|
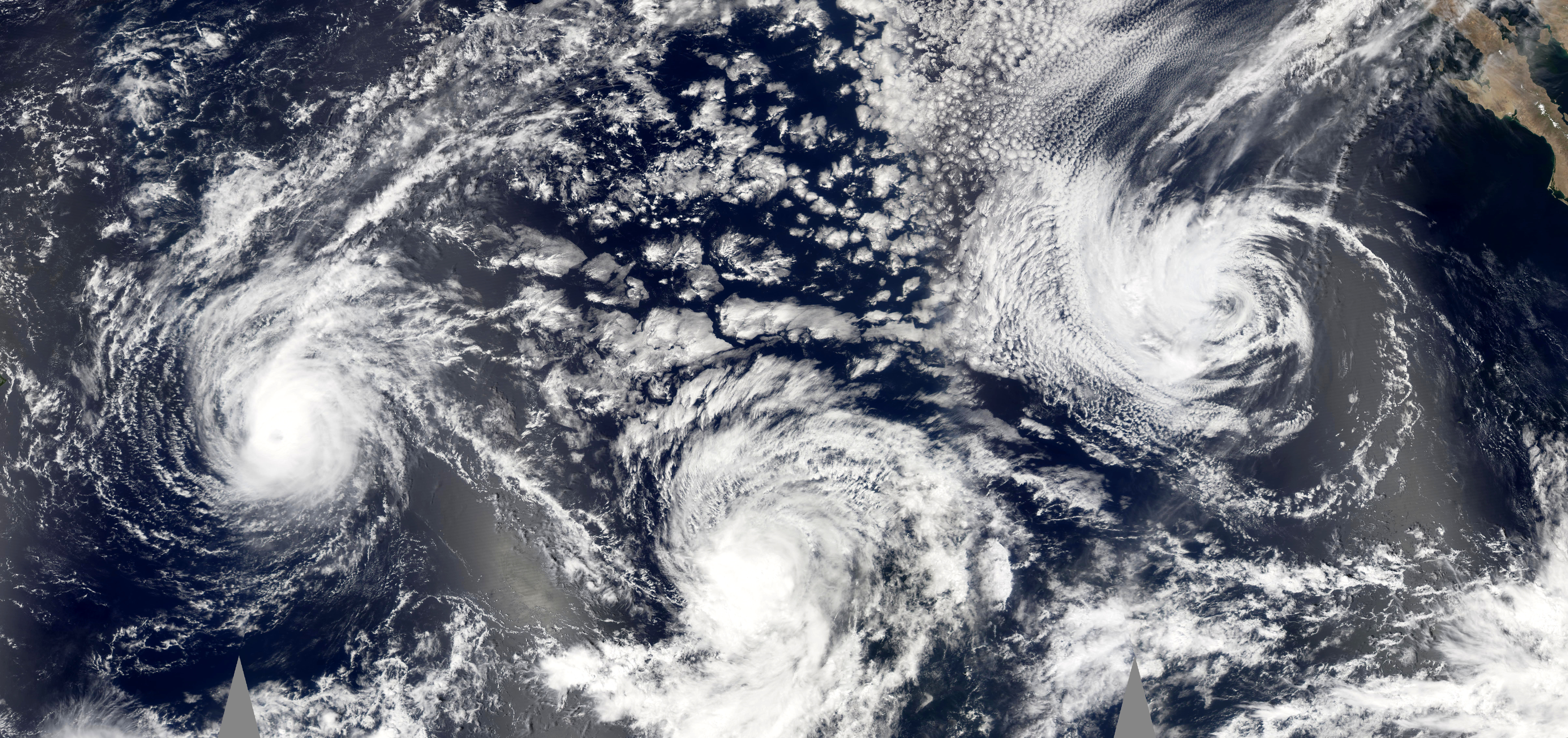
Hurricane Max
The name Max has been used for six tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean and for one in the Australian region of the Indian Ocean. In the Eastern Pacific: * Tropical Storm Max (1981) – formed in the open ocean * Hurricane Max (1987) – Category 4 hurricane that churned in the open ocean * Tropical Storm Max (1993) – formed in the open ocean * Hurricane Max (2005) – Category 1 hurricane that was no threat to land * Hurricane Max (2017) – Category 1 hurricane that made landfall in southwestern Mexico * Tropical Storm Max (2023) – made landfall in southwestern Mexico In the Australian region: * Cyclone Max (1981) – Category 3 tropical cyclone, crossed the Top End of Australia's Northern Territory, then moved west out to sea See also * List of storms named Mac, a similar name used for tropical cyclones in the Western Pacific Ocean {{DEFAULTSORT:Max Pacific hurricane set index articles Australian region cyclone set index articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . ''Encyclopædia Britannica, Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the Land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the Pole of inaccessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Max (1981)
The 1981 Pacific hurricane season was a slightly below average Pacific hurricane season. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific basin and June 1 in the central Pacific basin. Both basins' seasons ended on November 30; these dates conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first tropical cyclone of the season was designated on May 30, and the final storm of the season, Hurricane Otis, dissipated on October 30. The season produced fifteen named storms and a total of eight hurricanes, which was near normal. However, the total of one major hurricane was below the average of three. The strongest tropical cyclone of the season was Hurricane Norma, which was a powerful Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. The storm caused six deaths – five in Texas, and one in Mexico, due to severe flooding. Additionally, the storm caused $74 million (equivalent to $ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Max (1987)
The 1987 Pacific hurricane season was the last year in which the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center was the primary warning center for tropical cyclones in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started May 15, 1987, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1987, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1987. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when the vast majority of tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. Despite there being 20 named systems, five above the average, only four storms directly affected land. Hurricane Eugene was the first Pacific hurricane to make landfall in Mexico in July since the 1954 season and caused three deaths and $142.12 million damage. Tropical Storm Pilar and Hurricane Norma also came close to land, with the former producing record rain in Baja California Sur. The remnants of Hurricanes Ramon and Norma caused rain in the Continental United States, with the former responsible for five traffic- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Max (1993)
The 1993 Pacific hurricane season included more than double the average number of major hurricanes – Category 3 or stronger cyclones on the Saffir–Simpson scale. This activity was the result of an El Niño event, which is the main factor contributing to above-average activity across the Pacific basin. The season featured 15 named storms, 11 hurricanes, and 9 major hurricanes. While the number of named storms was near the long-term average, the number of hurricanes was above the average of 8, and the number of major hurricanes far exceeded the long-term average of 4. Seasonal activity began on May 17 and ended on November 8, within the confines of a traditional hurricane season which begins on May 15 in the East Pacific and June 1 in the Central Pacific. The season ends on November 30 in both basins. These dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones form. A majority of the season's storms formed from tropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Max (2005)
The 2005 Pacific hurricane season was a near-average Pacific hurricane season which produced fifteen named storms, seven hurricanes and two major hurricanes. It was also the second consecutive season in which no tropical cyclone of at least tropical storm intensity made landfall. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. Activity began with the formation of Hurricane Adrian, the fourth-earliest-forming tropical storm on record in the basin at the time. Adrian led to flash flooding and several landslides across Central America, resulting in five deaths and $12 million (2005 USD) in damage. Tropical storms Calvin and Dora caused minor damage along the coastline, while Tropical Storm Eugen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Max (2017)
Hurricane Max was a rapidly-forming tropical cyclone that made landfall in southwestern Mexico, causing minor damage. The sixteenth tropical cyclone, thirteenth named storm, and seventh hurricane of the 2017 Pacific hurricane season, Max developed from a trough of low pressure near the southwestern coast of Mexico on September 13. The storm tracked northeastward under the influence of a mid-level ridge and rapidly strengthened as a result of warm ocean temperatures in its path. Max strengthened into a hurricane on September 14 and peaked as a high-end Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson scale shortly before making landfall in the Mexican state of Guerrero. Rapid weakening ensued as Max moved over the mountainous terrain of Mexico, and it weakened below hurricane strength early on September 15. At 12:00 UTC that day, Max dissipated over the mountains of southern Mexico. The Government of Mexico issued numerous tropical storm and hurricane watches and warnings in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Max (2023)
Tropical Storm Max was the first of four tropical cyclones to make landfall along the Pacific Coast of Mexico in October 2023. The sixteenth tropical depression and thirteenth named storm of the 2023 Pacific hurricane season, Max originated from a trough that developed to the southwest of Central America on October 3, 2023. Showers and thunderstorms associated with the disturbance gradually became better organized over the following days as it moved west-northwestwards to the south of Mexico. The disturbance was designated Potential Tropical Cyclone Sixteen-E on October 7 by the United States National Hurricane Center (NHC), as it had not yet become a tropical cyclone but was threatening the southwestern coast of Mexico. The disturbance developed a more well-defined circulation the following day and developed into a tropical depression; the depression strengthened into a tropical storm late on October 8 and was assigned the name ''Max''. Max progressed northward toward the coast of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Max
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Storms Named Mac
The name Mac has been used for four tropical cyclone A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...s, all in the Western Pacific Ocean: * Severe Tropical Storm Mac (1979) (T7914, 27W, Pepang) – crossed southern Luzon and then made landfall near Hong Kong * Typhoon Mac (1982) (T8221, 28W, Uding) – an intense Category 5-equivalent typhoon that stayed at sea throughout its existence * Tropical Storm Mac (1986) (T8604, 04W, Klaring) – an early-season storm that brushed the coasts of Taiwan and northern Luzon * Typhoon Mac (1989) (T8913, 15W) – a moderately strong typhoon which struck Japan See also * List of storms named Max, a similar name used for tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific and Australian region basins {{DEFAULTSORT:Mac Pacific typhoon set index a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Hurricane Set Index Articles
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |