|
Hurricane Rachel (2014)
The 2014 Pacific hurricane season was one of the busiest and costliest Pacific hurricane seasons since the keeping of reliable records began in 1949. The season officially started on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in these regions of the Pacific. Entering the season, expectations of tropical activity were high, with most weather agencies predicting a near or above average season. The season began with an active start, with three tropical cyclones developing before June 15, including two Category 4 hurricanes, of which one became the strongest tropical cyclone ever recorded in May in the East Pacific. After a less active period in late June and early July, activity once again picked up in late July. Activity increased in August, which featured four major hurricanes, and persisted throughout Septe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Odile (2014)
Hurricane Odile is tied for the most intense landfalling tropical cyclone in the Baja California Peninsula during the weather satellite, satellite era. Sweeping across the peninsula in September 2014, Odile inflicted widespread damage, particularly in the States of Mexico, state of Baja California Sur, in addition to causing lesser impacts on the Mexican mainland and Southwestern United States. The precursor to Odile tropical cyclogenesis, developed into a tropical depression south of Mexico on September 10 and quickly reached tropical storm strength. After meandering for several days, Odile began to track northwestward, intensifying to hurricane status before rapidly reaching its Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, Category 4 hurricane peak intensity on September 14. The cyclone slightly weakened before making landfall near Cabo San Lucas with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). Odile gradually weakened as it tracked across the length of the Baja Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Norbert (2014)
Hurricane Norbert produced a 1-in-1,000 year rainfall event in Arizona in early September 2014. The fifteenth named storm, tenth hurricane, and seventh major hurricane of the 2014 Pacific hurricane season, Norbert originated from an area of disturbed weather in association with an area of low pressure on September 2. Tracking generally northwestward, the newly designated tropical storm steadily organized in a moderate shear environment. Norbert attained hurricane intensity early on September 4 and Category 2 hurricane strength the next afternoon. Thereafter, the cyclone began a period of rapid deepening, and it subsequently attained its peak intensity with winds of and a minimum pressure of early on September 6. A track over progressively cooler waters and into a more stable environment prompted a weakening trend after peak intensity, and by early on September 8, the system no longer maintained enough convection to be considered a tropical cyclon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Iselle
Hurricane Iselle was the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall on the island of Hawaii in recorded history. The tenth named storm, fifth hurricane, and fourth major hurricane of the 2014 hurricane season, Iselle developed from an area of disturbed weather southwest of Mexico on July 31, 2014. Assuming a west-northwest course that it would maintain throughout its existence, generally favorable atmospheric conditions allowed for gradual strengthening, with the cyclone attaining hurricane status a day after formation. Continued strengthening progressed for several days up until August 4, when Iselle reached peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 947 mbar (hPa; 27.96 inHg), making it a Category 4 hurricane. Thereafter, Iselle encountered hostile environmental conditions and quickly weakened before making landfall on the Big Island on August 8 as a moderate tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Genevieve (2014)
Hurricane Genevieve, also referred to as Typhoon Genevieve, was the first tropical cyclone to track across all three northern Pacific basins since Hurricane Dora (1999), Hurricane Dora in 1999. Genevieve developed from a tropical wave into the eighth tropical storm of the 2014 Pacific hurricane season well east-southeast of Hawaii on July 25. However, increased vertical wind shear caused it to weaken into a tropical depression by the following day and degenerate into a remnant low on July 28. Late on July 29, the system regenerated into a tropical depression, but it weakened into a remnant low again on July 31, owing to vertical wind shear and dry air. The remnants redeveloped into a tropical depression and briefly became a tropical storm south of Hawaii on August 2, yet it weakened back into a tropical depression soon afterwards. Late on August 5, Genevieve re-intensified into a tropical storm, and intensified into a Category 1 hurricane on the next day when undergoing rapid deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Boris (2014)
Tropical Storm Boris was a weak and short-lived tropical cyclone that brought rainfall to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec and surrounding areas in June 2014. The second named storm of the season, Boris developed from the interaction of a low-level trough and a Kelvin wave south of Mexico late on June 2. Initially a tropical depression, the system moved generally northward and strengthened into Tropical Storm Boris by midday on June 3. About six hours later, Boris peaked with maximum sustained winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) – indicative of a weak tropical storm. By early on June 4, interaction with land caused the storm to weaken, deteriorating to a tropical depression. Later that day, Boris degenerated into a remnant low pressure, before fully dissipating over the Gulf of Tehuantepec on June 5. As Boris approached land, tropical cyclone warnings and watches were issued, school classes were canceled, and evacuations occurred in Southwestern Mexico an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacific region: from the equator northward, 140°W–180°W, most significantly for Hawai‘i. It is the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclones in this region, and in this capacity is known as RSMC Honolulu. Based in Honolulu, Hawaii, the CPHC is co-located with the National Weather Service's Honolulu forecast office on the campus of the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. The Honolulu forecast office activates the CPHC when tropical cyclones form in, or move into, the Central Pacific region. The CPHC replaced the previous forecaster, the Joint Hurricane Warning Center, starting in the 1970 season. Area of responsibility The CPHC's area of responsibility is the Central Pacific (CP) region, which is an adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
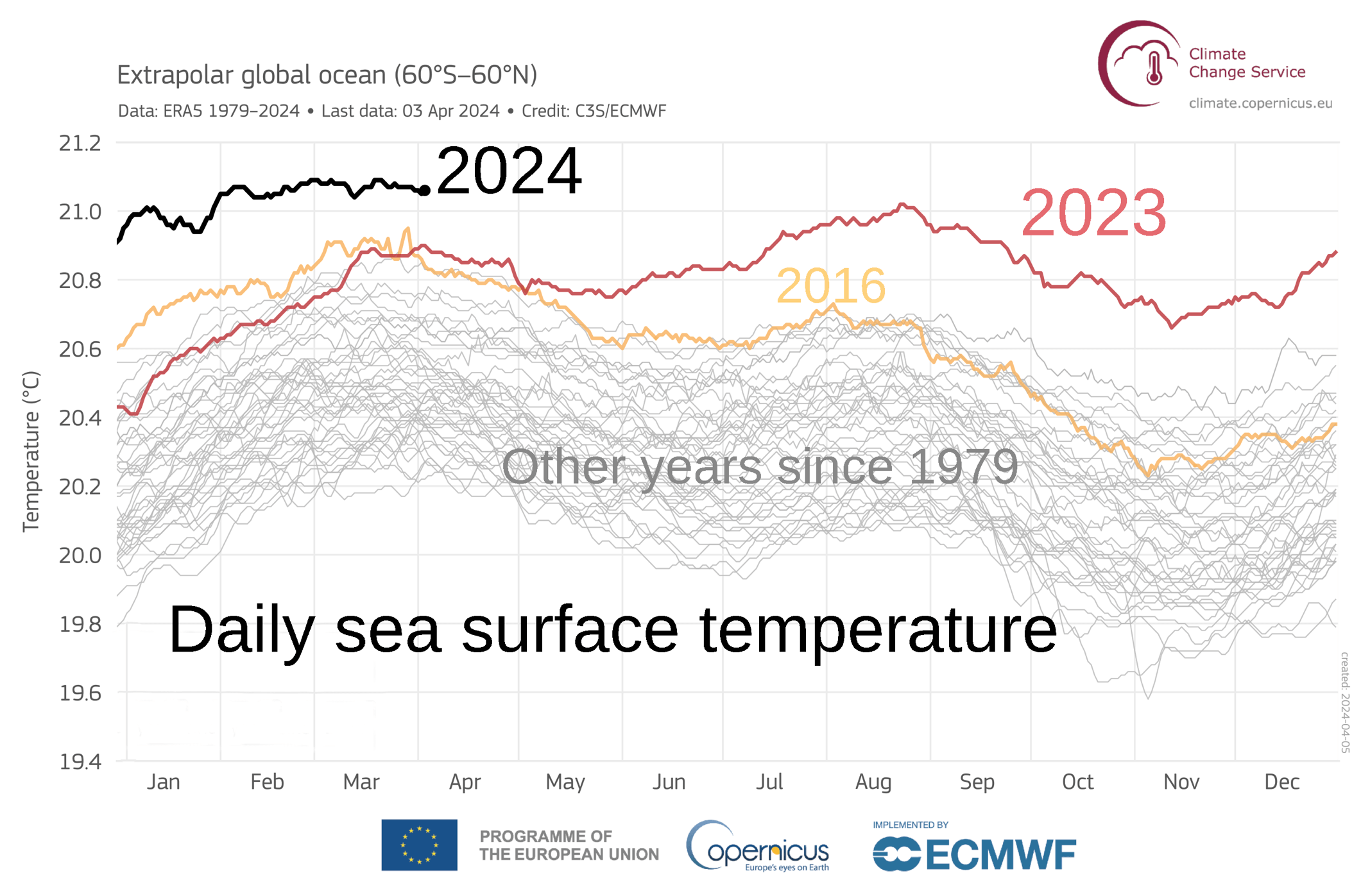
Sea Surface Temperatures
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea surface. Sea surface temperatures greatly modify air masses in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere within a short distance of the shore. The thermohaline circulation has a major impact on average sea surface temperature throughout most of the world's oceans. Warm sea surface temperatures can develop and Tropical cyclogenesis, strengthen cyclones over the ocean. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake. This is due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. Sea surface temperature changes during the day. This is like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less variation in sea surface temperature on breezy days than on calm days. Coastal sea surface temperatures can cause offshore winds to generate upwelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulated Cyclone Energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used to compare overall activity of tropical cyclones, utilizing the available records of windspeeds at six-hour intervals to synthesize storm duration and strength into a single index value. The ACE index may refer to a single storm or to groups of storms such as those within a particular month, a full season or combined seasons. It is calculated by summing the square of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds, as recorded every six hours, but only for windspeeds of at least tropical storm strength (≥ 34 kn; 63 km/h; 39 mph); the resulting figure is divided by 10,000 to place it on a more manageable scale. The calculation originated as the Hurricane Destruction Potential (HDP) index, which sums the squares of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds while at hurricane strength, at least 64 knots (≥ 119 km/h; 74 mph) at six-hour recorded intervals across an entire season. The HDP index was later modified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in the Superman dynasty * E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film '' Road Trip'' Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él ''(Lucerito album), a 1982 album by Lucerito * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from the album '' Caminando'' * "Él" (Lucía song), the Spanish entry performed by Lucía in the Eurovision Song Contest 1982 Other media * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (film), a 1953 film by Luis Buñuel based on the 1926 novel * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 1991 Japanese adult visual novel * EL TV, an Azerbaijani regional television channel Companies and organizations * Estée Lauder Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Prediction Center
The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) is a United States federal agency that is one of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction, which are a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. CPC is headquartered in College Park, Maryland. Its roots trace back to the climatological work of Thomas Jefferson, with the United States Army Signal Corp taking over responsibility of the climate program in the late 19th century. Once it became part of the United States Weather Bureau, it was known as the Weather Bureau Climate and Crop Services. From 1957 through 1966, the United States Weather Bureau's Office of Climatology, located in Washington, D.C., and then Suitland, Maryland, published the Mariners Weather Log publication. Late in the 20th century, it was known as the Climate Analysis Center for a time, before evolving into CPC in 1995. CPC issues climate forecasts valid for weeks and months in advance. History The roots of modern c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |