|
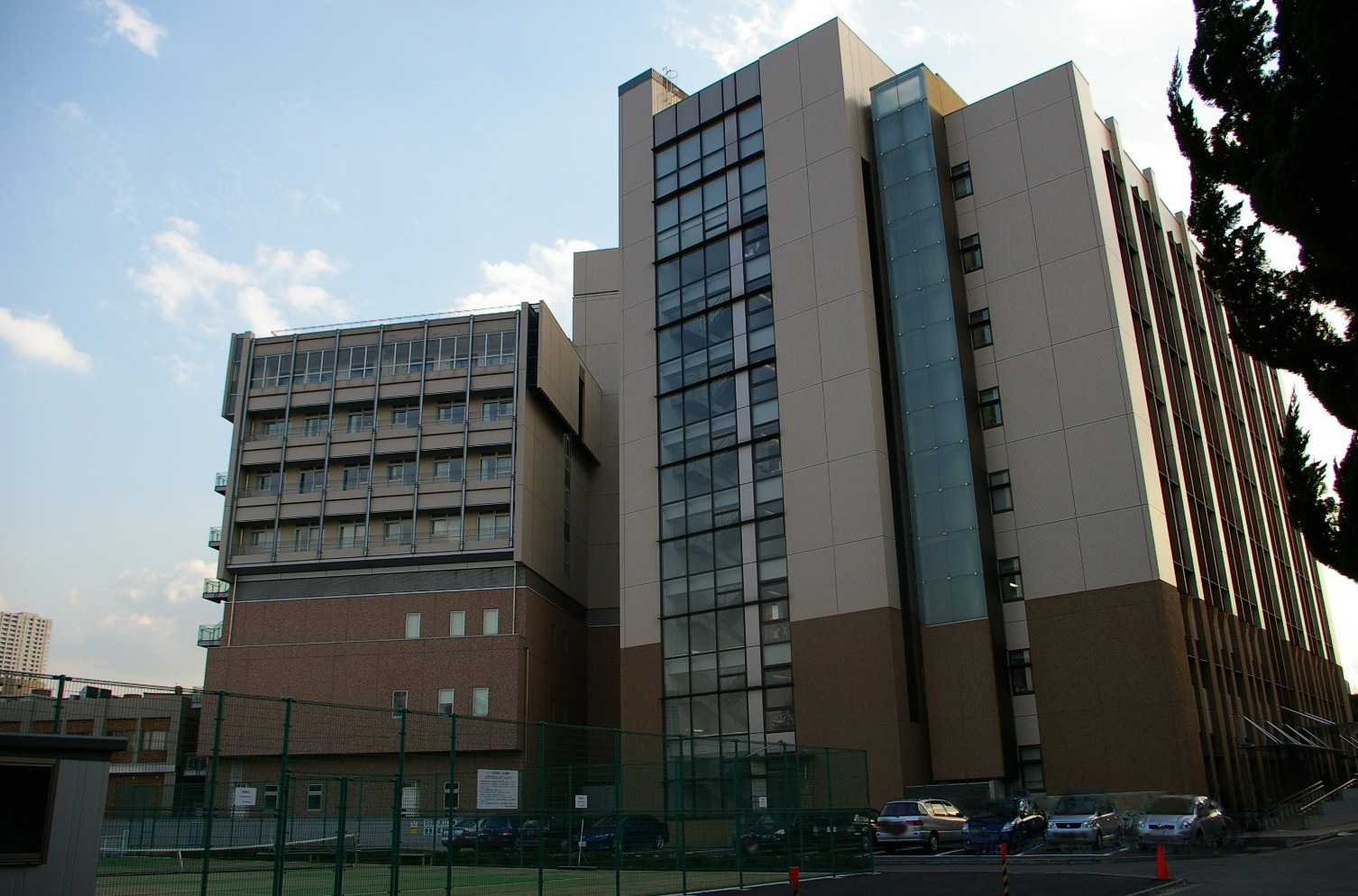
Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center
The Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center, also known as Hiroshima Synchrotron Orbital Radiation (HiSOR), at Hiroshima University is a national user research facility in Japan. It was founded in 1996 by the University Science Council at Hiroshima University initially as a combined educational and research facility before opening to users in Japan and across the world in 2002. It is the only synchrotron radiation experimental facility located at a national university in Japan. The HiSOR experimental hall contains two undulators that produce light in the ultraviolet to soft x-ray range. A total of 16 beamlines are supported by bending magnet and undulator radiation for use in basic studies of life sciences and physical sciences, especially solid-state physics. History Development began with an exploratory committee formed in 1982, which gathered input from Hiroshima University, local agencies, and prefectural agencies. Between 1986 and 1988, several proposals and budget requests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiroshima University
is a Japanese national research university located in Higashihiroshima and Hiroshima, Japan. Established in 1929, it was chartered as a university in 1949 following the merge of a number of national educational institutions. Its abbreviated form is Hirodai. History Under the National School Establishment Law, Hiroshima University was established on May 31, 1949. After World War II, the school system in Japan was entirely reformed and each of the institutions of higher education under the pre-war system was reorganized. As a general rule, one national university was established in each prefecture, and Hiroshima University became a national university under the new system by combining the pre-war higher educational institutions in Hiroshima Prefecture. The following eight schools were integrated or merged into Hiroshima University under the new system of education. * Hiroshima University of Literature and Science * Hiroshima Higher Normal School * Hiroshima Women's Higher Norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. Along with solid-state chemistry, it also has direct applications in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and Elasticity (physics), elasticity), Heat conduction, thermal, Electrical conduction, electrical, Magnetism, magnetic and Crystal optics, optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
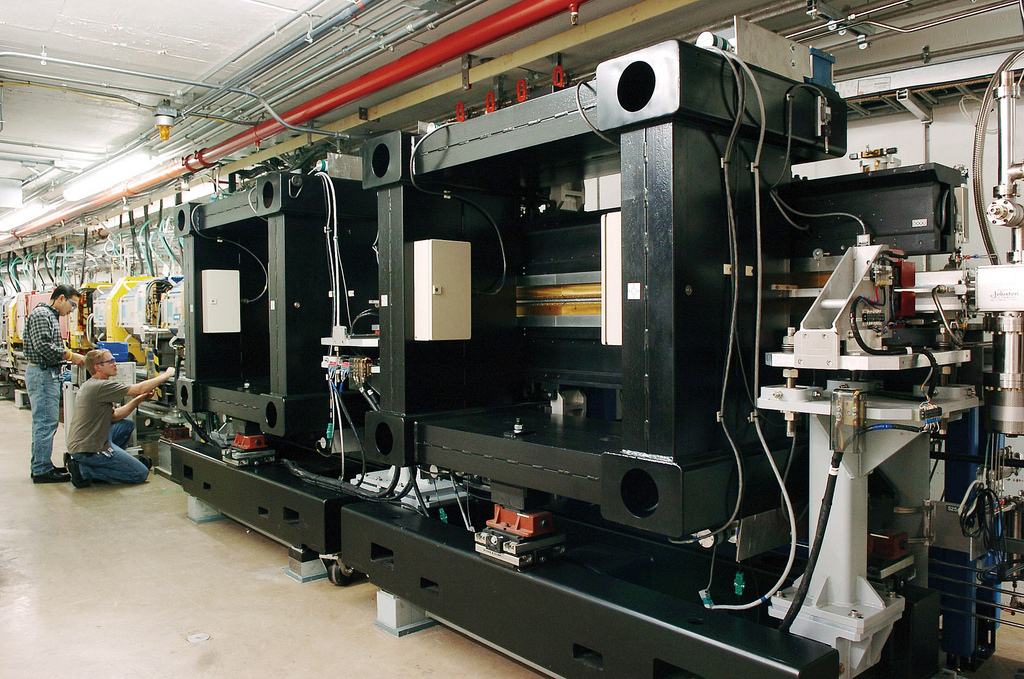
Insertion Device
An insertion device (ID) is a component in modern synchrotron light sources, so called because they are "inserted" into accelerator tracks. They are periodic magnetic structures that stimulate highly brilliant, forward-directed synchrotron radiation emission by forcing a stored charged particle beam to perform wiggles, or undulations, as they pass through the device. This motion is caused by the Lorentz force, and it is from this oscillatory motion that we get the names for the two classes of device, which are known as wigglers and undulators. As well as creating a brighter light, some insertion devices enable tuning of the light so that different frequencies can be generated for different applications. History The theory behind undulators was developed by Vitaly Ginzburg in the USSR. However it was Motz and his team who in 1953 installed the first undulator in a linac at Stanford, using it to generate millimetre wave radiation through to visible light. It was not until the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Radiation Center
The Synchrotron Radiation Center (SRC), located in Stoughton, Wisconsin, Stoughton, Wisconsin and operated by the University of Wisconsin–Madison, was a national synchrotron light source research facility, operating the Aladdin storage ring. From 1968 to 1987 SRC was the home of Tantalus, the first storage ring dedicated to the production of synchrotron radiation. History The Road to SRC: 1953–1968 15 universities formed the Midwest Universities Research Association (MURA) in 1953 to promote and design a high energy proton synchrotron, to be built in the Midwestern United States, Midwest. With the intent of constructing a large accelerator, MURA purchased a suitable area of land with an underlying flat limestone base near Stoughton, Wisconsin, about from the Madison, Wisconsin, Madison campus of the University of Wisconsin. MURA's first accelerator was a 45 MeV synchrotron, built in a concrete underground "vault", mostly for radiation protection purposes. A small elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumitomo Heavy Industries
(SHI) is an integrated manufacturer of industrial machinery, defence products, ships, bridges and steel structure, equipment for environmental protection, including recycling, power transmission equipment, plastic molding machines, laser processing systems, particle accelerators, material handling systems, cancer diagnostic and treatment equipment and others. History In 1888, a company was formed to provide equipment repair services to the Besshi copper mine. Almost 50 years later, in 1934, the company incorporated as Sumitomo Machinery Co., Ltd. to manufacture machinery for the steel and transportation industries in support of that period of rapid economic growth. In 1969, Sumitomo Machinery Co., Ltd. merged with Uraga Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. to create Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd. The company continues to innovate and expand to meet the demands of the new market frontiers. Today, Sumitomo Heavy Industries manufactures injection molding machines, laser systems, semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtron
A microtron is a type of particle accelerator concept originating from the cyclotron in which the accelerating field is not applied through large D-shaped electrodes, but through a linear accelerator structure. The classic microtron was invented by Vladimir Veksler around 1944. The kinetic energy of the particles is increased by a constant amount per field change (one half or a whole revolution). Microtrons are designed to operate at constant field frequency and magnetic field in the ultrarelativistic limit. Thus they are especially suited for very light elementary particles, namely electrons. In a microtron, due to the electrons' increasing momentum, the particle paths are different for each pass. The time needed for that is proportional to the pass number. The slow electrons need one electric field oscillation, the faster electrons need an integer multiple of this oscillation. Racetrack microtron A racetrack microtron is a larger-scale microtron which uses two electromagnets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscience
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okayama University
is a national university in Japan. The main campus is located in Tsushima-Naka, Okayama, Okayama Prefecture. The school was founded in 1870 and it was established as a university in 1949. In 2014, the university was selected as one of the 37 Top Global Universities by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). History Okayama University was originally founded as the in 1870 by Okayama-Han. After the abolition of the han system, it became the in 1880. In 1888 it was merged into a national school, to constitute the Medical Faculty. The Medical Faculty became an independent school in 1901 and was renamed , a four-year medical school for men ages 17–21 or above. In 1922, the school was chartered as , a four-year medical college for men ages 19–23 or above. In 1949, after World War II, the college was merged with other national and public colleges in Okayama Prefecture to establish Okayama University, under Japan's new education sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPring-8
SPring-8 (an acronym of Super Photon Ring – 8 GeV) is a synchrotron radiation facility located in Sayo Town, Sayo District, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, which is the main facility of Harima Science Garden City. It was developed jointly by RIKEN and the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, and is owned and managed by RIKEN, and run under commission by the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute. The machine consists of a storage ring containing an 8 GeV electron beam. On its path around the storage ring, the beam passes through insertion devices to produce synchrotron radiation with energies ranging from soft X-rays (300 eV) up to hard X-rays (300 keV). The synchrotron radiation produced at SPring-8 is used for materials analysis and biochemical protein characterization by many Japanese manufacturers and universities. Together with the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory and the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source at Cornell University in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Education Of Japan
The , also known as MEXT, is one of the eleven ministries of Japan that compose part of the executive branch of the government of Japan. History The Meiji government created the first Ministry of Education in 1871. In January 2001, the former Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture and the former merged to become the present MEXT. Organization The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology currently is led by the minister of education, culture, sports, science and technology. Under that position is two state ministers, two parliamentary vice-ministers, and administrative vice-minister, and two deputy ministers. Beyond that the organization is divided as follows. Minister's Secretariat The Minister's Secretariat is the department that manages general policies that affect the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology as a whole. These functions include many administrative jobs such as auditing policies, community relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Sciences
Physical science is a branch of natural science that studies non-living systems, in contrast to life science. It in turn has many branches, each referred to as a "physical science", together is called the "physical sciences". Definition Physical science can be described as all of the following: * A branch of science (a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe)."... modern science is a discovery as well as an invention. It was a discovery that nature generally acts regularly enough to be described by laws and even by mathematics; and required invention to devise the techniques, abstractions, apparatus, and organization for exhibiting the regularities and securing their law-like descriptions." —p.vii, J. L. Heilbron, (2003, editor-in-chief). ''The Oxford Companion to the History of Modern Science''. New York: Oxford University Press. . * A branch of natural science – nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |