|
Holger Braunschweig
Holger Braunschweig is Head and Chair of Inorganic Chemistry at the Julius-Maximilians-University of Würzburg in Würzburg, Germany. He is best known for founding the field of transition metal-boron multiple bonding (transition metal borylenes), the synthesis of the first stable compounds containing boron-boron and boron-oxygen triple bonds, the isolation of the first non-carbon/nitrogen main-group dicarbonyl, and the first fixation of dinitrogen at an element of the p-block of the periodic table. By modifying a strategy pioneered by Prof. Gregory Robinson of the University of Georgia, Braunschweig also discovered the first rational and high-yield synthesis of neutral compounds containing boron-boron double bonds ( diborenes). In 2016 Braunschweig isolated the first compounds of beryllium in the oxidation state of zero. Education and research career Braunschweig obtained his Ph.D. and Habilitation from RWTH Aachen with P. Paetzold and worked as a postdoctoral researcher wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c) organization, 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio. The ACS is a leading source of scientific information through its peer-reviewed scientific journals, national conferences, and the Chemical Abstracts Service. Its publications division produces over 80 Scientific journal, scholarly journals including the prestigious ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'', as well as the weekly tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diborene
Diborane(2), also known as diborene, is an inorganic compound with the formula B2H2. The number 2 in diborane(2) indicates the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the boron complex. There are other forms of diborane with different numbers of hydrogen atoms, including diborane(4) and diborane(6). Diborane(2) is a highly reactive molecule that rapidly decomposes, making it a challenge to study experimentally under ambient conditions. To observe diborane(2) experimentally, high-vacuum and low temperature conditions using matrix isolation techniques are required, such as trapping the molecule in inert matrices like neon or argon. As a result of these difficult synthesis conditions, its properties and behaviour have been predominantly studied using theoretical models and computational simulations. Diborene also refers to a series of molecules with the formula R:(BH)=(BH):R or R-B=B-R where R is an organic group. Diborene derivatives are relatively stable and can be stored at room te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in the United States. It is the flagship university, flagship school of the University System of Georgia. In addition to the main campuses in Athens with their approximately 470 buildings, the university has two smaller campuses located in Tifton, Georgia, Tifton and Griffin, Georgia, Griffin. The university has two satellite campuses located in Atlanta, Georgia, Atlanta and Lawrenceville, Georgia, Lawrenceville, and residential and educational centers in Washington, D.C., at Trinity College, Oxford, Trinity College of University of Oxford, Oxford University, and in Cortona, Italy. The total acreage of the university in 30 List of counties in Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia counties is . The university is Carnegie Classification of Institutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory H
Gregory may refer to: People and fictional characters * Gregory (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Gregory (surname), a surname *Gregory (The Walking Dead), fictional character from the walking dead * Gregory (Five Nights at Freddy's), main protagonist of '' Five Nights at Freddy's: Security Breach'' ** Places Australia *Gregory, a town in the Northern Territory *Gregory, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Burke **Electoral district of Gregory, Queensland, Australia * Gregory, Western Australia. United States *Gregory, South Dakota * Gregory, Tennessee * Gregory, Texas Outer space * Gregory (lunar crater) * Gregory (Venusian crater) Other uses * "Gregory" (''The Americans''), the third episode of the first season of the television series ''The Americans'' See also * Greg (other) * Greggory * Gregoire (other) * Gregor (other) * Gregores (other) * Gregorian (other) * Gregor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
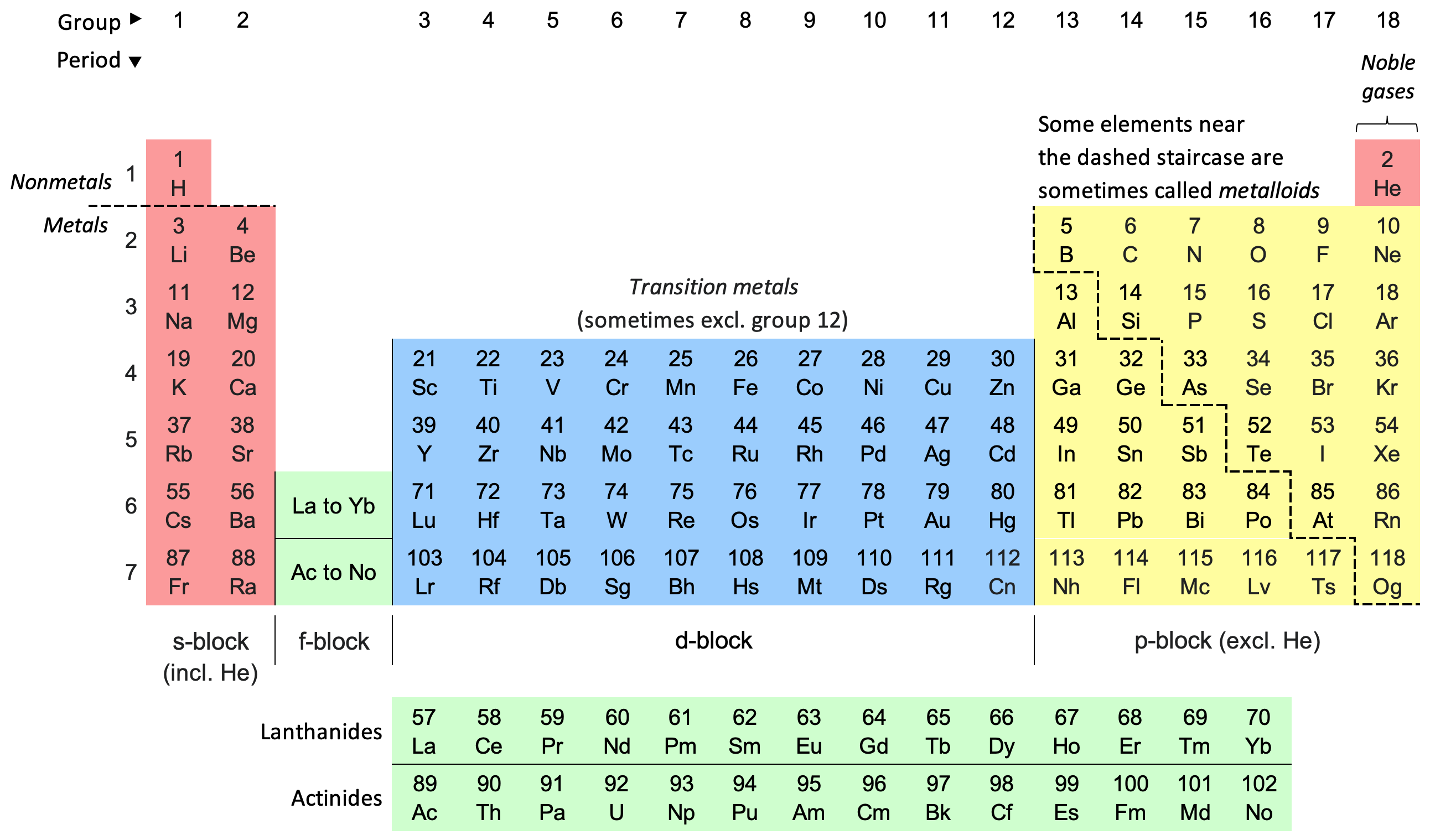
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-block
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term seems to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-block, p-block, d-block, f-block and g-block. The block names (s, p, d, and f) are derived from the spectroscopic notation for the value of an electron's azimuthal quantum number: sharp (0), principal (1), diffuse (2), and fundamental (3). Succeeding notations proceed in alphabetical order, as g, h, etc., though elements that would belong in such blocks have not yet been found. Characteristics There is an ''approximate'' correspondence between this nomenclature of blocks, based on electronic configuration, and sets of elements based on chemical properties. The s-block and p-block together are usually considered main-group elements, the d-block corresponds to the transition metals, and the f-block corresponds to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is catalyzed by enzymes called nitrogenases. These enzyme complexes are encoded by the Nif gene, ''Nif'' genes (or ''Nif'' homologs) and contain iron, often with a second metal (usually molybdenum, but sometimes vanadium). Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria have symbiotic relationships with plants, especially legumes, mosses and aquatic ferns such as ''Azolla''. Looser non-symbiotic relationships between diazotrophs and plants are often referred to as associative, as seen in nitrogen fixation on rice roots. Nitrogen fixation occurs between some termites and fungus, fungi. It occurs naturally in the air by means of NOx, NOx production by lightning. Fixed nitrogen is essential to life on Earth. Organic compounds such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxoborane
In chemistry, an oxoborane is any chemical compound containing a boron atom with a terminal oxygen atom (a functional group). The compound class is of some relevance to academic research. The parent compound, HBO, itself called "oxoborane", together with derivatives , , , and have been detected in matrix isolation or in the gaseous phase at high temperature. In these compounds the boron and oxygen form a triple bond prone to cyclotrimerization to boroxines. Derivatives Although monomeric oxoboranes have not been isolated, derivatives have been described. A Lewis acid-stabilized adduct of an oxoborane is ( NacNacB=O.AlCl3. In this compound the oxygen atom is coordinated to aluminium chloride. The BO bond length is 130 pm (compare to 136 pm in regular boronic acids). Related systems are known. In ''trans''- Cy3P)2PtBr(BO) platinum is coordinated to the BO unit.''Oxoboryl Complexes: Boron−Oxygen Triple Bonds Stabilized in the Coordination Sphere of Platinum'' Holger Brauns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borylene
A borylene is the boron analogue of a carbene. The general structure is R-B: with R an organic moiety (chemistry), moiety and B a boron atom with two unshared electrons. Borylenes are of academic interest in organoboron chemistry. A diradical, singlet ground state is predominant with boron having two vacant sp2 orbitals and one doubly occupied one. With just one additional substituent the boron is more electron deficient than the carbon atom in a carbene. For this reason stable borylenes are more uncommon than stable carbenes. Some borylenes such as boron monofluoride (BF) and boron monohydride (BH) the parent compound also known simply as borylene, have been detected in microwave spectroscopy and may exist in stars. Other borylenes exist as reactive intermediates and can only be inferred by chemical trapping. The first stable terminal borylene complex [(OC)5WBN(SiMe3)2] was reported by Holger Braunschweig et al. in 1998. In this compound a borylene is coordinated to a transition m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Bond
Multiple may refer to: Economics *Multiple finance, a method used to analyze stock prices *Multiples of the price-to-earnings ratio *Chain stores, are also referred to as 'Multiples' *Box office multiple, the ratio of a film's total gross to that of its opening weekend Sociology *Multiples (sociology), a theory in sociology of science by Robert K. Merton, see Science *Multiple (mathematics), multiples of numbers * List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings * Multiple birth, because having twins is sometimes called having "multiples" *Multiple sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ..., an inflammatory disease *Parlance for people with multiple identities, sometimes called "multiples"; oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovas and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental boron is found in smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |