|
History Of Bermuda
Bermuda was first documented by a European in 1503 by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez. In 1609, the English Virginia Company, which had established Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown in Colony of Virginia, Virginia two years earlier, permanently settled Bermuda in the aftermath of a hurricane, when the crew and passengers of steered the ship onto the surrounding reef to prevent it from sinking, then landed ashore. Bermuda's first capital, St. George's, Bermuda, St. George's, was established in 1612. The Virginia Company administered the island as an extension of Virginia until 1614; its Corporate spin-off, spin-off, the Somers Isles Company, took over in 1615 and managed the island until 1684, when the company's charter was revoked and Bermuda became an English Crown Colony. Following the Acts of Union 1707, 1707 unification of the parliaments of Scotland and England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain, the islands of Bermuda became a British Overseas Territory#Collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatio Babylonica
In 1501–1502, Peter Martyr d'Anghiera, an Italian humanist, was sent on a diplomatic mission to Mamluk Egypt by Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, in order to convince Sultan Qansuh al-Ghuri not to retaliate against his Christian subjects in response to the fall of Granada to the Spanish and the subsequent persecution of Moors. Martyr was instructed by the Catholic Monarchs to deny reports of forced conversions of their Spanish Muslim subjects. He began his voyage in August 1501, reaching Venice in October. The ambassador later sailed for Alexandria and reached the port city on December 23. He toured Alexandria after being initially denied an audience with the Sultan. When the approval finally came, he traveled to Cairo and met with al-Ghuri on February 6, 1502. The Sultan received Martyr well in his Cairo palace, amid local unrest fueled by envoys from other Muslim states. Another secret meeting was arranged, during which Martyr was inquired about the forced conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roanoke Colony
The Roanoke Colony ( ) refers to two attempts by Sir Walter Raleigh to found the first permanent English settlement in North America. The first colony was established at Roanoke Island in 1585 as a military outpost, and was evacuated in 1586. The more famous second colony, known as the Lost Colony, began when a new group of settlers under John White (colonist and artist), John White arrived on the island in 1587; a relief ship in 1590 found the colony mysteriously abandoned. The fate of the 112 to 121 colonists remains unknown. Roanoke Colony was founded by Governor Ralph Lane in 1585 on Roanoke Island in present-day Dare County, North Carolina. Lane's colony was troubled by a lack of supplies and poor relations with some of the local Native Americans in the United States, Indian tribes. A resupply mission by Sir Richard Grenville was delayed, so Lane abandoned the colony and returned to England with Sir Francis Drake in 1586. Grenville arrived two weeks later and also return ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Grenville
Sir Richard Grenville ( – ), also spelt Greynvile, Greeneville, and Greenfield, was an English privateer and explorer. Grenville was lord of the manors of Stowe, Cornwall and Bideford, Devon. He subsequently participated in the plantations of Ireland specifically the Munster plantations, the English colonisation of the Americas and the repulse of the Spanish Armada. Grenville also served as Member of Parliament for Cornwall, High Sheriff for County Cork and Sheriff of Cornwall. In 1591, Grenville died at the battle of Flores fighting against an overwhelmingly larger Spanish fleet near the Azores. He and his crew on board the galleon fought against the 53-strong Spanish fleet to allow the other English ships to escape. Grenville was the grandfather of Sir Bevil Grenville, a prominent military officer during the English Civil War. Origins Richard Grenville was the eldest son and heir of Sir Roger Grenville (d. 1545), who was captain of when she sank in Portsmouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
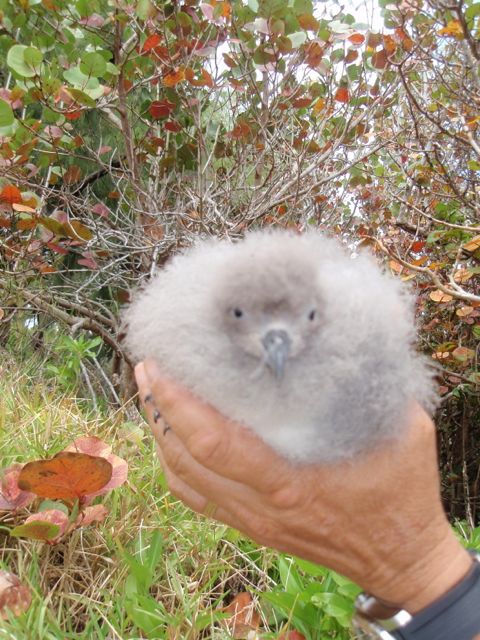
Bermuda Petrel
The Bermuda petrel (''Pterodroma cahow'') is a gadfly petrel. Commonly known in Bermuda as the cahow, a name derived from its eerie cries, this nocturnal ground-nesting seabird is the national bird of Bermuda, pictured on Bermudian currency. Bermuda petrels are the second rarest seabird on the planet. They have medium-sized bodies and long wings, a greyish-black crown and collar, dark grey upper-wings and tail, white upper-tail coverts and white under-wings edged with black, and the underparts are completely white. For 300 years, it was thought to be extinct. The dramatic rediscovery in 1951 of eighteen nesting pairs made this a " Lazarus species", that is, a species found to be alive after having been considered extinct. This has inspired a book and two documentary films. A national programme to preserve the bird and restore the species has helped increase its numbers, but scientists are still working to enlarge its nesting habitat on the restored Nonsuch Island. Diet and forag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about 30 degrees) and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Argentina, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
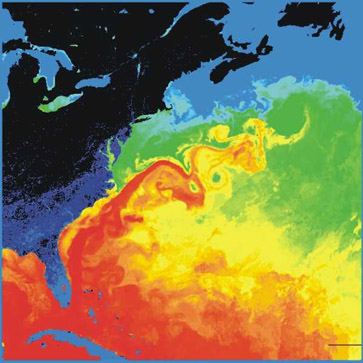
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolina) and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around , it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the coastal areas of the East Coast of the United States from Florida to southeast Virginia (near 36°N latitude), and to a greater degree, the climate of Northwest Europe. A consensus exists that the climate of Northwest Europe is warmer than other areas of similar latitude at least partially because of the stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponce De León
Ponce may refer to: *Ponce (surname) *Ponce (streamer) (born 1991), French streamer *Ponce, Puerto Rico, a city in Puerto Rico ** Ponce High School ** Ponce massacre, 1937 * USS ''Ponce'', several ships of the US Navy * Manuel Ponce, a Mexican composer active in the 20th century * British and Irish slang for a pimp, also used figuratively to refer to an effeminate man * Chaudin, cajun food, also referred to as ponce See also * Ponce Inlet, Florida, a town in Florida, US * Ponce de León (other) * Ponce de Leon, Florida, a town in Florida, US * Ponce de Leon, Missouri, an unincorporated community in Missouri, US * Ponce de Leon Avenue, Atlanta Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ..., Georgia, US * Ponce de Leon Bay, a bay in Florida, US * Ponce de Leon Springs St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Voyage Of Columbus
The fourth voyage of Columbus was a Spanish maritime expedition in 1502–1504 to the western Caribbean Sea led by Christopher Columbus. The voyage, Columbus's last, failed to find a western maritime route to the Far East, returned relatively little profit, and resulted in the loss of many crew men, all the fleet's ships, and a year-long marooning in Jamaica. It is deemed the first non-Amerindian discovery of mainland Middle America, and one of the first non-Amerindian, non- Norse discoveries of continental North America. Prelude Upon being released from prison on 17 December 1500, Columbus set about planning what he deemed would be 'his most significant, most profitable expedition yet.' The 1497 discovery of an eastern maritime passage to 'the opulent East,' by Vasco de Gama, had steeled Columbus's determination to find a shorter, more direct western route. Consequently, on 26 February 1502, Columbus requested licence to sail on a fourth voyage. Passage to the East, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening the way for the widespread European Age of Discovery, exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions were the first known European contact with the Caribbean and Central and South America. The name ''Christopher Columbus'' is the Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicization of the Latin . Growing up on the coast of Liguria, he went to sea at a young age and traveled widely, as far north as the British Isles and as far south as what is now Ghana. He married Portuguese noblewoman Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, who bore a son, Diego Columbus, Diego, and was based in Lisbon for several years. He later took a Castilian mistress, Beatriz Enríquez de Arana, who bore a son, Ferdinand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Eliot Morison
Samuel Eliot Morison (July 9, 1887 – May 15, 1976) was an American historian noted for his works of maritime history and American history that were both authoritative and popular. He received his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1912, and taught history at the university for 40 years. He won Pulitzer Prizes for ''Admiral of the Ocean Sea'' (1942), a biography of Christopher Columbus, and ''John Paul Jones: A Sailor's Biography'' (1959). In 1942, he was commissioned to write a history of United States naval operations in World War II, which was published in 15 volumes between 1947 and 1962. Morison wrote the popular ''Oxford History of the American People'' (1965), and co-authored the classic textbook ''The Growth of the American Republic'' (1930) with Henry Steele Commager. Over the course of his career, Morison received eleven honorary doctoral degrees, and garnered numerous literary prizes, military honors, and national awards from both foreign countries and the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Henry Lefroy
Sir John Henry Lefroy (28 January 1817 – 11 April 1890) was an English military officer and later colonial administrator who also distinguished himself with his scientific studies of the Earth's magnetism. Biography Lefroy was a son of the Rev. John Henry George Lefroy, of Ewshot House (subsequently Itchel) in Hampshire, England, and his wife, Sophia Cottrell. His sister Anne married the Irish landowner and politician John McClintock, who was created the 1st Baron Rathdonnell in 1868. Lefroy was also a first cousin to Thomas Lefroy (1776-1869), the future Chief Justice of Ireland. Lefroy entered the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich in London in 1831 and became a 2nd lieutenant of the Royal Artillery in 1834. When the British government launched a project under the direction of Edward Sabine to study terrestrial magnetism, he was chosen to set up and supervise the observatory on Saint Helena. He embarked on 25 September 1839, for Saint Helena, and carried out his task thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |