|
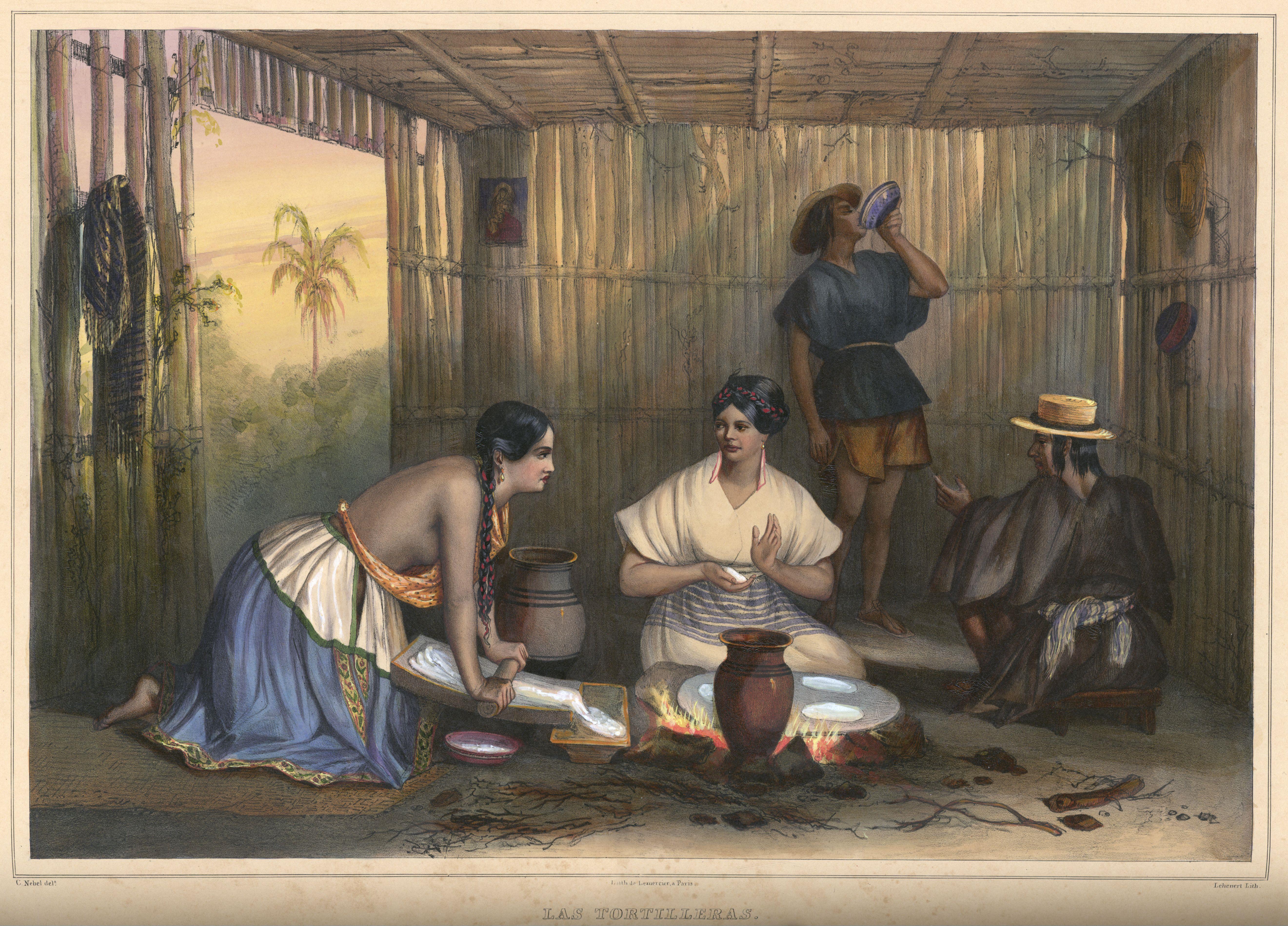
Hominy
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye. History The process of nixtamalization has been fundamental to Mesoamerican cuisine since ancient times. The lime used to treat the maize can be obtained from several different materials. Among the Lacandon Maya who inhabited the tropical lowland regions of eastern Chiapas, the caustic powder was obtained by toasting freshwater shells over a fire for several hours. In the highland areas of Chiapas and throughout much of the Yucatán Peninsula, Belize River valley and Petén Basin, limestone was used to make slaked lime for steeping the shelled kernels. The Maya used nixtamal to produce beers that more resembled ''chicha'' than '' pulque''. When bacteria were introduced to nixtamal it created a type of sourdough. The process of nixtamalization spread from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nixtamalization
Nixtamalization ( ) is a process for the preparation of maize (corn), or other cereal grain, grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooking, cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater (but sometimes aqueous alkali metal carbonates), washed, and then hulling, hulled. The term can also refer to the removal via an alkali process of the pericarp from other grains such as sorghum. Nixtamalized corn has several benefits over unprocessed grain: It is more easily ground, its nutritional value is increased, Flavor (taste), flavor and aroma are improved, and mycotoxins are reduced by up to 97–100% (for aflatoxin, aflatoxins). Lime and ash are highly alkaline: the alkalinity helps the dissolution of hemicellulose, the major glue-like component of the maize cell walls, and loosens the hulls from the kernels and softens the maize. The tryptophan in corn proteins is made more available for human absorption, thus helping to prevent niacin deficiency (pellagra). Tryptophan is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powhatan Language
Powhatan or Virginia Algonquian is an Eastern Algonquian subgroup of the Algonquian languages. It was formerly spoken by the Powhatan people of tidewater Virginia. Following 1970s linguistic research by Frank Thomas Siebert, Jr., some of the language has been reconstructed with assistance from better-documented Algonquian languages, and attempts are being made to revive it. The sole documentary evidence for this language is two short wordlists recorded around the time of first European contact. William Strachey recorded about 500 words and Captain John Smith recorded only about 50 words. Smith also reported the existence of a pidgin form of Powhatan, but virtually nothing is known of it. Strachey's material was collected sometime between 1610 and 1611, and probably written up from his notes in 1612 and 1613, after he had returned to England. It was never published in his lifetime, although he made a second copy in 1618. The second copy was published in 1849, and the first in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
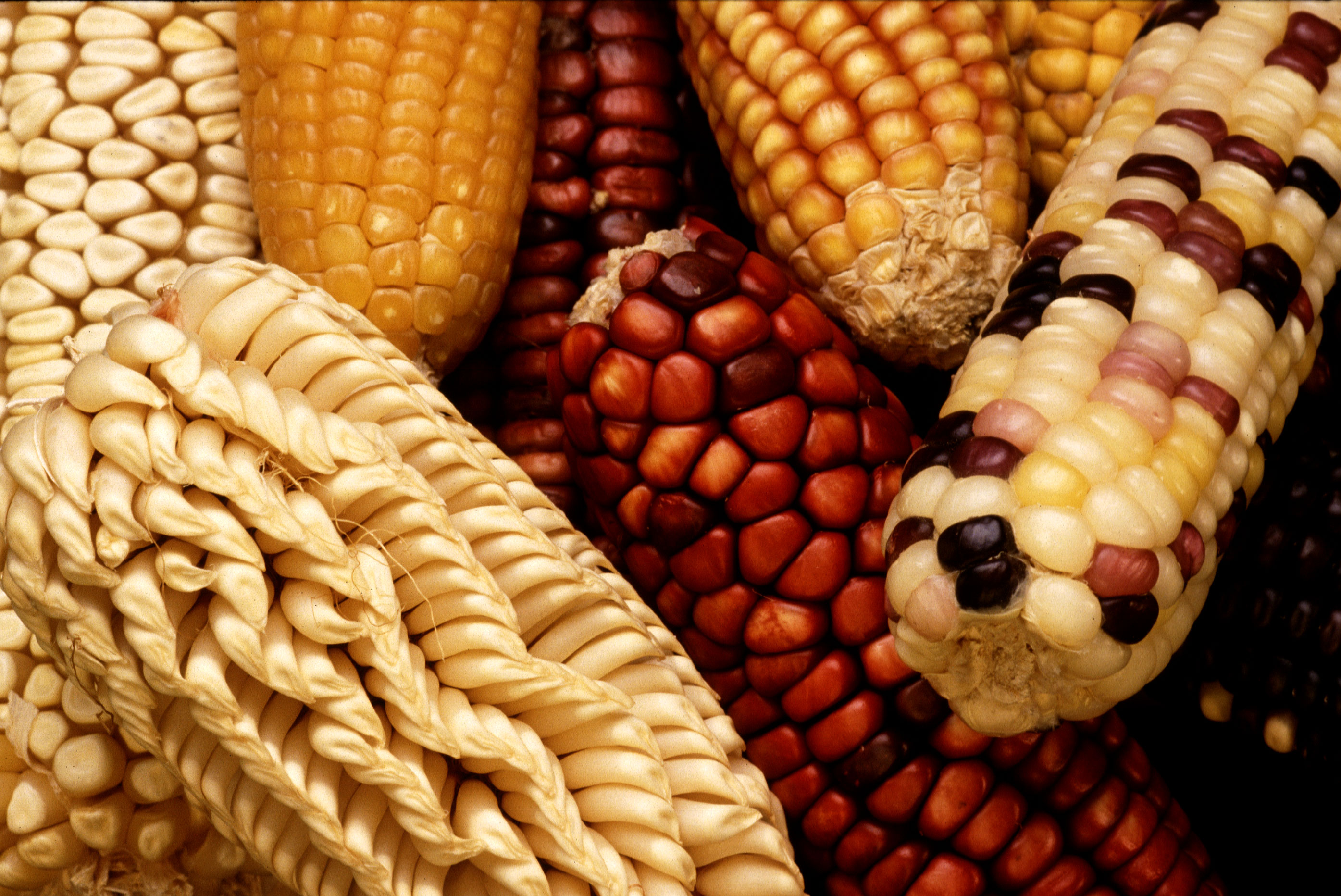
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Ash
Wood ash is the powder (substance), powdery residue remaining after the combustion of wood, such as burning wood in a fireplace, bonfire, or an industrial power plant. It is largely composed of calcium compounds, along with other non-combustible trace elements present in the wood, and has been used for many purposes throughout history. Composition Variability in assessment A comprehensive set of analyses of wood ash composition from many tree species has been carried out by Emil Wolff, among others. Several factors have a major impact on the composition: #Fine ash: Some studies include the solids escaping via the flue during combustion, while others do not. #Temperature of combustion. Ash content yield decreases with increasing combustion temperature which produces two direct effects: #*Dissociation: Conversion of carbonates, sulfides, etc., to oxides results in no carbon, sulfur, carbonates, or sulfides. Some metallic oxides (e.g. mercuric oxide) even dissociate to their elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
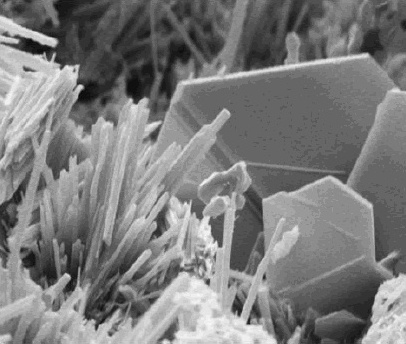
Slaked Lime
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approximately 125 million tons of calcium hydroxide are produced worldwide. Calcium hydroxide has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Solubility Calcium hydroxide is moderately soluble in water, as seen for many dihydroxides. Its solubility increases from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. Its solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Corn
Field corn is a North American term for maize (''Zea mays'') grown for livestock fodder (silage and meal), ethanol, cereal, and processed food products. The principal field corn varieties are dent corn, flint corn, flour corn (also known as soft corn) which includes blue corn (''Zea mays amylacea''), and waxy corn. Field corn primarily grown for livestock feed and ethanol production is allowed to mature fully before being shelled off the cob and being stored in silos, pits, bins, or grain "flats". Part of it is used to make corn syrup, especially with dent corn. Field corn can also be harvested as high-moisture corn, shelled off the cob and piled and packed like silage for fermentation; or the entire plant may be chopped while still very high in moisture, with the resulting silage either loaded and packed in plastic bags, piled and packed in pits, or blown into and stored in vertical silos. Uses Large-scale applications for field corn include: * Livestock fodder, whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famine Food
A famine food or poverty food is any inexpensive or ready available food used to nourish people in times of hunger and starvation, whether caused by extreme poverty, such as during economic depression or war, or by natural disasters such as drought. Foods associated with famine need not be nutritionally deficient, or unsavory. People who eat famine food in large quantity over a long period may become averse to it over time. In times of relative affluence, these foods may become the targets of social stigma and rejection. For example, some cultures that consider cats and dogs to be taboo foods may have historically consumed them during times of famine. The characterization of some foodstuffs as "famine" or "poverty" food can be social. For example, lobster and other crustaceans have been considered poverty food in some societies and luxury food in others, depending on the period and situation. Examples Several foodstuffs have been strongly associated with famine, war, or ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicha
''Chicha'' is a Fermentation, fermented (alcoholic) or non-fermented beverage of Latin America, emerging from the Andes and Amazonia regions. In both the pre- and post-Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest periods, corn beer (''chicha de jora'') made from a variety of maize landraces has been the most common form of ''chicha''. However, ''chicha'' is also made from a variety of other cultigens and wild plants, including, among others, quinoa (''Chenopodium quinia''), Chenopodium pallidicaule, kañiwa (''Chenopodium pallidicaule''), peanut, manioc (also called yuca or cassava), palm fruit, rice, potato, Oxalis tuberosa, oca (''Oxalis tuberosa''), and Geoffroea decorticans, chañar (''Geoffroea decorticans''). There are many regional variations of ''chicha''. In the Inca Empire, ''chicha'' had Ceremony, ceremonial and ritual uses. Etymology and related phrases The exact origin of the word ''chicha'' is debated. One belief is that the word ''chicha'' is of Taino origin and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utilize its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Western United States, with the Midwestern United States, Midwestern and Northeastern United States to its north and the Gulf of Mexico and Mexico to its south. Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th-century Mason–Dixon line, the Ohio River, and the Parallel 36°30′ north, 36°30′ parallel.The South . ''Britannica''. Retrieved June 5, 2021. Within the South are different subregions such as the Southeastern United States, Southeast, South Central United States, South Central, Upland South, Upper South, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica Online''.Taboo. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Retrieved 21 Mar. 2012 Such prohibitions are present in virtually all societies. Taboos may be prohibited explicitly, for example within a legal system or religion, or implicitly, for example by social norms or conventions followed by a particular culture or organization. Taboos are often meant to protect the individual, but there are other reasons for their development. An ecological or medical background is apparent in many, including some that are seen as religious or spiritual in origin. Taboos can help use a resource more efficiently, but when applied to only a subsection of the community they can also serve to suppress said subsection of the community. A taboo acknowledged by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |