|
Hull–White Model
In financial mathematics, the Hull–White model is a model of future interest rates. In its most generic formulation, it belongs to the class of no-arbitrage models that are able to fit today's term structure of interest rates. It is relatively straightforward to translate the mathematical description of the evolution of future interest rates onto a tree or lattice and so interest rate derivatives such as bermudan swaptions can be valued in the model. The first Hull–White model was described by John C. Hull and Alan White in 1990. The model is still popular in the market today. The model One-factor model The model is a short-rate model. In general, it has the following dynamics: :dr(t) = \left theta(t) - \alpha(t) r(t)\right,dt + \sigma(t)\, dW(t). There is a degree of ambiguity among practitioners about exactly which parameters in the model are time-dependent or what name to apply to the model in each case. The most commonly accepted naming convention is the following: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Mathematics
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the Finance#Quantitative_finance, financial field. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: Derivative (finance), derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk management, risk and Investment management#Investment managers and portfolio structures, portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often with the help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when investment ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itô's Lemma
In mathematics Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ..., Itô's lemma or Itô's formula (also called the Itô–Döblin formula) is an identity used in Itô calculus to find the differential of a time-dependent function of a stochastic process. It serves as the stochastic calculus counterpart of the chain rule. It can be heuristically derived by forming the Taylor series expansion of the function up to its second derivatives and retaining terms up to first order in the time increment and second order in the Wiener process increment. The Lemma (mathematics), lemma is widely employed in mathematical finance, and its best known application is in the derivation of the Black–Scholes equation for option values. This result was discovered by Japanese mathematician Kiyoshi It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotic Derivatives
An exotic derivative, in finance, is a derivative (finance), derivative which is more complex than commonly traded "vanilla" products. This complexity usually relates to determination of payoff; see option style. The category may also include derivatives with a non-standard subject matter - i.e., underlying - developed for a particular client or a particular market.Understanding derivative contracts: types of derivatives The term "exotic derivative" has no precisely defined meaning, being a colloquialism that reflects how common a particular derivative is in the marketplace. As such, certain derivative instruments have been considered exotic when conceived of and sold, but lost this status when they were traded with significant enough volume. Examples of this phenomenon incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
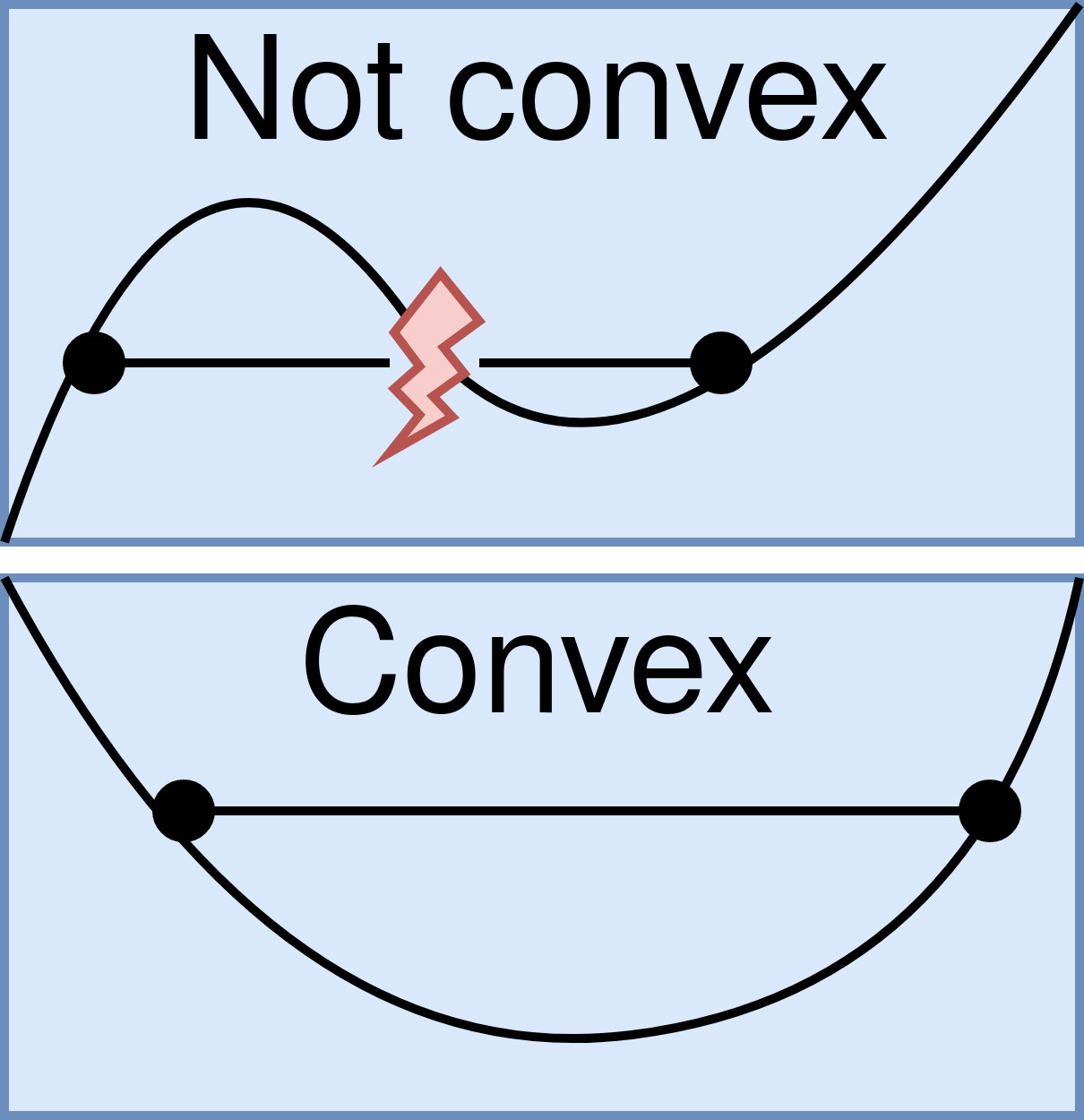
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above or on the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), ''epigraph'' (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. In simple terms, a convex function graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. A twice-differentiable function, differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain of a function, domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). Convex functions pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonic Function
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if it is either entirely non-decreasing, or entirely non-increasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is termed ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y\right), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamshidian's Trick
Jamshidian's trick is a technique for one-factor asset price models, which re-expresses an option on a portfolio of assets as a portfolio of options. It was developed by Farshid Jamshidian in 1989. The trick relies on the following simple, but very useful mathematical observation. Consider a sequence of monotone (increasing) functions f_i of one real variable (which map onto strike Strike may refer to: People *Strike (surname) * Hobart Huson, author of several drug related books Physical confrontation or removal *Strike (attack), attack with an inanimate object or a part of the human body intended to cause harm * Airstrike, ... of the option on the portfolio of assets. We can therefore express the payoff of an option on a portfolio of assets in terms of a portfolio of options on the individual assets f_i(W) with corresponding strikes f_i(w). References *Jamshidian, F. (1989). "An exact bond option pricing formula," Journal of Finance, Vol 44, pp 205-209 Mathematical fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate Caps/floors
In finance, an interest rate cap is a type of interest rate derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price. An example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the LIBOR rate exceeds 2.5%. Similarly, an interest rate floor is a derivative contract in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate is below the agreed strike price. Caps and floors can be used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations. For example, a borrower who is paying the LIBOR rate on a loan can protect himself against a rise in rates by buying a cap at 2.5%. If the interest rate exceeds 2.5% in a given period the payment received from the derivative can be used to help make the interest payment for that period, thus the interest payments are effectively "capped" at 2.5% from the borrowers' point of view. Interest rate cap An interest rate cap is a derivati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black–Scholes Model
The Black–Scholes or Black–Scholes–Merton model is a mathematical model for the dynamics of a financial market containing Derivative (finance), derivative investment instruments. From the parabolic partial differential equation in the model, known as the Black–Scholes equation, one can deduce the Black–Scholes formula, which gives a theoretical estimate of the price of option style, European-style option (finance), options and shows that the option has a ''unique'' price given the risk of the security and its expected return (instead replacing the security's expected return with the risk-neutral rate). The equation and model are named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes. Robert C. Merton, who first wrote an academic paper on the subject, is sometimes also credited. The main principle behind the model is to hedge (finance), hedge the option by buying and selling the underlying asset in a specific way to eliminate risk. This type of hedging is called "continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put Option
In finance, a put or put option is a derivative instrument in financial markets that gives the holder (i.e. the purchaser of the put option) the right to sell an asset (the ''underlying''), at a specified price (the ''strike''), by (or on) a specified date (the '' expiry'' or ''maturity'') to the ''writer'' (i.e. seller) of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment about the future value of the underlying stock. page 15 , 4.2.3 Positive and negative sentiment The term "put" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "put up for sale" the stock or index. Puts may also be combined with other derivatives as part of more complex investment strategies, and in particular, may be useful for hedging. Holding a European put option is equivalent to holding the corresponding call option and selling an appropriate forward contract. This equivalence is called " put-call parity". Put options are most commonly used in the stock market to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Measure
In finance, a ''T''-forward measure is a pricing measure equivalent to a risk-neutral measure, but rather than using the money market as numeraire, it uses a bond with maturity ''T''. The use of the forward measure was pioneered by Farshid Jamshidian (1987), and later used as a means of calculating the price of options on bonds. Mathematical definition Let : B(T) = \exp\left(\int_0^T r(u)\, du\right) be the bank account or money market account numeraire and : D(T) = 1/B(T) = \exp\left(-\int_0^T r(u)\, du\right) be the discount factor in the market at time 0 for maturity ''T''. If Q_* is the risk neutral measure, then the forward measure Q_T is defined via the Radon–Nikodym derivative given by :\frac = \frac = \frac. Note that this implies that the forward measure and the risk neutral measure coincide when interest rates are deterministic. Also, this is a particular form of the change of numeraire formula by changing the numeraire from the money market or bank accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Theorem Of Arbitrage-free Pricing
The fundamental theorems of asset pricing (also: of arbitrage, of finance), in both financial economics and mathematical finance, provide necessary and sufficient conditions for a market to be arbitrage-free, and for a market to be complete. An arbitrage opportunity is a way of making money with no initial investment without any possibility of loss. Though arbitrage opportunities do exist briefly in real life, it has been said that any sensible market model must avoid this type of profit.Pascucci, Andrea (2011) ''PDE and Martingale Methods in Option Pricing''. Berlin: Springer-Verlag The first theorem is important in that it ensures a fundamental property of market models. Completeness is a common property of market models (for instance the Black–Scholes model). A complete market is one in which every contingent claim can be replicated. Though this property is common in models, it is not always considered desirable or realistic. Discrete markets In a discrete (i.e. finite state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |