|
Hurricane Alma (1966)
Hurricane Alma was a rare June major hurricane in the 1966 Atlantic hurricane season. It was the earliest North Atlantic tropical cyclone, Atlantic hurricane in the calendar year in 1951 Atlantic hurricane season, fifteen years, as well as the earliest continental U.S. hurricane strike since 1825. Alma developed on June 4 over Central America, and while moving through Honduras, it dropped heavy rainfall that killed at least 73 people in the city of San Rafael, Lempira, San Rafael. Offshore northern Honduras, the system produced heavy rainfall in Swan Islands, Honduras, Swan Island. Alma moved northeastward and intensified into a hurricane on June 6. It crossed western Cuba, causing heavy crop damage and water shortages. Alma destroyed over 1,000 houses, and damage was estimated around $200 million (1966 United States dollar, USD). The storm killed 11 people in the country. After crossing Cuba, Alma intensified further to reach winds of in the Gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America after Guatemala and Honduras. Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean and shares maritime borders with El Salvador to the west and Colombia to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is Managua, the List of largest cities in Central America#Largest cities proper, fourth-largest city in Central America, with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is Spanish language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area (LPA), low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. It is the opposite of a high-pressure area. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of a tropical cyclone. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds of the cyclone occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is where the barometer reading is lowest. Structure A typical tropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park of the United States located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's coral reefs are the least disturbed of the Florida Keys reefs. The park is noted for abundant sea life, tropical bird breeding grounds, colorful coral reefs, and shipwrecks and sunken treasures. The park's centerpiece is Fort Jefferson, a massive but unfinished coastal fortress. Fort Jefferson is the largest brick masonry structure in the Western Hemisphere, composed of more than 16 million bricks. Dry Tortugas is unique in its combination of a largely undisturbed tropical ecosystem with significant historic artifacts. The park is accessible only by seaplane or boat and has averaged about 63,000 visitors annually in the period from 2008 to 2017. Activities include snorkeling, picnicking, birdw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isla De La Juventud
Isla de la Juventud (; ) is the second-largest Cuban island (after Cuba's mainland) and the seventh-largest island in the West Indies (after mainland Cuba itself, Hispaniola, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Trinidad, and Andros Island). The island was called the Isle of Pines () until 1978. It has an area and is south of the island of Cuba, across the Gulf of Batabanó. The island lies almost directly south of Havana and Pinar del Río Province, Pinar del Río and is a Special Municipality (), not part of any Provinces of Cuba, province and is therefore administered directly by the central government of Cuba. The island has only one municipality, also named Isla de la Juventud. The largest of the 350 islands in the Canarreos Archipelago (''Archipiélago de los Canarreos''), the island had an estimated population of 83,544 in 2019. The capital and largest city is Nueva Gerona in the north, and the second largest and oldest city is Santa Fe, Cuba, Santa Fe in the interior. Other commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Able (1951)
Hurricane Able was a rare hurricane that formed outside the typical North Atlantic hurricane season. The second tropical storm and first hurricane of 1951, Able developed from a trough of low pressure on May 15 about south of Bermuda. Initially subtropical in nature, Able acquired tropical characteristics as it moved over the warm waters of the Gulf Stream and attained hurricane status on May 17 off the coast of Florida. This made Able one of only four May Atlantic hurricanes on record. On May 22 Able reached peak winds of about off Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. The hurricane weakened as it turned eastward, and became an extratropical cyclone on May 23, before dissipating on the next day. Hurricane Able did not affect land significantly. In Florida, the storm dropped light precipitation, while in the Bahamas it produced winds of up to . From North Carolina through New England, Able produced higher than normal tides. No casualties were reported. Meteorological history An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclone, anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are close, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection (meteorology)
Atmospheric convection is the vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. It occurs when warmer, less dense air rises, while cooler, denser air sinks. This process is driven by Air parcel, parcel-environment instability, meaning that a "parcel" of air is warmer and less dense than the surrounding environment at the same altitude. This difference in temperature and density (and sometimes humidity) causes the parcel to rise, a process known as buoyancy. This rising air, along with the compensating sinking air, leads to mixing, which in turn expands the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), the lowest part of the atmosphere directly influenced by the Earth's surface. This expansion contributes to increased Wind, winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface Dew point, dew points (the temperature below which condensation occurs). Convection plays a crucial role in weather patterns, influencing cloud formation, wind, and the development of Thunderstor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
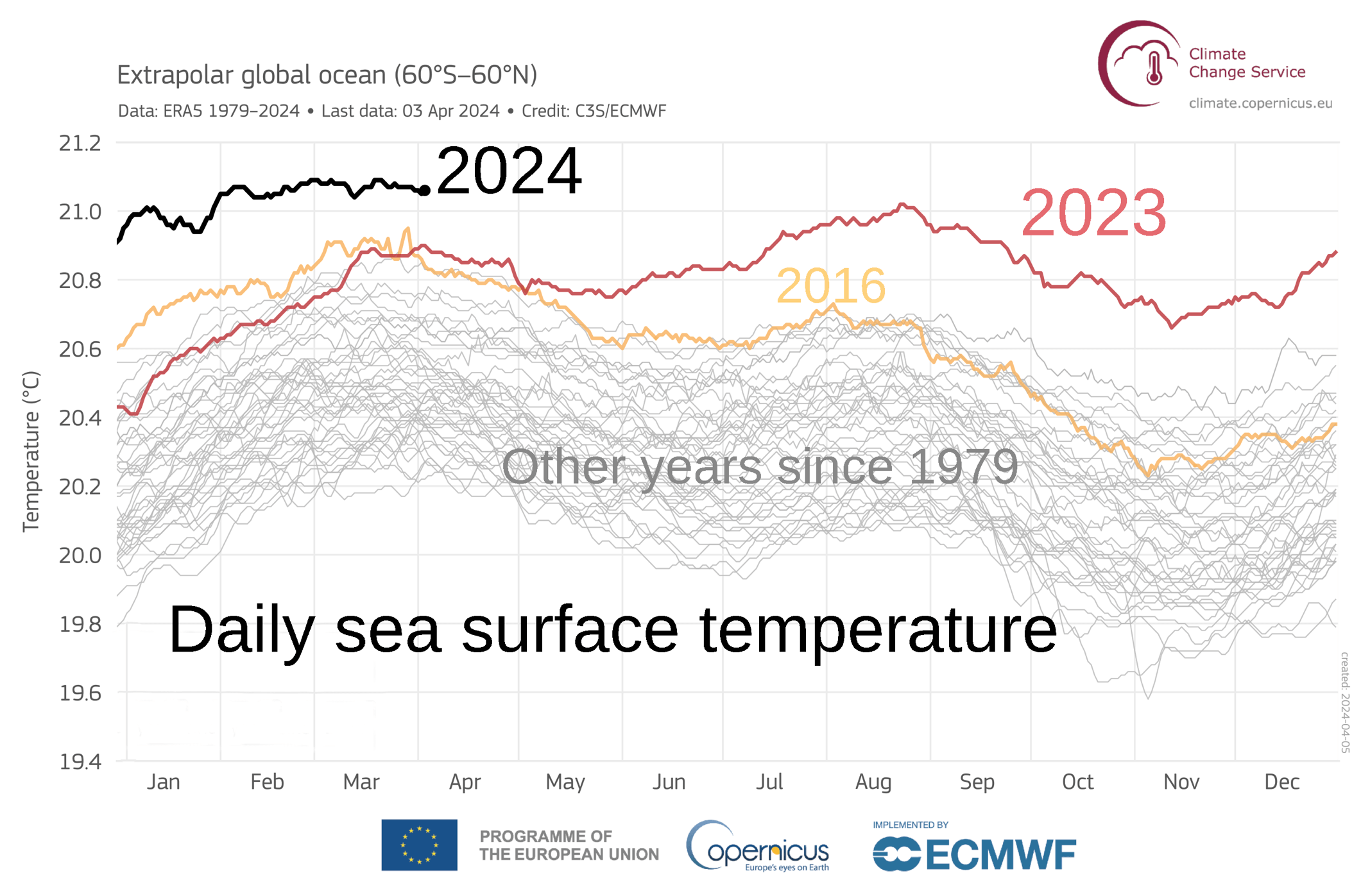
Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea surface. Sea surface temperatures greatly modify air masses in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere within a short distance of the shore. The thermohaline circulation has a major impact on average sea surface temperature throughout most of the world's oceans. Warm sea surface temperatures can develop and Tropical cyclogenesis, strengthen cyclones over the ocean. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake. This is due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. Sea surface temperature changes during the day. This is like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less variation in sea surface temperature on breezy days than on calm days. Coastal sea surface temperatures can cause offshore winds to generate upwelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland. History NOAA traces its history back to multiple agencies, some of which are among the earliest in the federal government: * United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, formed in 1807 * National Weather Service, Weather Bureau of the United States, formed in 1870 * United States Fish Commission, Bureau of Commercial Fisheries, formed in 1871 (research fleet only) * NOAA Commissioned Corps, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, formed in 1917 The most direct predecessor of NOAA was the Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Weather Review
The ''Monthly Weather Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Meteorological Society. It covers research related to analysis and prediction of observed and modeled circulations of the atmosphere, including technique development, data assimilation, model validation, and relevant case studies. This includes papers on numerical techniques and data assimilation techniques that apply to the atmosphere and/or ocean environment. The current editor-in-chief is Ron McTaggart-Cowan (Environment and Climate Change Canada). History Source: The journal was first published in January 1873 by the United States Army Signal Corps, but issues were later extended back to the start of the federal government's fiscal year (July 1872). It was issued by the Office of the Chief Signal Officer until 1891. In 1891, the Signal Office's meteorological responsibilities were transferred to the Weather Bureau under the United States Department of Agriculture. The Weather Burea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabo Gracias A Dios
Cabo Gracias a Dios is a cape located in the middle of the east coast of Central America, within what is variously called the Mosquito Coast and La Mosquitia. It is the point where the Rio Coco flows into the Caribbean, and is the border between the Nicaraguan North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region and the Honduran department also known as Gracias a Dios. The point was designated as the official Honduras–Nicaragua border by an award of King Alfonso XIII of Spain in 1906, and confirmed by the International Court of Justice in 1960. The exact terminal point was determined to be at 14°59.8'N 83°08.9'W. The name is Spanish for "Cape Thank God" and is said to have been bestowed by Christopher Columbus on his last voyage in 1502 when the weather calmed suddenly as he rounded the cape during a severe storm. This incident also gave the name to Honduras Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |