|
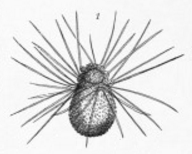
Hirsutospirellidae
The Hirsutospirellidae, established for the Late Triassic genus '' Hirsutospirella'', are a family of Foraminifera within the Involutinida that produced calcareous tests Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to: * Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities Arts and entertainment * ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film * ''Test'' (2014 film) ... with a proloculus followed by an undivided trochospirally enrolled tubular second chamber, in which the spiral side has prominent spinelike protrusions and umbilical side has a shallow umbilical filling. Loeblich & Tappan, 1988 in GSI e-book References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involutinida
Involutinida is an order of foraminifera included in the Spirillinata found in the fossil record from the early Permian to early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). Diagnosis The Involutinida are characterized by a two chambered aragonite, aragonitic Test (biology), test consisting of an initial spheroidal chamber, or proloculus, enclosed by a tubular second, or main chamber. The test wall may be bilamellar (two layered), the inner layer being microgranular and often dark, the outer hyaline (clear, glassy). Coiling may be planispiral or trochospiral, forming a cone. Lamellar thickenings or pillar-like structures may be found in the umbilical region on one or both sides.Alfred R. Loeblich Jr & Helen Tappan,1988. Forminiferal Genera and their Classification. Van Nostrand Reinhold. Taxonomy Four families are included in Involutinida, three of which, the Involutinidae, Hirsutospirellidae, and Planispirillinidae all have undivided tubular second chambers. The fourth, the Ventrolaminidae ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic geological period, Period. It has the rank of an age (geology), age (geochronology) or stage (stratigraphy), stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227.3 to Mya (unit), million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Johann August Georg Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar, Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of ''Klamathites, Klamathites macrolobatus'' and ''Stikinoceras, Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of ''Metapolygnathus, Metapolygnathus communisti'' and ''Metapolygnathus, Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appeara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters ( synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons ( thecae or loricas), which are in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retaria
Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa Cercozoa (now synonymised with Filosa) is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by phylogeny, molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or Ubiqu .... References External links Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith Rhizaria phyla Rhizaria taxa {{Retaria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and ''Textularia'' in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic, with different sized species playing a role within the macrobenthos, meiobenthos, and Benthos, microbenthos), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirillinata
The Spirillinata are a group of Foraminifera Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell bio ... established by Maslakova, 1990, for spirally wound forms, where the Foraminifera are regarded as a phylum. Two subclasses are included, the agglutinated Ammodiscana and the calcareous Spirillinana. Tests of the Spirillinata consist typically of a proloculus followed by an undivided planospirally or trochospirally wound tubular chamber such that the test is either planar or conical. Some however are pseudochambered as the result of constrictions of the test wall or by short septula (incomplete septa). The two orders are distinguished by their composition. The Ammodiscana are composed of fine agglutinated matter. The Spirillinana, in the original sense, are composed of an optically sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', ''Herrerasaurus'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test (biology)
In biology, a test is the hard Seashell, shell of some spherical aquatic animals and protists, notably sea urchins and microorganisms such as testate foraminiferans, radiolarians, and testate amoebae. The term is also applied to the covering of scale insects. The related Latin term testa (botany), testa is used for the outer layer of the hard seed coat of plant seeds. Etymology The anatomical term "test" derives from the Latin word ''wikt:testa#Latin, testa'', which refers to an earthenware object, for example, a piece of pottery, a tile, or a potshard, and by extension, the mollusc shell, shell of a mollusc or a skull. Structure The test is a skeletal structure, made of hard material such as calcium carbonate, silica, chitin or composite materials. As such, it allows the protection of the internal organs and the attachment of soft flesh. The structure is notable for its Ambulacral, ambulacra, alternating in wide and narrow patterns. Small serrations, bumps, ridges or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |