|
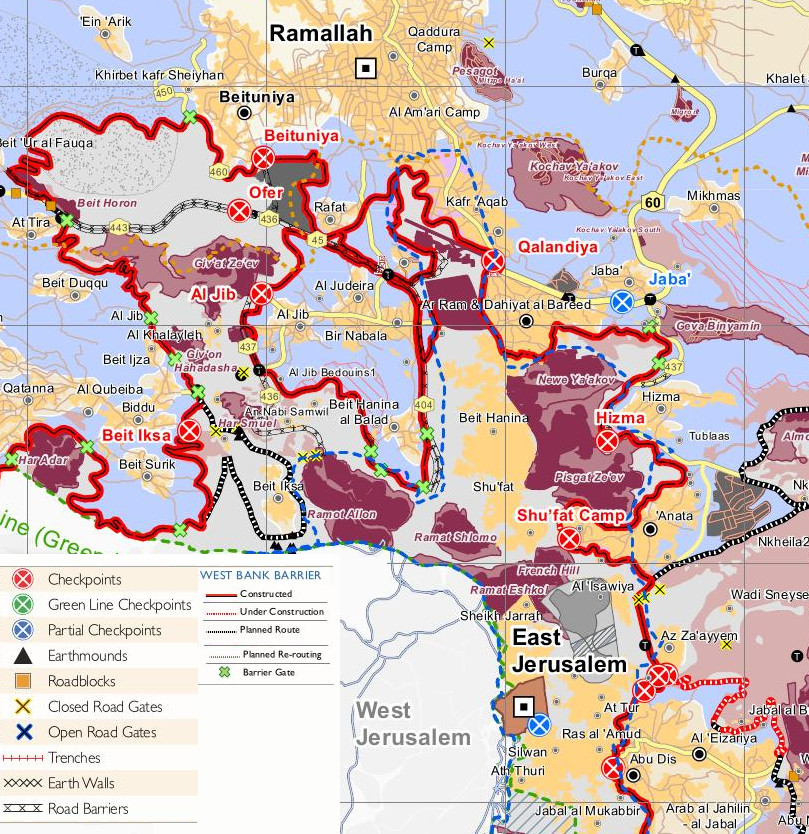
Hizma
Hizma () is a Palestinian town in the Jerusalem Governorate, seven kilometers from Jerusalem's Old City. The town, mostly located in Area C of the West Bank, borders four Israeli settlements, Neve Yaakov and Pisgat Ze'ev (both officially considered part of Jerusalem), Geva Binyamin and Almon. Hizma is identified with the biblical town of ''Azmaveth'' of the Israelite tribe of Benjamin. Archaeological findings confirm a Jewish presence during Roman times, marked by a thriving stoneware industry, and the discovery of a burial cave housing ossuaries inscribed in the Hebrew alphabet. Byzantine period ceramics were also found at the site. Throughout Ottoman, British, and Jordanian rule, Hizma was a small village inhabited by Muslims. Since 1967, Hizma has been occupied by Israel. The village is cut off from Jerusalem by the Israeli West Bank barrier in the west and from the West Bank by settlements in the east. As of 2017, Hizma had a population of about 7,118 residents. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisgat Ze'ev
Pisgat Ze'ev (, lit. ''Ze'ev's Peak'') is an Israeli settlement in East Jerusalem and the largest residential neighborhood in Jerusalem with a population of over 50,000. Pisgat Ze'ev was established by Israel as one of the city's five Ring Neighborhoods on land effectively annexed after the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli settlements in East Jerusalem illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this. Pisgat Ze'ev is situated east of Shuafat and Beit Hanina, west of Hizma, south of Neve Yaakov, and north of 'Anata and the Shuafat refugee camp. The Israeli West Bank barrier includes Pisgat Ze'ev in the northern section of Jerusalem while excluding Shuafat refugee camp from the city by running in an S-shape here. History Antiquity Archeological evidence shows that in the biblical period, the site encompassed small agricultural villages along routes north from Jerusalem to Nablus and the Galilee. The villages made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neve Yaakov
Neve Yaakov (; also ''Neve Ya'aqov'', lit. Jacob's Oasis) is an Israeli settlement in East Jerusalem, part of the Israeli-occupied territories, north of the settlement of Pisgat Ze'ev and south of the Palestinian locality of al-Ram. Established in 1924 during the period of the British Mandate, it was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The area was captured by Israel in the Six-Day War and a new neighborhood was built nearby, at which time international opposition to its legitimacy began. The international community considers Israeli settlements in East Jerusalem illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this, defining it as a neighborhood within the jurisdiction of the Jerusalem Municipality, which provides all services. The population of Neve Yaakov is 23,300. Neve Yaakov is one of the Ring Settlements of East Jerusalem. The settlement is also the location of the IDF's Central Command for the West Bank, Jerusalem, Sharon, Gush Dan an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Governorate
The Quds Governorate (), also known as Jerusalem Governorate, is one of the 16 governorates of Palestine and located in the central part of the West Bank. The current governor, appointed by the Palestinian National Authority, is Adnan Ghaith since 2018, who succeeded Adnan al-Husayni, appointed in 2008. The Governorate has two sub-districts: ''Jerusalem J1'', which includes the localities within the territory controlled by the Israeli Jerusalem municipality (East Jerusalem), and ''Jerusalem J2'', which includes the remaining parts of the Jerusalem Governorate. The district capital of the Governorate is East Jerusalem (al-Quds). The total land area of the governorate is 344 km2. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the governorate had a population of 429,500 residents in 2005, accounting for 10.5% of Palestinians living in the Palestinian territories in 2022 population had risen to 482,854 as official Statistics. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almon, Mateh Binyamin
Almon (), also known as Anatot (), is an Israeli settlement in the West Bank, organized as a community settlement. Built over land confiscated from the nearby Palestinian town of 'Anata, it falls under the jurisdiction of the Mateh Binyamin Regional Council. In it had a population of . The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this. History According to ARIJ, Almon is located on 783 dunams of land which Israel confiscated from the Palestinian town of 'Anata. 'Anata Town Profile ARIJ, 2012, p. 19 Anatot was established in 1982 by secular families with the help of the Amana organisation. It was named Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geva Binyamin
Geva Binyamin (), also known as Adam (), is an Israeli settlement in the West Bank, built over land expropriated from the Palestinian village of Jaba'. It is organised as a community settlement and falls under the jurisdiction of Mateh Binyamin Regional Council. In , it had a population of . The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this. Etymology The name Geva Binyamin comes from an eponymous Biblical site – Geba of Benjamin – which is believed to have stood around the same location. According to contemporary scholarship, Geba of Benjamin was located in the nearby village of Jaba', which preserves the biblical name. History According to ARIJ, Israel confiscated 1,139 dunams of land from the Palestinian village of Jaba' in order to construct Geva Binyamin. Some Jaba' residents have reportedly managed to return to part of their land fenced off by the settlers of Geva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet (, ), known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is a unicase, unicameral abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Judaeo-Spanish, Ladino, Judeo-Arabic languages, Judeo-Arabic, and Judeo-Persian. In modern Hebrew, vowels are increasingly introduced. It is also used informally in Israel to write Levantine Arabic, especially among Druze in Israel, Druze. It is an offshoot of the Aramaic alphabet, Imperial Aramaic alphabet, which flourished during the Achaemenid Empire and which itself derives from the Phoenician alphabet. Historically, a different abjad script was used to write Hebrew: the original, old Hebrew script, now known as the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, has been largely preserved in a variant form as the Samaritan script, Samaritan alphabet, and is still used by the Samaritans. The present ''Jewish script'' or ''square script'', on the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock-cut Tombs In Ancient Israel
The use of rock-cut cave tombs in the region of ancient Israel began in the early Canaanite period, from 3100–2900 BCE. The custom lapsed a millennium, however, before re-emerging in the earliest Israelite tombs, dating to the 9th century BCE in Jerusalem. The use of rock-cut tombs reached its peak in the 8th and 7th centuries BCE, before rapidly declining and eventually falling out of use in the 6th century BCE in some regions.Faust, Avraham, and Bunimovitz, Shlomo. "The Judahite Rock-Cut Tomb: Family Response at a Time of Change." In ''Israel Exploration Journal'', vol. 58, no. 2, 2008, pp. 150–170. . Accessed 16 Nov. 2020. It reappeared during the Second Temple period and continued into the Late Roman and Byzantine periods. Use of the tombs has been recorded as recently as the late Roman period around the 3rd century CE. Rock-cut tombs were a form of burial and interment chamber used in ancient Israel. Cut into the landscapes surrounding ancient Judean cities, their de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossuary
An ossuary is a chest, box, building, well, or site made to serve as the final resting place of human skeletal remains. They are frequently used where burial space is scarce. A body is first buried in a temporary grave, then after some years the skeletal remains are removed and placed in an ossuary ("os" is "bone" in Latin). The greatly reduced space taken up by an ossuary means that it is possible to store the remains of many more people in a single tomb than possible in coffins. The practice is sometimes known as grave recycling. Persian ossuaries In Persia, the Zoroastrianism, Zoroastrians used a deep well for this function from the earliest times (c. 3,000 years ago) and called it ''Tower of Silence, astudan'' (literally, "the place for the bones"). There are many rituals and regulations in the Zoroastrian faith concerning the ''astudans''. Jewish ossuaries During the Second Temple period, Jewish burial customs were varied, differing based on class and belief. For the wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly interrelated, as Judaism is their ethnic religion, though it is not practiced by all ethnic Jews. Despite this, religious Jews regard Gerim, converts to Judaism as members of the Jewish nation, pursuant to the Conversion to Judaism, long-standing conversion process. The Israelites emerged from the pre-existing Canaanite peoples to establish Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Judah in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age.John Day (Old Testament scholar), John Day (2005), ''In Search of Pre-Exilic Israel'', Bloomsbury Publishing, pp. 47.5 [48] 'In this sense, the emergence of ancient Israel is viewed not as the cause of the demise of Canaanite culture but as its upshot'. Originally, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine. After an Arab Revolt, Arab uprising against the Ottoman Empire during the First World War in 1916, British Empire, British Egyptian Expeditionary Force, forces drove Ottoman Empire, Ottoman forces out of the Levant. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence in case of a revolt but, in the end, the United Kingdom and French Third Republic, France divided what had been Ottoman Syria under the Sykes–Picot Agreement—an act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Another issue was the Balfour Declaration of 1917, in which Britain promised its support for the establishment of a Homeland for the Jewish people, Jewish "national home" in Palestine. Mandatory Palestine was then establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |