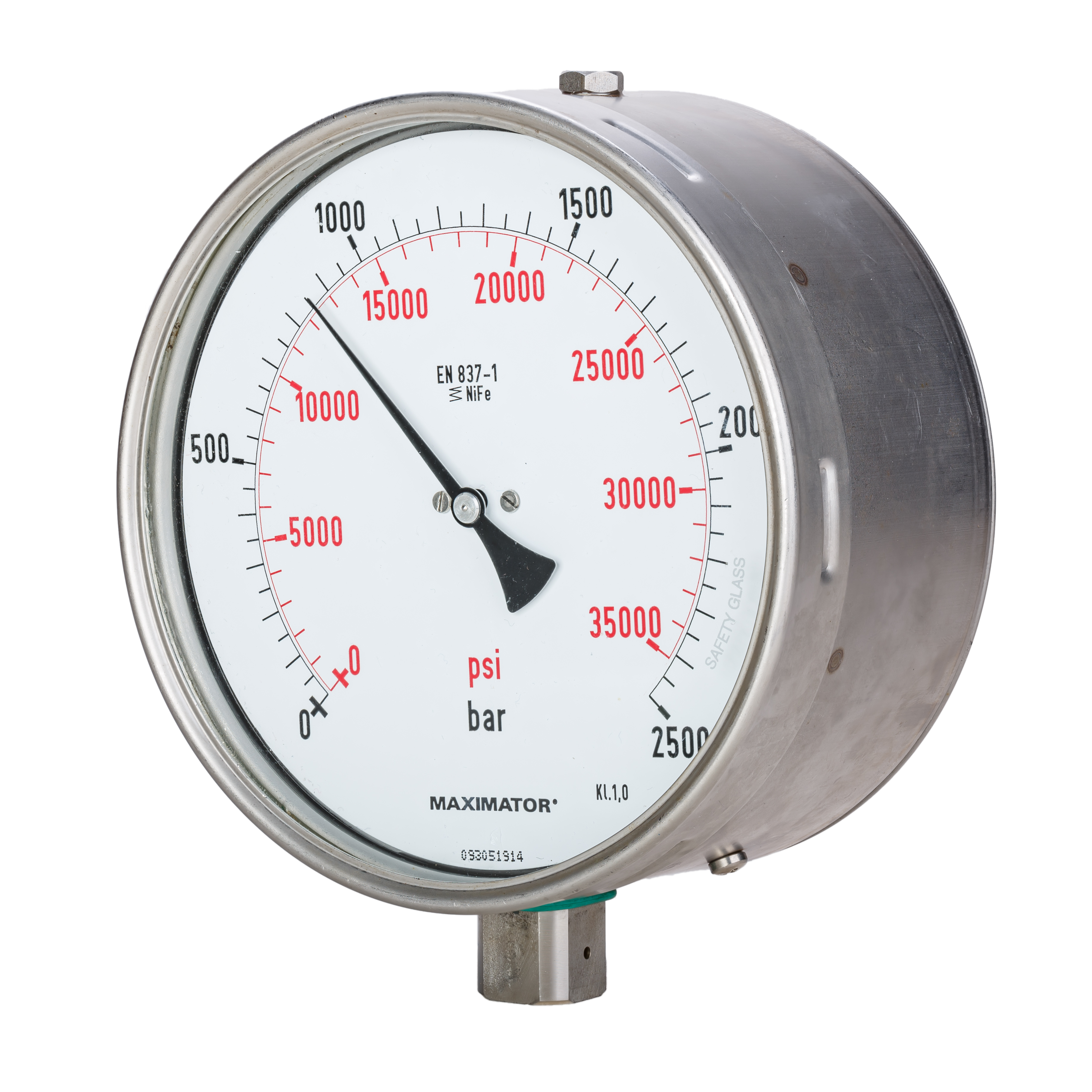
Pressure Measurement
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge (engineering)
In science and engineering, a dimensional gauge or simply gauge is a device used to make measurements or to display certain dimensional information. A wide variety of tools exist which serve such functions, ranging from simple pieces of material against which sizes can be measured to complex pieces of machinery. Dimensional properties include thickness, gap in space, diameter of materials.Ray Herren, ''Agricultural Mechanics: Fundamentals & Applications'' (2009), p. 109.Barry Hollembeak, ''Today's Technician: Automotive Electricity and Electronics'' (2010). Basic types All gauges can be divided into four main types, independent of their actual use. # Analogue instrument meter with ''analogue display'' ("needles"). Until the later decades the most common basic type. # Digital instrument meter with ''analogue display''. A screen that shows an "analogue meter", commonly used in modern aircraft cockpits, and some hospital equipment etc. # Digital instrument meter with ''digital dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |