|
Hwasong-14
The Hwasong-14 () is a mobile intercontinental ballistic missile developed by North Korea. It had its maiden flight on 4 July 2017, which coincided with the United States' Independence Day. North Korea is the only known operator of this missile. Description The Hwasong-14 is likely a two-stage version of the Hwasong-12 first tested in May 2017. The second stage appears to have increased its range. The first stage engine appears very similar to the Hwasong-12. With a single liquid fuel engine, it has four vernier thrusters for stability and guidance. Based on images, the missile is estimated to be long and wide, and has a takeoff mass of . A detailed analysis by the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists claims that the current variant of the Hwasong-14 may not even be capable of delivering a first-generation nuclear warhead to Anchorage, Alaska. But even if North Korea is now capable of fabricating a relatively light-weight, "miniaturized" atomic bomb that can survive the extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KN Number
The KN number () is the designation used by the United States for describing North Korean missiles. Description The "KN" stands for "Korea, North", which is the reverse form of "North Korea". It is used by United States Forces Korea, United States military for designating North Korean missiles. The number following "KN" represents the order of the missile learned about by South Korea and the United States. For example, "Hwasong-11B, KN-24" is the 24th North Korean missile recognized by South Korea and the U.S. militaries. List of KN numbers Official numbers Unofficial numbers See also * Hwasong (missile family) * NATO reporting name References {{DPRK missiles Guided missiles of North Korea Naming conventions Code names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean People's Army Strategic Force
The Korean People's Army Strategic Force (), previously known as the Korean People's Army Strategic Rocket Force (), is a military branch of the Korean People's Army (KPA) founded in 2012 that operates surface-to-surface missiles in the nuclear and conventional strike roles. It is mainly armed with ballistic missiles. The inventory includes domestic and Soviet Union, Soviet designs. History North Korea received rocket artillery, surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), and anti-ship missiles from the Soviet Union in the 1960s and then from China in the 1970s. The decision to develop a domestic missile production capability was likely made by 1965 after the Soviet Union refused to supply ballistic missiles. Military and industrial preparations began shortly afterward. China agreed to assist North Korea develop ballistic missiles. A joint development program for the DF-61 missile began in 1977. It was cancelled in 1978 due to Chinese domestic politics. In the late-1970s or early-1980s, Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 () is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MIRV (multiple re-entry vehicle, multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M, also known as RS20, was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of atmospheric re-entry, re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
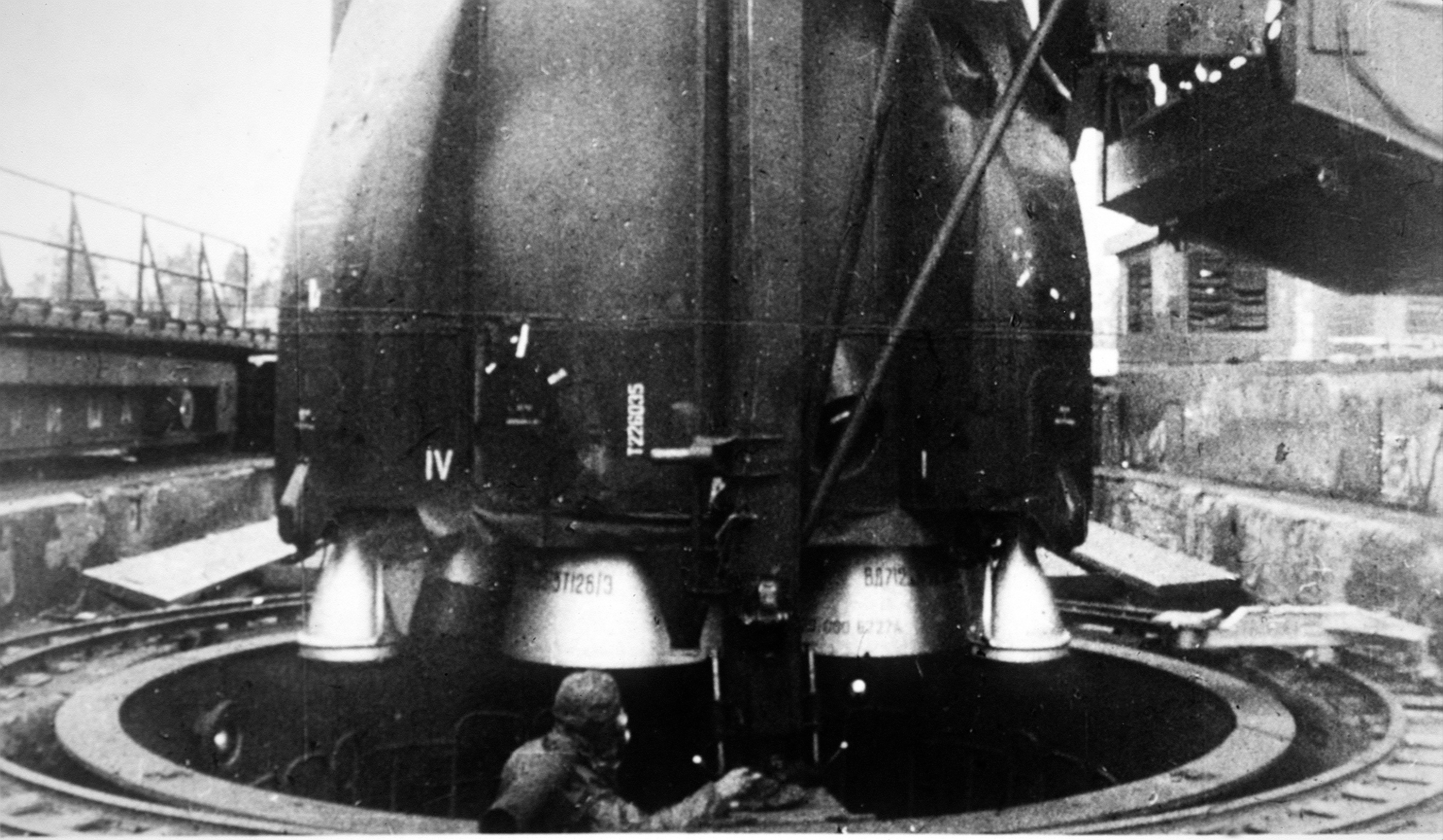
RD-250
The RD-250 (, GRAU index: 8D518) is the base version of a dual-nozzle family of liquid-fuel rocket engines, burning a hypergolic mixture of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) fuel with dinitrogen tetroxide () oxidizer in a gas-generator open cycle. The RD-250 was developed by OKB-456 for Yangel's PA Yuzhmash ICBM, the R-36 (8K67). Its variations were also used on the Tsyklon-2 and Tsyklon-3 launch vehicles. It was supposed to be used on the Tsyklon-4, but since the cancellation of the project it should be considered as out of production. Versions The engine has seen different versions made: * RD-250 (GRAU index: 8D518): Base engine of the family. Used on the R-36. A bundle of three RD-250 form the RD-251 cluster. * RD-250P (GRAU index: 8D518P): Improved version of the RD-250. Used on the R-36P. A bundle of three RD-250P form the RD-251P cluster. * RD-250M (GRAU index: 8D518M): Improved version of the RD-250P. Used on the R-36-O. A bundle of three RD-250M form the RD-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hwasong-12
The Hwasong-12 () is a mobile intermediate-range ballistic missile developed by North Korea. The Hwasong-12 was first revealed to the international community in a military parade on 15 April 2017 celebrating the Day of the Sun which is the birth anniversary of North Korea's founding president, Kim Il Sung. Description Based on photos of the launch on 14 May 2017, the Hwasong-12 appears to be a single-stage, liquid-fueled missile, using an engine configuration of a single combustion chamber and four vernier engines. The arrangement appears similar to the "high-thrust" engine test conducted in March 2017. Alternatively, it could be based on the engine used in the older Hwasong-10 with the addition of two more verniers. The Hwasong-12's engine is tentatively named ''Paektusan'', which is based on the RD-250 engine design. Initial estimates suggest the Hwasong-12 would have a maximum range from between with a payload and with a payload to as much as . The missile is also clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington D
Washington most commonly refers to: * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States * Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Fort Washington (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reentry Vehicle
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass (ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Concerned Scientists
The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) is a nonprofit science advocacy organization based in the United States. The UCS membership includes many private citizens in addition to professional scientists. Anne Kapuscinski, Professor of Environmental Studies and Director of the Coastal Science and Policy Program at the University of California, Santa Cruz, chairs the UCS Board of Directors , having replaced James J. McCarthy, Professor of Biological Oceanography at Harvard University and past president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. History The Union of Concerned Scientists was founded in 1969 by faculty and students of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The organization's founding document says it was formed to "initiate a critical and continuing examination of governmental policy in areas where science and technology are of actual or potential significance" and to "devise means for turning research applications away from the present emphasis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
38 North
''38 North'' is a website devoted to analysis about North Korea. Its name refers to the 38th parallel north which passes through the Korean peninsula and from 1945 until the start of the Korean War in 1950 divided the peninsula into North and South Korea. Formerly a program of the US-Korea Institute at Johns Hopkins University's Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies, it is now housed at the Stimson Center and is directed by Senior Fellow Jenny Town. Notable contributors include nuclear scientist Sigfried Hecker, former Associated Press Pyongyang Bureau Chief Jean H. Lee, cybersecurity expert James Andrew Lewis, and North Korea Tech founder Martyn Williams. Satellite imagery analysis ''38 North'' is an authoritative source of policy and technical analysis regarding North Korea's internal and external affairs. It aims to facilitate an informed public policy debate about peace and security on the Korean Peninsula and provide policymakers, practitioners and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |