|
Hubert Gough
General (United Kingdom), General Sir Hubert de la Poer Gough ( ; 12 August 1870 – 18 March 1963) was a senior officer in the British Army in the First World War. A controversial figure, he was a favourite of the Commander-in-chief, Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (World War I), British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, Sir Douglas Haig, and the youngest of his Army commanders. Gough was educated at Eton College, Eton and the Royal Military College, Sandhurst before commissioning into the 16th The Queen's Lancers, 16th Lancers in 1889. His early career included notable service in the Second Boer War, and a more controversial role in the Curragh incident, in which he was one of the leading officers who threatened to accept dismissal rather than deploy into Protestant Ulster. Gough experienced a meteoric rise during the First World War, from command of a cavalry brigade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General (United Kingdom)
General (or full general to distinguish it from the lower general officer ranks) is the highest rank achievable by serving officers of the British Army and the Royal Marines. The rank can also be held by Royal Marines officers in tri-service posts, for example, Generals Sir Gordon Messenger and Gwyn Jenkins, Sir Gwyn Jenkins, former Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff (United Kingdom), Vice-Chiefs of the Defence Staff. It ranks above Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), lieutenant-general and, in the Army, is subordinate to the rank of Field marshal (United Kingdom), field marshal, which is now only awarded as an honorary rank. The rank of general has a NATO-code of Ranks and insignia of NATO, OF-9, and is a four-star rank. It is equivalent to a Admiral (Royal Navy), full admiral in the Royal Navy or an air chief marshal in the Royal Air Force. Officers holding the ranks of Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), lieutenant-general and Major-general (United Kingdom), major-general m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
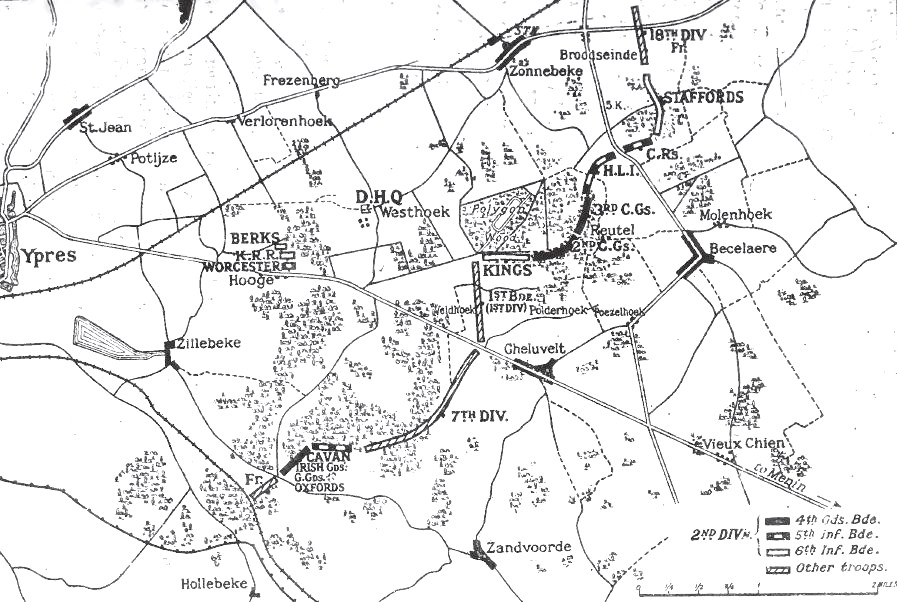
First Battle Of Ypres
The First Battle of Ypres (, , – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the First Battle of Flanders, in which German Army (German Empire), German, French Army in World War I, French, Belgian Land Component, Belgian armies and the British Expeditionary Force (World War I), British Expeditionary Force (BEF) fought from Arras in France to Nieuwpoort, Belgium, Nieuwpoort (Nieuport) on the Belgian coast, from 10 October to mid-November. The battles at Ypres began at the end of the Race to the Sea, reciprocal attempts by the German and Franco-British armies to advance past the northern flank of their opponents. North of Ypres, the fighting continued in the Battle of the Yser between the German 4th Army (German Empire), 4th Army, the Belgian army and French marines. The fighting has been divided into five stages, an encounter battle from 19 to 21 October, the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve personnel and 4,697 "other personnel", for a total of 108,413. The British Army traces back to 1707 and the Acts of Union 1707, formation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain which joined the Kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland into a Political union, single state and, with that, united the English Army and the Scots Army as the British Army. The Parliament of England, English Bill of Rights 1689 and Convention of the Estates, Scottish Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the Charles III, monarch as their commander-in-chief. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence (United Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gough (British Army Officer)
Brigadier-General Sir John Edmond Gough (25 October 1871 – 22 February 1915), was a British Army officer and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. Early military career Gough, known as "Johnnie", was the son of General Sir Charles Gough, and nephew of General Sir Hugh Gough, both of whom won the Victoria Cross (VC) during the Indian Mutiny in 1857. This gave the family the rare distinction of holding the VC simultaneously by father, brother and (father's) son. He was also the younger brother of General Sir Hubert Gough (1870–1963), who led the British Fifth Army on the Western Front during the First World War. Gough was, after graduating from the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, commissioned as a second lieutenant in the Rifle Brigade (The Prince Consort's Own) on 12 March 1892, and promoted to lieutenant on 6 December 1893. He served in British Central Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Henry Gough
General (United Kingdom), General Sir Hugh Henry Gough ( ; 14 November 1833 – 12 May 1909) was a senior British Indian Army officer and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth forces. Early life Gough was born into a family of Anglo-Irish landed gentry, gentry in Calcutta, Bengal, India, on 14 November 1833. He was commissioned Ensign (rank)#United Kingdom, ensign in the 3rd Bengal Light Cavalry in September 1853 aged 19, and was still serving with the British Indian Army, Indian Army on the outbreak of the First Indian War of Independence in 1857. Victoria Cross Gough was 23 years old, and a lieutenant in the 1st Bengal European Light Cavalry (later 19th Hussars) during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, 1857 Rebellion, when the following deeds took place for which he was awarded the VC: Later career Gough commanded the 5th Horse, 12th Bengal Cavalry in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles John Stanley Gough
General Sir Charles John Stanley Gough, ( ; 28 January 1832 – 6 September 1912) was a senior British Indian Army officer and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. Early life Gough was born into a family of Anglo-Irish gentry in Chittagong, Bengal, British India on 28 January 1832. Career At age 16, Gough moved back to India, joined the 8th Bengal Cavalry, and served through the Second Anglo-Sikh War. By the age of 25, he was a major in the 5th Bengal European Cavalry. During the Indian Mutiny, Gough and his brother Hugh were members of the Guides Corps, where they took part in the Siege of Lucknow and Gough was awarded the Victoria Cross (VC) for deeds which included saving his brother. The award was announced on 21 October 1859, and the citation read: After the Mutiny, Gough continued to serve as a cavalry officer with the Indian Army, and took part in the Bh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Victorian Order
The Royal Victorian Order () is a dynastic order of knighthood established in 1896 by Queen Victoria. It recognises distinguished personal service to the monarch, members of the royal family, or to any viceroy or senior representative of the monarch. The present monarch, King Charles III, is the sovereign of the order. The order's motto is ''Victoria.'' The order's official day is 20 June. The order's chapel is the Savoy Chapel in London. There is no limit on the number of individuals honoured at any grade. Admission is at the sole discretion of the monarch. Each of the order's five grades represent different levels of service, as does the medal, which has three levels of service. While all those honoured may use the prescribed styles of the order – the top two grades grant titles of knighthood, and all grades accord distinct post-nominal letters – the Royal Victorian Order's precedence amongst other honours differs from realm to realm and admission to some grades may be ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St Michael And St George
The Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George is a British order of chivalry founded on 28 April 1818 by George, Prince of Wales (the future King George IV), while he was acting as prince regent for his father, King George III. It is named in honour of two military saints, Michael (archangel), Michael and Saint George, George. The Order of St Michael and St George was originally awarded to those holding commands or high position in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean territories acquired in the Napoleonic Wars, and it was subsequently extended to holders of similar office or position in other territories of the British Empire. It is at present awarded to men and women who hold high office or who render extraordinary or important non-military service to the United Kingdom in a foreign country, and it can also be conferred for important or loyal service in relation to foreign and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth affairs. Description The three classes of ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by King George I of Great Britain, George I on 18 May 1725. Recipients of the Order are usually senior British Armed Forces, military officers or senior Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil servants, and the monarch awards it on the advice of His Majesty's Government. The name derives from an elaborate medieval ceremony for preparing a candidate to receive his knighthood, of which ritual bathing (as a symbol of Ritual purification, purification) was an element. While not all knights went through such an elaborate ceremony, knights so created were known as "knights of the Bath". George I constituted the Knights of the Bath as a regular Order (honour), military order. He did not revive the order, which did not previously exist, in the sense of a body of knights governed by a set of statutes and whose numbers were replenished when vacancies occurred. The Order consists of the Sovereign of the United King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
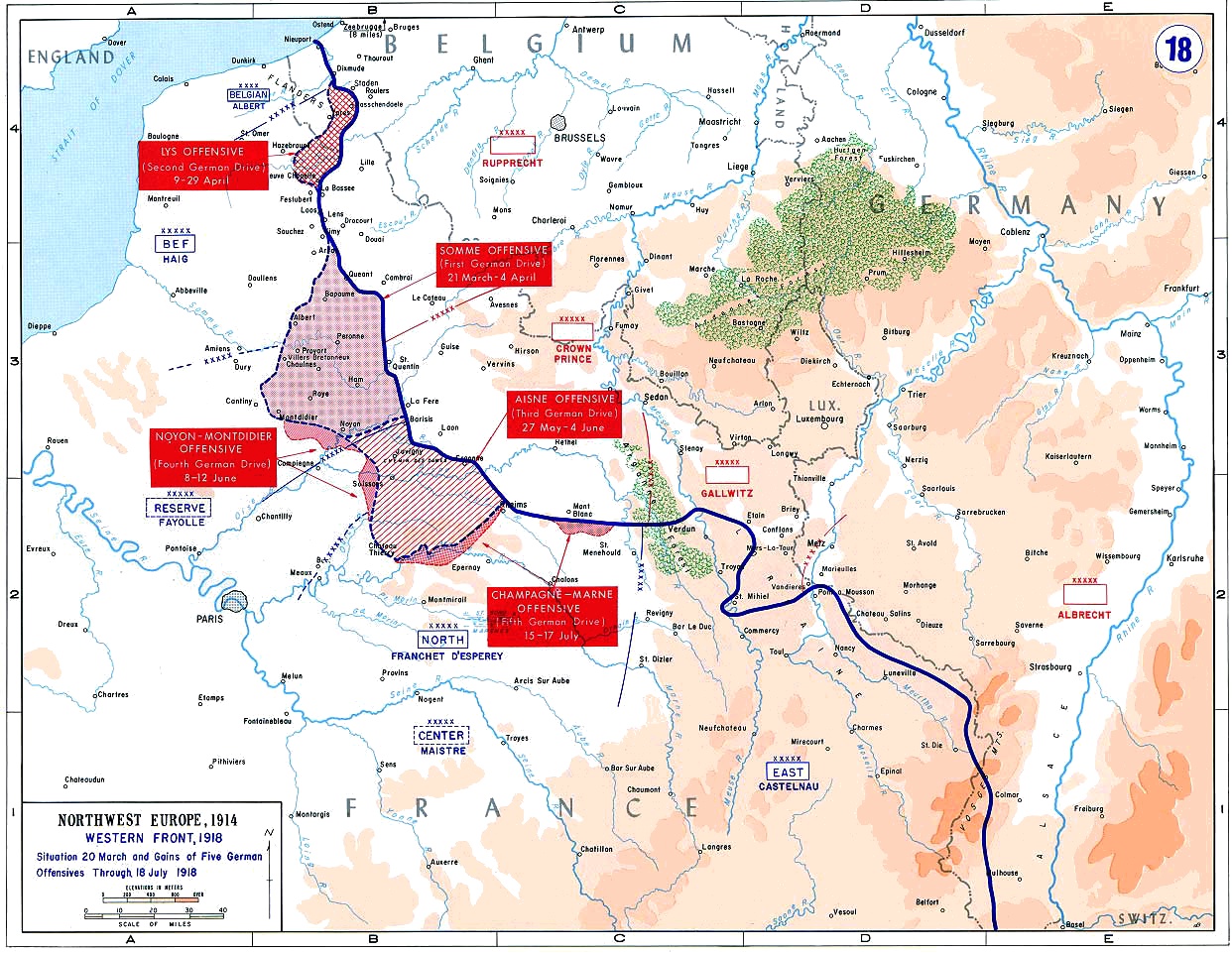
Operation Michael
Operation Michael () was a major German military offensive during World War I that began the German spring offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was to break through the Allied (Entente) lines and advance in a north-westerly direction to seize the Channel Ports, which supplied the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), and to drive the BEF into the sea. Two days later General Erich Ludendorff, the chief of the German General Staff, adjusted his plan and pushed for an offensive due west, along the whole of the British front north of the River Somme. This was designed to first separate the French and British Armies before continuing with the original concept of pushing the BEF into the sea. The offensive ended at Villers-Bretonneux, to the east of the Allied communications centre at Amiens, where the Allies managed to halt the German advance; the German Army had suffered many casualties and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of Ypres
The Third Battle of Ypres (; ; ), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele ( ), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Entente at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere ( Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuwpoort), combined with an amphibious landing ( Operation Hush), were to have reached Bruges and then the Dutch fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |