|
Hokurikudō
is a Japanese geographical term. It means both an ancient division of the country and the main road running through the old Japanese geographical region.Nussbaum, "''Hokurikudō''" in Both were situated along the northwestern edge of Honshū. The name literally means 'North Land Way'. It also refers to a series of roads that connected the capitals (国府 ''kokufu'') of each of the provinces that made up the region. When the Gokishichidō system was initially established after the Taika reforms, it consisted of just two provinces: Wakasa and Koshi. During the reign of Emperor Temmu, Koshi was divided into three regions: Echizen, Etchū and Echigo and Sado Island was added as a fifth province. Later, Noto and Kaga were carved out of Echizen to form seven provinces in total. The Hokuriku subregion of Chūbu region constitutes Hokurikudō region today. See also * Comparison of past and present administrative divisions of Japan * Hokuriku subregion * Koshi Province Note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokuriku Expressway
The , (abbreviated as , is a 4-laned national Expressways of Japan, expressway in Japan. It is owned and managed by East Nippon Expressway Company and Central Nippon Expressway Company. Overview The first section was opened in 1972 by Japan Highway Public Corporation and construction proceeded in stages until the entire route was completed in 1988. On October 1, 2005, all national expressways were privatized and management of the Hokuriku Expressway was divided between the East and Central Nippon Expressway Companies. The route serves the Hokuriku region on the north central coast of Honshū, Japan's largest island. For most of its length it parallels Japan National Route 8, National Route 8 and the Hokuriku Main Line of West Japan Railway Company. Although the route officially originates in Niigata and terminates at Maibara, exit numbers and kilometer markings originate from Maibara. Features Around Tsuruga Interchange, the south-bound lanes cross over the north-bound lane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circuit (administrative Division)
A circuit ( or ) was a historical political division of China and is a historical and modern administrative unit in Japan. The primary level of administrative division of Korea under the Joseon and in modern North and South Korea employs the same Chinese character as the Chinese and Japanese divisions but, because of its relatively greater importance, is usually translated as province instead. China Circuits originated in China during the Han dynasty and were used as a lower-tier administrative division, comparable to the county (, also translated as "districts"). They were used only in the fringes of the empire, which were either inhabited primarily by non-Han Chinese peoples or too geographically isolated from the rest of the Han centers of power. The system fell into disuse after the collapse of the Western Jin dynasty. The administrative division was revived in 627 when Tang Emperor Taizong made it the highest level administrative division and subdivided China into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokishichidō
was the name for ancient administrative units organized in Japan during the Asuka period (AD 538–710), as part of a legal and governmental system borrowed from the Chinese. Though these units did not survive as administrative structures beyond the Muromachi period (1336–1573), they did remain important geographical entities until the 19th century. Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). The Gokishichidō consisted of five provinces in the Kinai () or capital region, plus seven ''dō'' () or circuits, each of which contained provinces of its own. When Hokkaido was included as a circuit after the defeat of the Republic of Ezo in 1869, the system was briefly called . The abolition of the ''han'' system abolished the -han (early modern feudal domains) in 1871, -dō/circuits and provinces were per se not abolished by the abolition of domains; but the prefectures that sprang from the domains became the primary administrative division of the country and were soon merged and reorganized to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echigo Province
was an old provinces of Japan, old province in north-central Japan, on the shores of the Sea of Japan. It bordered on Uzen Province, Uzen, Iwashiro Province, Iwashiro, Kōzuke Province, Kōzuke, Shinano Province, Shinano, and Etchū Province, Etchū Provinces.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Echigo''" in . It corresponds today to Niigata Prefecture, minus the island of Sado, Niigata, Sado. Its abbreviated form name was , with Echizen Province, Echizen and Etchū Province, Etchū Provinces. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Echigo was ranked as one of the 35 "superior countries" (上国) in terms of importance, and one of the 30 "far countries" (遠国) in terms of distance from the capital Kyoto. Echigo and Kōzuke Province were known as the Jōetsu region. History In the late 7th century, during the reign of Emperor Monmu, the ancient province of was divided into three separate provinces: Echizen Province, Echizen, Etchū Province, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Past And Present Administrative Divisions Of Japan
The geography and administrative subdivisions of Japan have evolved and changed during the course of its history. These were sometimes grouped according to geographic position. Kinai *Yamashiro Province, Yamashiro **southern Kyoto Prefecture, Kyoto *Yamato Province, Yamato (northern Nara Prefecture, Nara without Yoshino) **entire Nara Prefecture, Nara *Yoshino Province, Yoshino (created from Yamato in 716, later rejoined back in 738) **southern Nara Prefecture, Nara (Yoshino District, Nara, Yoshino District + Gojō, Nara, Gojō city) *Kawachi Province, Kawachi **eastern Osaka Prefecture, Osaka *Izumi Province, Izumi (created in 716 from Kawachi, then rejoined back in 740, later re-split in 757) **southern/southwestern Osaka Prefecture, Osaka *Settsu Province, Settsu **northeastern Hyōgo Prefecture, Hyōgo including Kōbe, Hyōgo, Kōbe city **northern/northwestern Osaka Prefecture, Osaka including Osaka city Tōkaidō (region), Tōkaidō ''Tōkaidō'' literally means 'Eastern Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
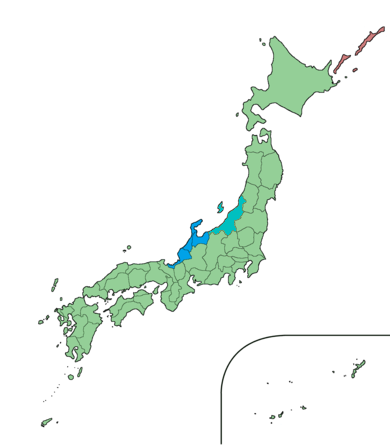
Hokuriku Region
The is located in the northwestern part of Honshu, the main island of Japan. It lies along the Sea of Japan and is part of the larger Chūbu region. It is almost equivalent to the former Koshi Province (Japan), Koshi Province and Hokurikudō area in pre-modern Japan. From the Heian period until the Edo period, the region was a core recipient of population, and grew to be proportionately much larger than it is today, despite the rural character; in modern times, its population has remained consistent, with most urban growth in the 20th century instead taking place in Kantō region, Kanto, Nagoya, Chūkyō, and Kansai region, Kansai. The Hokuriku region is also known for traditional culture that originated from elsewhere that has been long lost along the Taiheiyō Belt. The Hokuriku region includes the four prefectures of Ishikawa Prefecture, Ishikawa, Fukui Prefecture, Fukui, Niigata Prefecture, Niigata and Toyama Prefecture, Toyama, although Niigata is sometimes included as an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaga Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the south and western portion of Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Kaga bordered on Echizen, Etchū, Hida, and Noto Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its abbreviated form name was . History was an ancient province of Japan and is listed as one of the original provinces in the '' Nihon Shoki''. The region as a whole was sometimes referred to as . In 701 AD, per the reforms of the Taihō Code, Koshi was divided into three separate provinces: Echizen, Etchū, and Echigo. In 823 AD, the two eastern districts of Echizen Province (Kaga and Enuma) were separated to form Kaga Province. Kaga was thus the last province to be created under the ''ritsuryō'' system. The same year, the northern portion of Enuma District became Nomi District, and the southern portion on Kaga District became Ishikawa District. Kaga District itself was renamed Kahoku District. The provincial capital and provincia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakasa Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the southwestern portion of Fukui Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Wakasa''" in . Wakasa bordered on Echizen, Ōmi, Tanba, Tango, and Yamashiro Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its abbreviated form name was . Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Wakasa was ranked as a "medium country" (中国) and a near country (近国) in terms of its importance and distance from the capital. History Ancient and classical Wakasa Wakasa existed as a political entity before the ''Ritsuryō'' system and the implementation of the Taihō Code of the Nara period. Wooden shipping tags labelled "Wakasa" have been found in the ruins of Fujiwara-kyō. Per the ''Nihon Shoki'', ancient Wakasa was governed by a Kuni no miyatsuko, who was a descendant of Amenohiboko, a semi-legendary prince of Silla, Shilla, who settled in Tajima province during the reign of Emperor Suinin. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koshi Province (Japan)
was an ancient province or region of Japan in what is now the Hokuriku region. The region as a whole was sometimes referred to as . Koshi appears as one of the original provinces in the ''Nihon Shoki''. In 598 AD, the residents of Koshi presented a white deer to Empress Suiko as tribute. At the end of the 7th century, Koshi was divided into three separate provinces: Echizen, Etchū, and Echigo (as noted in the Taihō Code). The names of these provinces mean 'Inner-Koshi' (Echizen), 'Middle-Koshi' (Etchu), and 'Outer-Koshi' (Echigo), respectively, indicating their relative positions with respect to the capital region (Kinki) at the time the Ritsuryō system was enacted. Later, parts of Echizen were separated off into Noto and Kaga provinces. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Koshi''" in . See also * Koshibito * Hokurikudō * Hokuriku subregion Notes References * Asiatic Society of Japan. (1874). ''Transactions of the Asiatic Society of Japan.'' Yokohama: The Societ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echizen Province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan in the area that is today the northern portion of Fukui Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Echizen bordered on Kaga Province, Kaga, Wakasa Province, Wakasa, Hida Province, Hida, and Ōmi Province, Ōmi Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Gokishichidō, Circuit. Its abbreviated form name was . History Ancient and classical Echizen was an Old provinces of Japan, ancient province of Japan and is listed as one of the original provinces in the ''Nihon Shoki''. The region as a whole was sometimes referred to as . In 507, during a succession crisis, the king of Koshi was chosen to become the 26th emperor of Japan, Emperor Keitai. In 701 AD, per the reforms of the Taihō Code, Koshi was divided into three separate provinces: Echizen, Etchū Province, Etchū, and Echigo Province, Echigo. The original Echizen included all of what is now Ishikawa Prefecture. In 718 A.D., four districts of Japan, districts of northern Echizen (Hakui D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is an academic publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University. It is a member of the Association of University Presses. Its director since 2017 is George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint (trade name), imprint, which it inaugurated in May 1954 with the publication of the ''Harvard Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noto Province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan in the area that is today the northern part of Ishikawa Prefecture in Japan, including the Noto Peninsula (''Noto-hantō'') which is surrounded by the Sea of Japan. Noto bordered on Etchū Province, Etchū and Kaga Province, Kaga provinces to the south, and was surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the east, north and west. Its abbreviated form name was . History In 718 A.D., four districts of Japan, districts of Echizen Province, Hakui District, Ishikawa, Hakui District, Kashima District, Ishikawa, Noto District (also called Kashima District), Fugeshi District, Ishikawa, Fugeshi District and Suzu District, Ishikawa, Suzu District, were separated into Noto Province. However, in the year 741, the province was abolished, and merged into Etchū Province. Noto Province was subsequently re-established in 757. The province disappears from history until the ''Wamyō Ruijushō'' of 930 AD, in which Minamoto no Shitagō is named as kokushi (offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |