|
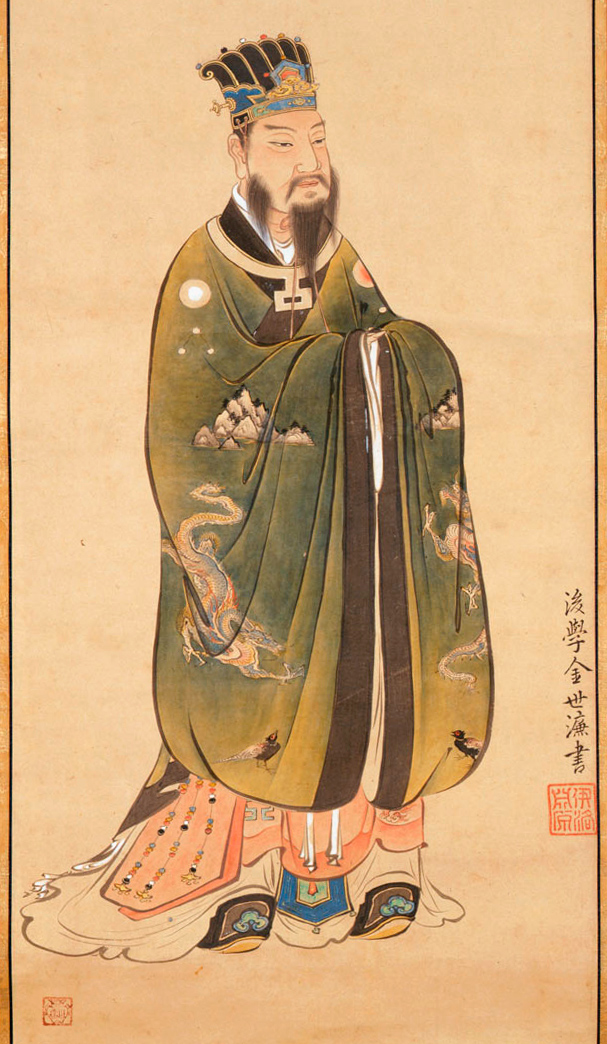
Huang Feihu
Huang Feihu is a fictional character in the Chinese epic fantasy novel ''Fengshen Bang''. Originally known as Prince Wucheng () of the Shang Dynasty, he defects to Xiqi (西岐; the precursor to the Zhou Dynasty), a vassal state under Shang, after the tyrannical King Zhou of Shang caused the death of his wife. He brings along his two younger brothers, three sons, four close friends, and hundreds of followers loyal to him. Huang Feihu later participates in the campaign led by King Wu of the Zhou Dynasty to overthrow King Zhou of Shang. He is killed in action during a battle against the Shang general Zhang Kui (張奎). Biography Huang Feihu is born in a family of officials who have served the Shang Dynasty for seven generations. Huang Feihu's father Huang Gun is a Shang general tasked with defending the border. Huang Feihu himself is granted the title of "Prince Wucheng Who Guards the Kingdom" (鎮國武成王; usually shortened to "Prince Wucheng"). Huang Feihu's younger siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ping Sien Si - 004 Huang Feihu (16134825352)
Ping may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Ping, a domesticated Chinese duck in the illustrated book '' The Story about Ping'', first published in 1933 * Ping, a minor character in ''Seinfeld'', an NBC sitcom * Ping, a character in the webcomic ''Megatokyo'' * Ping, the disguised identity of Hua Mulan in the animated film ''Mulan'' * '' Ping the Elastic Man'', a comic strip character introduced in ''The Beano'' in 1938 * "The machine that goes ''Ping!''", a fictitious obstetric medical device featured in the film ''Monty Python's The Meaning of Life'' * Mr. Ping, a character in the ''Kung Fu Panda'' franchise * Professor Ping, a character in the film '' Barbarella'' * Ping, a character in Carole Wilkinson's novel ''Dragonkeeper'' Other uses in arts and entertainment * "Ping" (short story), by Samuel Beckett * ''Ping!'', a 2000 film featuring Shirley Jones * Ping.fm, a microblog social network * Ping, an ability in the trading card game ''Magic: The Gath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wen Of Zhou
King Wen of Zhou (; 1152–1050 BC, the Cultured King) was Count of Zhou during the late Shang dynasty in ancient China. Although frequently confused with his fourth son Duke of Zhou, also known as "Lord Zhou", they are different historical persons. Although it was his son Wu who conquered the Shang following the Battle of Muye, Count Wen was posthumously honored as the founder of the Zhou dynasty and posthumously titled King. Many of the hymns of the ''Classic of Poetry'' are praises to the legacy of King Wen. Some consider him the first epic hero of Chinese history. Archaeology Chinese scholars (e.g. Wang Yunwu ( 王雲五), Li Xueqin ( 李学勤), etc.) identified King Wen with a mentioned in inscriptions H11:82 & H11:84 among oracle bones excavated at Zhouyuan (), Qishan County. Biography Born Ji Chang (), Wen was the son of Tairen and Ji Jili, the Count of Zhou, a vassal state of the Kingdom of Shang along the Wei River in present-day Shaanxi. Jili was betrayed and exec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Zhonglin
Xu Zhonglin (; 1567 - c. 1619 or 1620) was a Chinese writer who lived in the Ming dynasty. He is best known as the author of the 16th century semi-mythical novel ''Investiture of the Gods'' (). He was born in Yingtian Prefecture, present-day Nanjing. An original copy of ''Investiture of the Gods'' is held in the Japanese Library of the Grand Secretariat, printed by Shu Zaiyang. The second section of the book is inscribed with the words "edited by Xu Zhonglin, the Old Recluse of Mount Zhong." This is likely the source of his possible pseudonym A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individua ... "Zhongshan Yisou" (), which literally means "a carefree old man living in Mount Zhong". Some say that Xu wrote the novel for a trousseau for his daughter. See also * Chinese literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huang Tianhua
''The Investiture of the Gods'', also known by its Chinese names () and is a 16th-century Chinese novel and one of the major vernacular Chinese works in the gods and demons (''shenmo'') genre written during the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). Consisting of 100 chapters, it was first published in book form between 1567 and 1619. Another source claims it was published in 1605. The work combines elements of history, folklore, mythology, legends and fantasy.Chew, Katherine Liang (2002). ''Tales of the Teahouse Retold: Investiture of the Gods''. Page XI. . The story is set in the era of the decline of the Shang dynasty (1600–1046 BC) and the rise of the Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC). It intertwines numerous elements of Chinese mythology, including deities, immortals and spirits. The authorship is attributed to Xu Zhonglin. Plot The novel is a romanticised retelling of the overthrow of King Zhou, the last ruler of the Shang dynasty, by Ji Fa, who would establish the Zhou dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Tai
Mount Tai () is a mountain of historical and cultural significance located north of the city of Tai'an. It is the highest point in Shandong province, China. The tallest peak is the '' Jade Emperor Peak'' (), which is commonly reported as being tall. Mount Tai is known as the eastern mountain of the Sacred Mountains of China. It is associated with sunrise, birth, and renewal, and is often regarded the foremost of the five. Mount Tai has been a place of worship for at least 3,000 years and served as one of the most important ceremonial centers of China during large portions of this period. Because of its sacred importance and dramatic landscape, it was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987. It meets 7 of the 10 evaluation standards of World Heritage, and is listed as a World Heritage site that meets the most standards, along with the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area in Australia. An earthquake or thunderstorm occurred in Mount Tai in 1831 BC or 1652 BC, also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diyu
Diyu () is the realm of the dead or " hell" in Chinese mythology. It is loosely based on a combination of the Buddhist concept of Naraka, traditional Chinese beliefs about the afterlife, and a variety of popular expansions and reinterpretations of these two traditions. Diyu is typically depicted as a subterranean maze with various levels and chambers, to which souls are taken after death to atone for the sins they committed when they were alive. The exact number of levels in Diyu and their associated deities differ between Buddhist and Taoist interpretations. Some speak of three to four "courts"; others mention "Ten Courts of Hell", each of which is ruled by a judge (collectively known as the Ten Yama Kings); other Chinese legends speak of the "Eighteen Levels of Hell". Each court deals with a different aspect of atonement and different punishments; most legends claim that sinners are subjected to gruesome tortures until their "deaths", after which they are restored to their or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
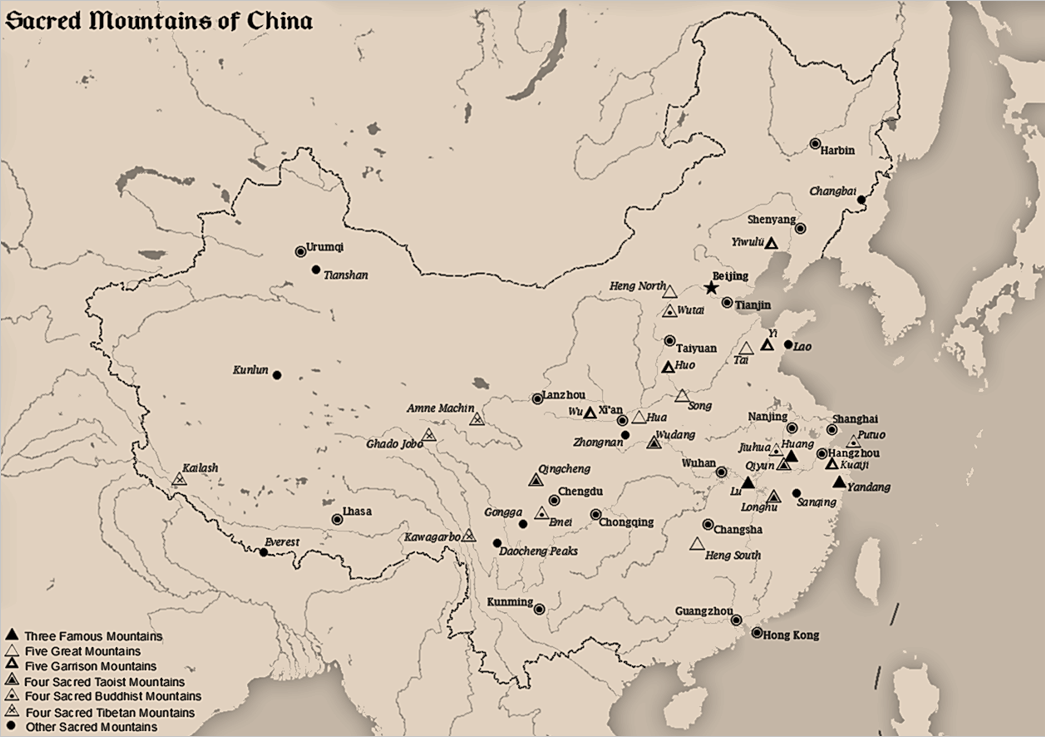
Five Sacred Mountains
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The ''Five Great Mountains'' () refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, and they were the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of Chinese traditional religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism'' (), and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism'' (). The sacred mountains have all been important destinations for pilgrimage, the Chinese expression for pilgrimage () being a shortened version of an expression which means ''"paying respect to a holy mountain"'' (). The Five Great Mountains The ''Five Great Mountains'' or ''Wuyue'' are arranged according to the five cardinal directions of Chinese geomancy, which includes the center as a direction. The grouping of the five mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Ziya
Jiang Ziya ( century BC – century BC), also known by several other names, was a Chinese noble who helped kings Wen and Wu of Zhou overthrow the Shang in ancient China. Following their victory at Muye, he continued to serve as a Zhou minister. He remained loyal to the regent Duke of Zhou during the Rebellion of the Three Guards; following the Duke's punitive raids against the restive Eastern Barbarians or ''Dongyi'', Jiang was enfeoffed with their territory as the marchland of Qi. He established his seat at Yingqiu (in modern Linzi). Names The first marquis of Qi bore the given name Shang. The nobility of ancient China bore two surnames, an ancestral name and a clan name. His were Jiang (姜) and Lü (呂), respectively. He had two courtesy names, Shangfu (尚父; lit. "Esteemed Father") and Ziya (lit. "Master Ivory, Master Tusk"), which were used for respectful address by his peers. The names Jiang Shang and Jiang Ziya became the most common after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mianchi County
Mianchi County is a county under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Sanmenxia, in the northwest of Henan province, bordering Shanxi province to the north and northwest. Its population in 2019 was 353,200. History Mianchi is known for the ancient Yangshao Culture, the remains of which were first found by Swedish geologist Johan Gunnar Andersson. In 1921, he discovered some pieces of pottery in the north of Mianchi County, near the town of Yangshao. In 2006, the government of Mianchi County experimented with direct democracy, allowing citizens could voice their thoughts about proposed projects through petitions. Administrative divisions As of 2020, Mianchi is divided in 6 towns and 6 townships. ;Towns ;Townships Climate Economy Mianchi is wealthy in resources, having coal resources are up to 1.19 billion tons. It has 11.5 million tons of Bauxite resources, with the highest aluminium content in Asia. The reserves of quartz sand are 77.8 million tons. Indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FengShen2
{{disambiguation ...
Fengshen is the romanization of several Chinese words, (, or ) may refer to: * ''Investiture of the Gods'' (''Fengshen Bang''), a Chinese epic fantasy novel written during the Ming Dynasty ** ''Hoshin Engi'' a Japanese anime loosely based on the ''Investiture of the Gods'' * Dongfeng Fengshen, a Chinese automobile marque owned by Dongfeng Motor Group * Typhoon Fengshen (2002), a Category 5 super typhoon which took place in the West Pacific in July 2002 * Typhoon Fengshen (2008), a Category 3 typhoon which killed more than 1,300 people in June 2008, primarily in the Philippines See also * Feng Sheng (other) * List of wind deities A wind god is a god who controls the wind(s). Air deities may also be considered here as wind is nothing more than moving air. Many polytheistic religions have one or more wind gods. They may also have a separate air god or a wind god may doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huang (surname)
Huang (; ) is a Chinese surname that originally means and refers to jade people were wearing and decorating in ancient times. While ''Huáng'' is the pinyin romanization of the word, it may also be romanized as Hwang, Wong, Waan, Wan, Waon, Hwong, Vong, Hung, Hong, Bong, Eng, Ng, Uy, Wee, Oi, Oei, Oey, Ooi, Ong, or Ung due to pronunciations of the word in different dialects and languages. It is the 96th name on the '' Hundred Family Surnames'' poem.K. S. Tom. 989(1989). Echoes from Old China: Life, Legends and Lore of the Middle Kingdom. University of Hawaii Press. . This surname is known as Hwang in Korean. In Vietnamese, the name is known as Hoàng or Huỳnh. Huang is the 7th most common surname in China. Huynh is the 5th most common surname in Vietnam. The population of Huangs in China and Taiwan was estimated at more than 35 million in 2020; it was also the surname of more than 2 million overseas Chinese, 5.7 million Vietnamese (6%), and an estimated 1 million Kore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)