|
Histochemistry And Cell Biology
''Histochemistry and Cell Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of molecular histology and cell biology, publishing original articles dealing with the localization and identification of molecular components, metabolic activities, and cell biological aspects of cells and tissues. The journal covers the development, application, and evaluation of methods and probes that can be used in the entire area of histochemistry and cell biology. The journal is published by Springer Science+Business Media and the official journal of the Society for Histochemistry. Earlier names of the journal are ''Histochemie'' and ''Histochemistry''. The editors-in-chief are Jürgen Roth ( University of Zurich), Takehiko Koji ( University of Nagasaki), Michael Schrader (University of Exeter) and Douglas J. Taatjes (University of Vermont The University of Vermont (UVM), officially the University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, is a Public university, public Land-grant un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Zurich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of theology, law, medicine which go back to 1525, and a new faculty of philosophy. Currently, the university has seven faculties: Philosophy, Human Medicine, Economic Sciences, Law, Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Theology and Veterinary Medicine. The university offers the widest range of subjects and courses of any Swiss higher education institution. History The University of Zurich was founded on April 29, 1833, when the existing colleges of theology, the ''Carolinum'' founded by Huldrych Zwingli in 1525, law and medicine were merged with a new faculty of Philosophy. It was the first university in Europe to be founded by the state rather than a monarch or church. In the university's early years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
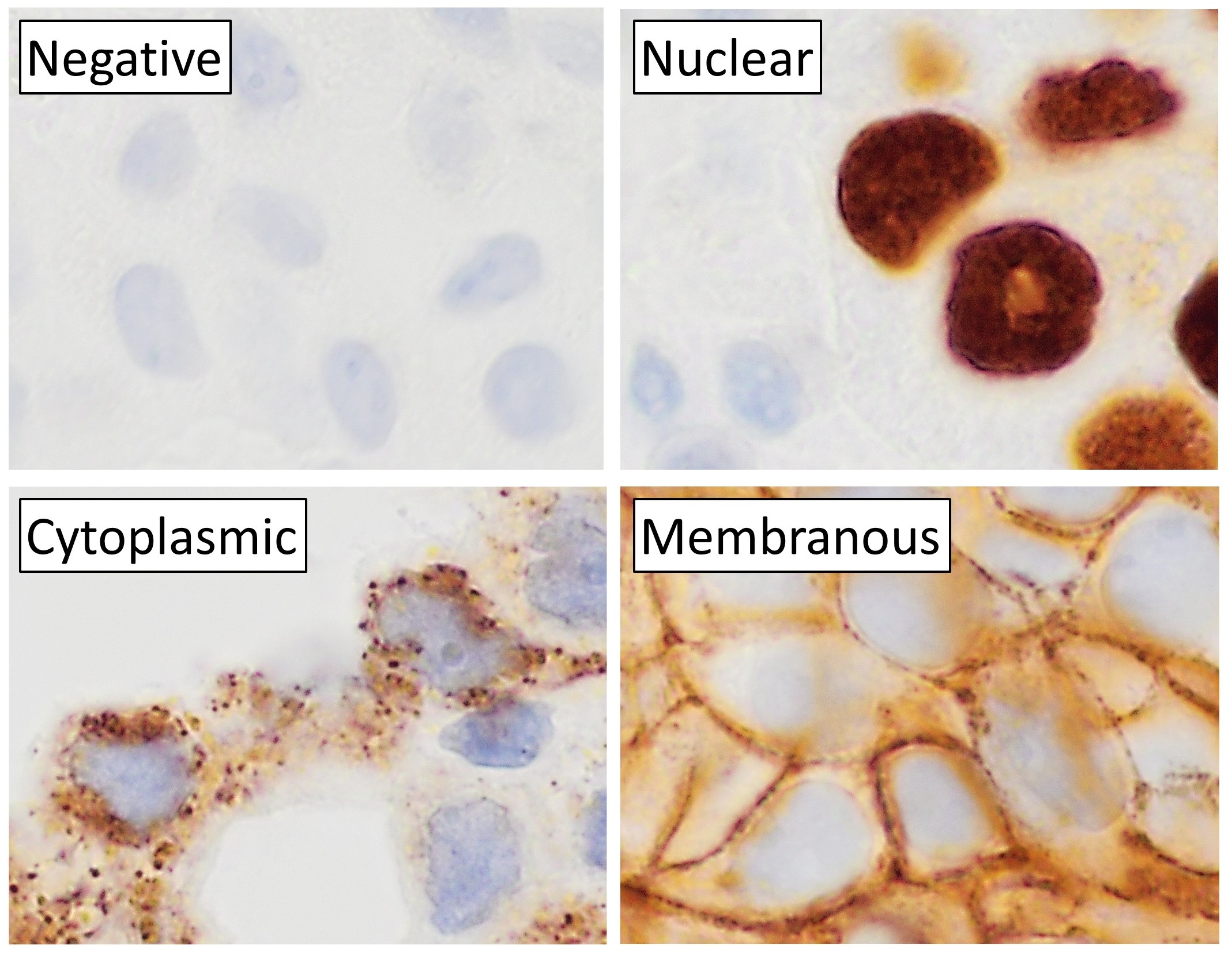
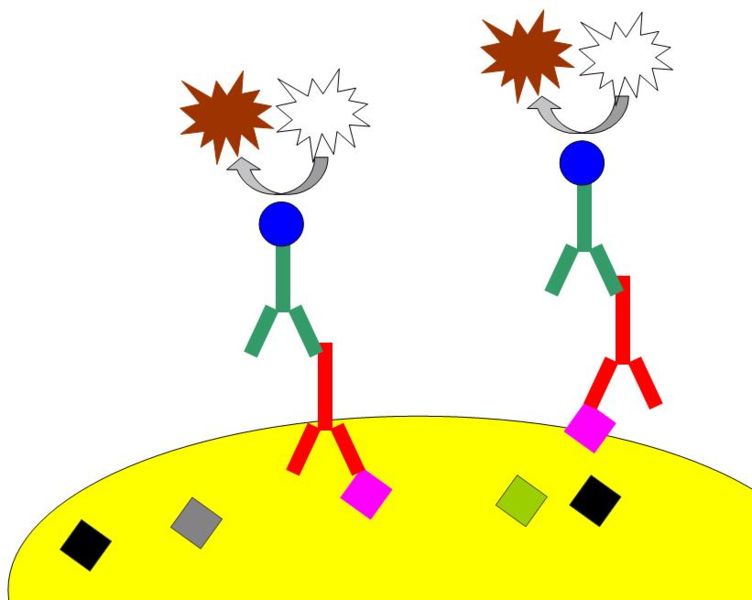
Histochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * ''Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Journals Established In 1958
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and Skills, skill, north of Ancient Athens, Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive Grove (nature), grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular And Cellular Biology Journals
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-language Journals
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Vermont
The University of Vermont (UVM), officially the University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, is a public land-grant research university in Burlington, Vermont. It was founded in 1791 and is among the oldest universities in the United States as it was the fifth institution of higher education established in the New England region of the U.S. northeast. It is listed as one of the original eight " Public Ivy" institutions in the United States and is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". The largest hospital complex in Vermont, the University of Vermont Medical Center, has its primary facility on the UVM campus and is affiliated with the Robert Larner College of Medicine. History The University of Vermont was founded as a private university in 1791, the same year Vermont became the 14th U.S. state. The university enrolled its first students 10 years later. Its first president, The Rev. Daniel C. Sanders, was hired in 1800, and served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light" , established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter) , type = Public , endowment = £49.5 million , budget = £503.1 million , chancellor = Sir Michael Barber , vice_chancellor = Lisa Roberts , head_label = Visitor , head = Charles III '' ex officio'' , city = Exeter, Devon Penryn, Cornwall , country = England , coor = , administrative_staff = 2,647 , faculty = 3,145 (2020) , students = 23,613 (2018/19) , undergrad = 18,932 (2018/19) , postgrad = 4,681 (2018/19) , colours = Green and white , doctoral = , campus = Streatham – Penryn – St Luke's – , affiliations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Nagasaki
is a public university in Sasebo, Nagasaki, Japan. The school was established in 2008 as a result of merger of Siebold University of Nagasaki and Nagasaki Prefectural University. References External links Official website Educational institutions established in 2008 Public universities in Japan University A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ... 2008 establishments in Japan {{nagasaki-university-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Editors-in-chief
An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing editor, or executive editor, but where these titles are held while someone else is editor-in-chief, the editor-in-chief outranks the others. Description The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accountable for delegating tasks to staff members and managing them. The term is often used at newspapers, magazines, yearbooks, and television news programs. The editor-in-chief is commonly the link between the publisher or proprietor and the editorial staff. The term is also applied to academic journals, where the editor-in-chief gives the ultimate decision whether a submitted manuscript will be published. This decision is made by the editor-in-chief after seeking input from reviewers selected on the basis of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * ''Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |