|
Hor States
The Hor States (; ), also known as the Horpa States (), were a group of five principalities located in the Tibetan region of Kham that existed from the 14th century to the mid-1900s. Today, the historical territory of the Hor States comprises Garzê County, Luhuo County, and part of Dawu County. Etymology The name "Hor" is usually considered to be Turkic; because the Hor states were Tibetic in culture, their population is thought to be Turks that were influenced by Tibetic culture. Geography The Hor States were located in the region of Trehor (named after one of the states) or Horkhok () in northern Kham on the upper portion of the Yalong River. The traditional five states were: * Khangsar () * Mazur () * Drango (); now the Tibetan name of Luhuo County * Beri () * Trehor () Each state governed families rather than distinct territory; as a result, there were no clear borders and some land was owned by multiple principalities. History The Hor States originated when a pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often used to describe small monarchies, particularly those in Europe, where the ruler holds the title of prince or an equivalent. Historically, principalities emerged during the Middle Ages as part of the feudal system, where local princes gained significant power within a king's domain. This led to political fragmentation and the creation of mini-states. Over time, many of these principalities consolidated into larger kingdoms and empires, while others retained their independence and prospered. Sovereign principalities which exist today include Liechtenstein, Monaco, and the co-principality of Andorra. Additionally, some royal primogenitures, such as Asturias in Spain, are styled as principalities. The term is also used generically for smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups such as Mongols, Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa, Lhoba people, Lhoba, and since the 20th century Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibetan Empire extended far beyond the Tibetan Plateau, from the Tarim Basin and Pamirs in the west, to Yunnan and Bengal in the southeast. It then divided into a variety of territories. The bulk of western and central Tibet (Ü-Tsang) was often at least nominally unified under a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham covers a land area distributed in multiple province-level administrative divisions in present-day China, most of it in Tibet Autonomous Region and Sichuan, with smaller portions located within Qinghai and Yunnan. Densely forested with grass plains, its convergence of six valleys and four rivers supported independent Kham polities of Tibetan warrior kingdoms together with Tibetan Buddhist monastic centers.Jann Ronis"An Overview of Kham (Eastern Tibet) Historical Polities" The University of Virginia The early trading route between Central Tibet and China traveled through Kham, and Kham is said to be the inspiration for Shangri-La in James Hilton's nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
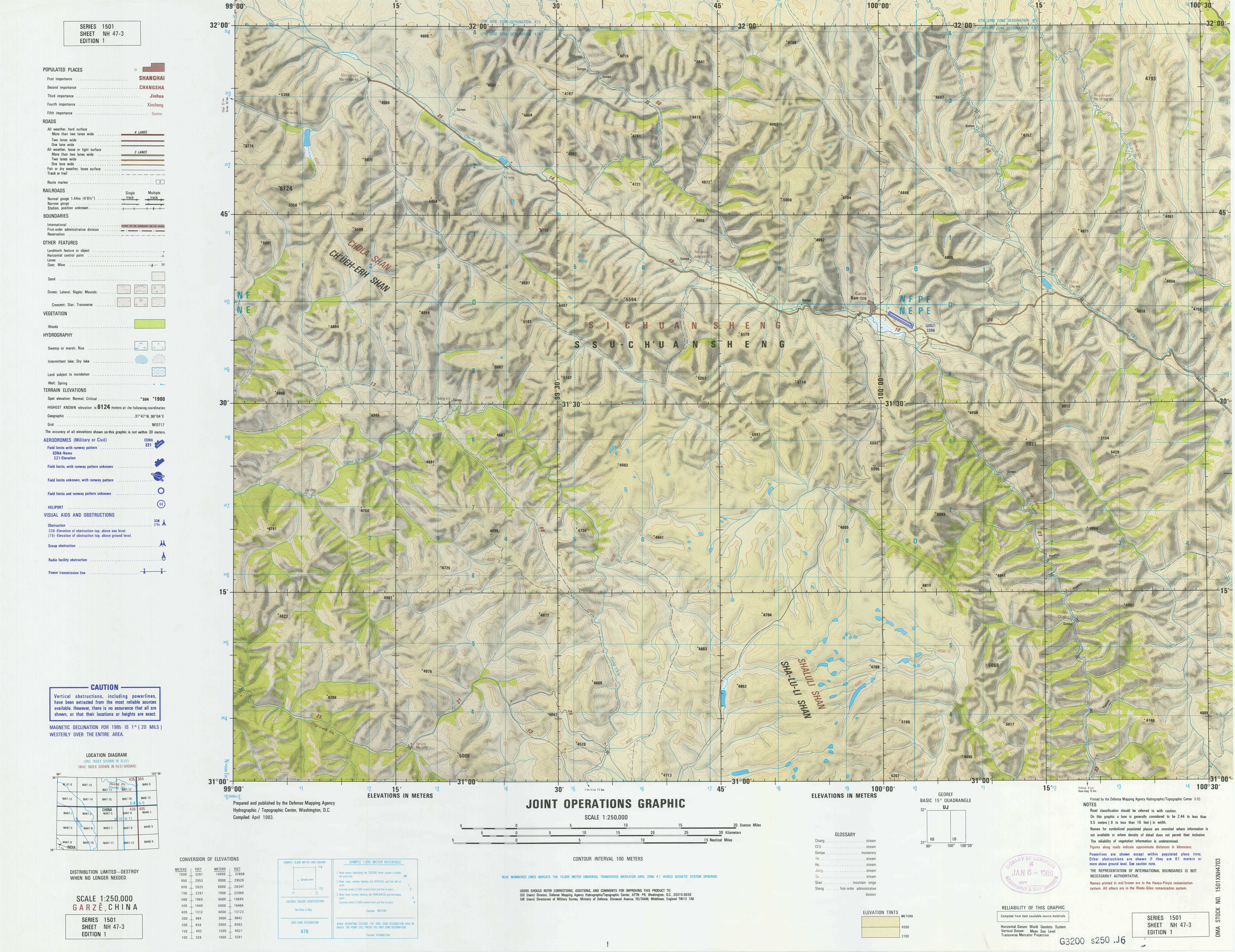
Garzê County
Garzê County or Kardze County (), called Ganzi County in Chinese ( zh, s=甘孜县, p=Gānzī xiàn), is one of the 18 subdivisions of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, in northwestern Sichuan province, China. The Yalong River passes just south of the town Garzê, also known as Ganzi, the capital town of the county, which has some 16,920 inhabitants (2010), many of them ethnic Tibetans, and is famous for its Tibetan lamasery. Historically, it is part of the Tibetan cultural region of Kham and now defunct province of Xikang (or Sikang). It lies on the northern section of the Sichuan-Tibet Highway. Geography and climate Due to its elevation, Garzê County has a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dwb'') and subarctic climate, with cold but very dry winters, and warm summers with frequent rain. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from in January to in July, while the annual mean is . Over two-thirds of the annual precipitation of occurs f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhuo County
Luhuo County or Zhaggo ( zh, s=炉霍县; ) is a county of Sichuan Province, China. It is under the administration of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. History On March 24, 1923, a magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck between Luhuo and Dawu and killed 4800 people. On February 6, 1973, a magnitude 7.6 earthquake occurred near Zhaggo, a town in the county. United States Geological Survey Administrative divisions Zhaggo County is divided into 4 and 11townships
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawu County, Sichuan
Dawu County (), also written Tawu County or Daofu County ( zh, s=道孚县), is a county of northwestern Sichuan Province, China. It is under the administration of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, and , had a population of 46,900 residing in an area of . By road it is from Kangding, the prefectural seat, and from Chengdu, the provincial capital. It borders the counties of Xinlong to the west, Kangding and Yajiang to the south, and Jinchuan and Zamtang of Ngawa Prefecture as well as Luhuo to the north. In January 1981 it was struck by an earthquake. Administrative divisions Dawu County is divided into 7 towns A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ... and 12 townships: Climate References External links See this link for a book-length study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalong River
The Yalong River ( zh, 雅砻江, Pinyin, p ''Yǎlóngjiāng'', Wade–Giles, w ''Ya-lung Chiang'', Help:IPA/Mandarin, IPA ), or Nyag Chu (Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: , Tibetan pinyin, z ''Nyag Qu''), is a major tributary river of the Yangtze, Yangtze River in Southwest China. With a length of , the Yalong River flows from north to south through the Hengduan Mountains in western Sichuan, Sichuan Province. Course The Yalong has its source in the Bayan Har Mountains on the Tibetan Plateau, Tibet–Qinghai Plateau in Chindu County, Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Yushu, Qinghai, where it is known as the Za Qu ( zh, 扎曲). Flowing southeasterly, the Yalong gradually turns south at Garzê Town, Garzê and travels between the Shaluli Mountains to the west and the Daxue Mountains to the east. The Yalong River channel runs through a deep gorge for much of its length south of Garzê. The southern China National Highway 318, Sichuan-Tibet Highway crosses t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelugpa
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodh_Gaya.html" ;"title="Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya">Bodhgaya (India) The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous')Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantation, Development and Adaptation,'' p. 39. Routledge. is the newest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It was founded by Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), a Tibetan people, Tibetan philosopher, Vajrayana, tantric yogi and lama and further expanded and developed by his disciples (such as Khedrup Je, Gyaltsap Je, Dulzin Drakpa Gyaltsen, and Gendün Drubpa). The Gelug school is alternatively known as Kadam (''bKa’-gdams gsar-pa''), since it sees itself as a continuation of the Kadam tradition of Atisha (c. 11th century). The school of New Kadam, or New Kadampa is an offshoot of the Gelug-tradition. Furthermore, it is also called the Ganden school, after the first monastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganden Podrang
The Ganden Phodrang or Ganden Podrang (; ) was the Tibetan system of government established by the 5th Dalai Lama in 1642, when the Oirat lord Güshi Khan who founded the Khoshut Khanate conferred all spiritual and political power in Tibet to him in a ceremony in Shigatse. During the ceremony, the Dalai Lama "made a proclamation declaring that Lhasa would be the capital of Tibet and the government of would be known as Gaden Phodrang" which eventually became the seat of the Gelug school's leadership authority. The Dalai Lama chose the name of his monastic residence at Drepung Monastery for the new Tibetan government's name: ''Ganden'' (དགའ་ལྡན), the Tibetan name for Tushita heaven, which, according to Buddhist cosmology, is where the future Buddha Maitreya resides; and ''Phodrang'' (ཕོ་བྲང), a palace, hall, or dwelling. Lhasa's Red Fort again became the capitol building of Tibet, and the Ganden Phodrang operated there and adjacent to the Potala Palac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horpa Language
Horpa (also known in some publications as Stau – Chinese: 道孚语 ''Daofu'', 爾龔語 ''Ergong'') are a cluster of closely related Gyalrongic languages of China. Horpa is better understood as a cluster of closely related yet unintelligible dialect groups/languages closely related to Horpa Shangzhai or Stodsde skad. The term ''Stodsde skad'' is a Tibetan name meaning "language of the upper village". Names ''Ethnologue'' lists alternate names and dialect names for Horpa as Stau/Daofuhua, Bawang, Bopa, Danba, Dawu, Geshitsa/Geshiza/Geshizahua, Hor, Huo’er, Hórsók, Nyagrong-Minyag, Pawang, Rgu, Western Gyarong/Western Jiarong, Xinlong-Muya, and rTa’u. Classification Horpa is a type of Gyalrongic language, a branch of the Qiangic languages of the Sino-Tibetan family. Gyalrong (proper), Khroskyabs, and Horpa are in the Gyalrongic subgroup. From a genetic perspective, Horpa is a branch within West Gyalrongic, the other being Khroskyabs. Shangzhai is a sub-type of Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |