|
Hott Peak
The Helicopter Mountains () are a series of rugged mountains west of Mount Mahony in the Saint Johns Range, Antarctica. They rise to at Mount James and include also from west to east Touchstone Crag, Mick Peak and Hott Peak. The mountains form the northwest end of the Saint Johns Range. Name The Helicopter Mountains were so named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 2007 in recognition of the wide use of helicopters in supporting the U.S. Antarctic Program at McMurdo Sound and the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Peaks in the mountains have been named after personnel in the helicopter group. Features Touchstone Crag . A rugged mountain high, west of Mick Peak in the west part of Helicopter Mountains. The abrupt south-facing cliffs of the feature also mark the northwest extremity of Saint Johns Range. Named by US-ACAN (2007) after Steven Touchstone, helicopter mechanic in support of the United States Antarctic Program at McMurdo Sound and McMurdo Dry Valleys The Mc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Mahony
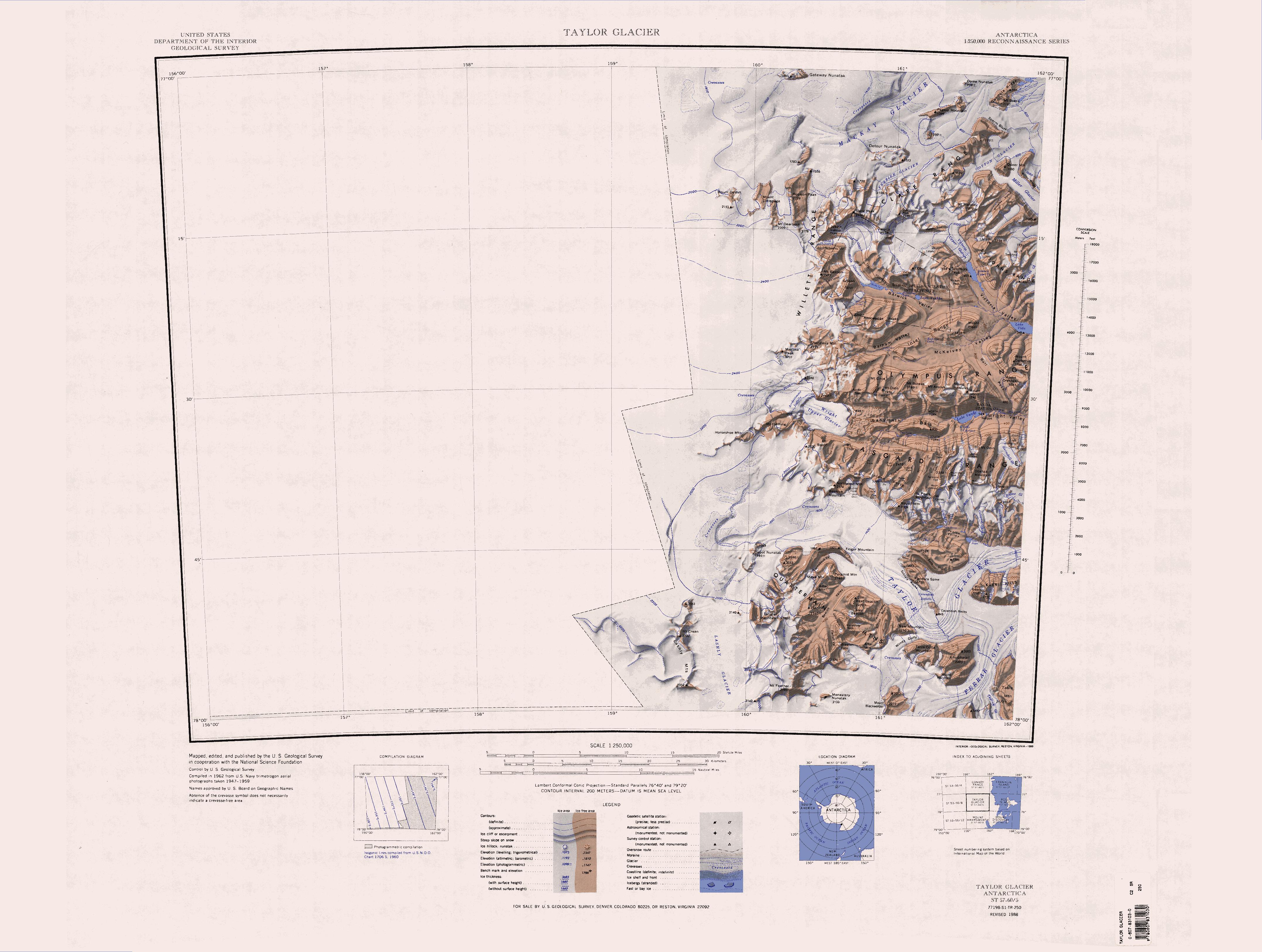
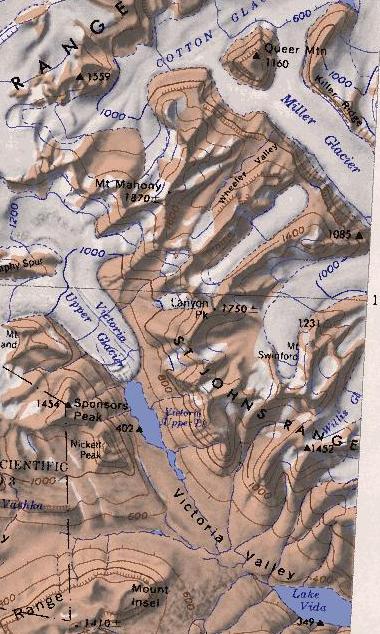
Saint Johns Range () is a crescent-shaped mountain range about long, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is bounded on the north by the Cotton Glacier, Miller Glacier and Debenham Glacier, and on the south by Victoria Valley and the Victoria Upper Glacier and Victoria Lower Glacier. Name Saint Johns Range was named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE), 1956–58, which surveyed peaks in the range in 1957. Named for St John's College, Cambridge, England, with which several members of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 were associated during the writing of their scientific reports, and in association with the adjacent Gonville and Caius Range. Location Saint Johns Range is bounded to the west by the Victoria Upper Glacier and the Victoria Valley, which runs in a south-southeast direction to Lake Vida. Below Lake Vida the Victoria Valley turns to an east-northeast direction. It is filled by the Victoria Lower Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Johns Range
Saint Johns Range () is a crescent-shaped mountain range about long, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is bounded on the north by the Cotton Glacier, Miller Glacier and Debenham Glacier, and on the south by Victoria Valley and the Victoria Upper Glacier and Victoria Lower Glacier. Name Saint Johns Range was named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE), 1956–58, which surveyed peaks in the range in 1957. Named for St John's College, Cambridge, England, with which several members of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 were associated during the writing of their scientific reports, and in association with the adjacent Gonville and Caius Range. Location Saint Johns Range is bounded to the west by the Victoria Upper Glacier and the Victoria Valley, which runs in a south-southeast direction to Lake Vida. Below Lake Vida the Victoria Valley turns to an east-northeast direction. It is filled by the Victoria Lower Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. Research stations in Antarctica, scientific research and related Transport in Antarctica, logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
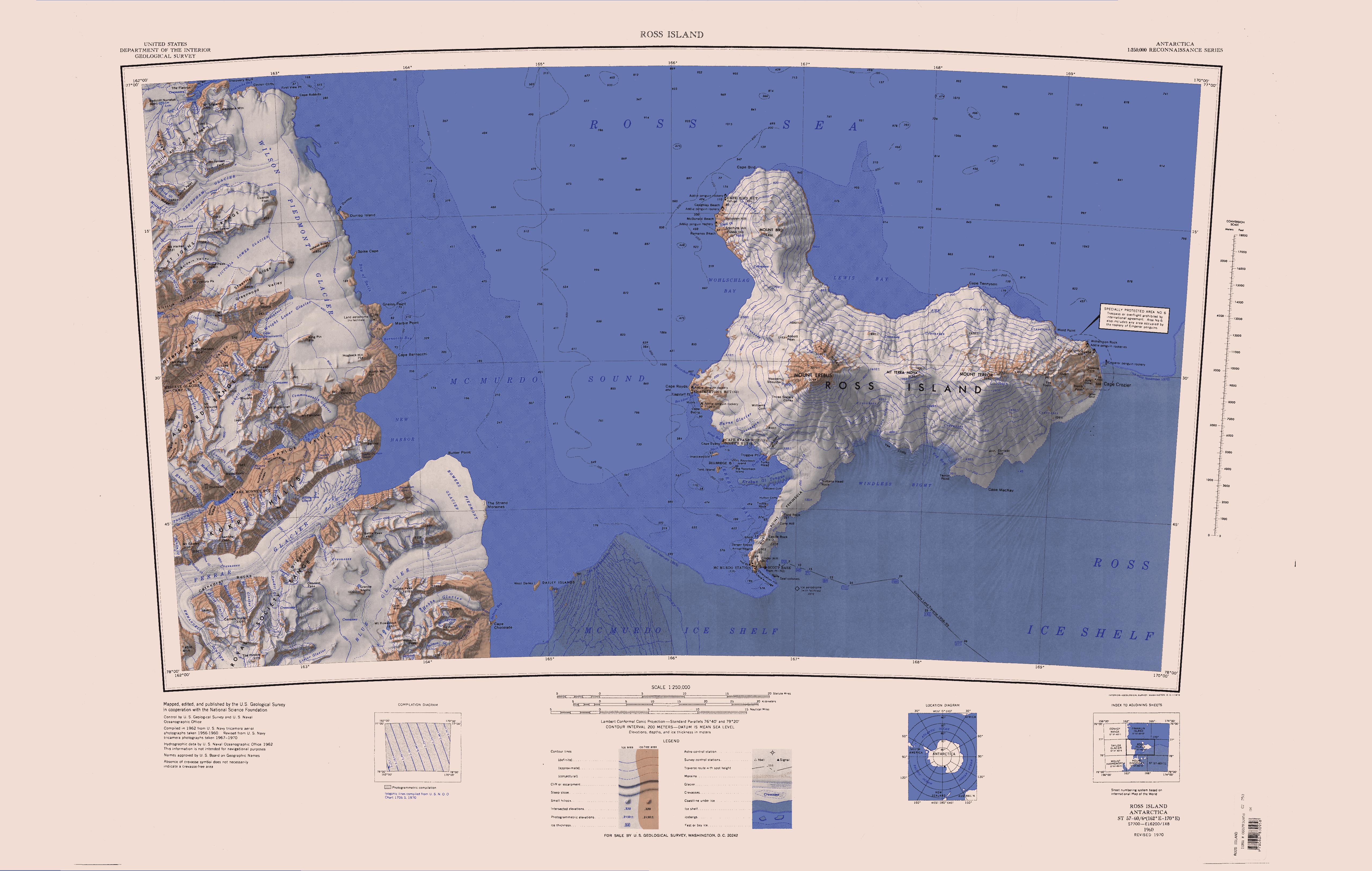
McMurdo Sound
The McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica, known as the southernmost passable body of water in the world, located approximately from the South Pole. Captain James Clark Ross discovered the sound in February 1841 and named it after Lieutenant Archibald McMurdo of HMS ''Terror''. The sound serves as a resupply route for cargo ships and airplanes that land on floating ice airstrips near McMurdo Station. The McMurdo seasonal Ice Runway was operated from October to December from the 1950s to the 2010s, then in December the ice breaks up and McMurdo port is opened by an Icebreaker ship and ships can resupply the Antarctic bases. Physical characteristics Boundary and extents The sound extends approximately 55 kilometers (34 mi) in length and width, and opens into the larger Ross Sea to the north. To the south, the sound is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf cavity, to the west lies the Royal Society Range, and to the east is Ross Island. McMurdo Sound is separated from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely Antarctic oasis, snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby glaciers. The rocks there are granites and gneisses, and glacial tills dot this bedrock landscape, with loose gravel covering the ground. It is one of the driest places on Earth, though there are several anecdotal accounts of rainfall within the Dry Valleys. The region is one of the world's most extreme deserts, and includes many features including Lake Vida, a saline lake, and the Onyx River, a meltwater stream and Antarctica's longest river. Although no living organisms have been found in the permafrost here, Endolithic lichen, endolithic Photosynthesis, photosynthetic bacteria have been found living in the relatively moist interior of rocks, and anaerobic bacteria, with a metabolism based on iron and sulfur, live under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |