|
Hippias (son Of Pisistratus)
Hippias (; 490 BC) was the last tyrant of Athens, ruling from 527 to 510 BC. He was one of the Peisistratids, a group of tyrants from the same family in ancient Greece. His father was Pisistratus, who preceded him as ruler of Athens, while his brother Hipparchus may have ruled jointly with him. Hippias also had an illegitimate son, Hegesistratus, whom he made tyrant of Sigeion. He was deposed when Cleomenes I of Sparta successfully invaded Athens and forced him to flee to the Achaemenid Empire. Early life Hippias was born around 570 BC as the eldest son of Pisistratus, the first tyrant of Athens. When his father was forced to flee to Eretria after insulting Megakles by having intercourse with his daughter in an indecent way, Peisistratos held counsel with his sons. Hippias suggested that they should retake the tyranny, which his father agreed to. Preparations began for which Athens fell to Peisistratos for the third time in 546 BC. Tyrant of Athens Hippias suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemnos
Lemnos ( ) or Limnos ( ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos (regional unit), Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean modern regions of Greece, region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina, Greece, Myrina. At , it is the Greek islands, 8th-largest island of Greece. Geography Lemnos is primarily a flat island, but the western region, particularly the northwest, is rocky and mountainous. At 430 meters above sea level, Mount Skopia is the highest point. The chief towns are Myrina, Greece, Myrina, on the western coast, and Moudros on the eastern shore of a large bay in the middle of the island. Myrina (also called Kastro, meaning "castle") possesses a good harbour. It is the seat of all trade carried on with the mainland. Lemnos also has a 7-hectare desert, the Pachies Ammoudies of Lemnos. Climate The climate in Lemnos is mainly Mediterranean c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleomenes I
Cleomenes I (; Greek Κλεομένης; died c. 490 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from c. 524 to c. 490 BC. One of the most important Spartan kings, Cleomenes was instrumental in organising the Greek resistance against the Persian Empire of Darius, as well as shaping the geopolitical balance of Classical Greece. Herodotus' account Most of the life of Cleomenes is known through the '' Histories'' of Herodotus, an Athenian historian of the second half of the 5th century. He is one the most important characters of books 5 and 6, covering the decades before the Persian Wars. Herodotus' account however contains many mistakes, especially on the chronology of several major events, and is also very biased against Cleomenes. It seems that Herodotus got his information on Cleomenes from his opponents: the descendants of his half-brothers Leonidas and Cleombrotus, as well as those of Demaratus, the other Spartan king who was deposed by Cleomenes in 491.Cartledge, ''Sparta and Lakonia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampsakos
Lampsacus (; ) was an ancient Greek city located in modern day Turkey, strategically situated on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitted in the nearby modern town of Lapseki. Ancient history Originally known as Pityusa or Pityussa (), it was colonized from Phocaea and Miletus. In the 6th century BC Lampsacus was attacked by Miltiades the Elder and Stesagoras, the Athenian tyrants of the nearby Thracian Chersonese. During the 6th and 5th centuries BC, Lampsacus was successively dominated by Lydia, Persia, Athens, and Sparta. The Greek tyrants Hippoclus and later his son Acantides ruled under Darius I. Artaxerxes I assigned it to Themistocles with the expectation that the city supply the Persian king with its famous wine. When Lampsacus joined the Delian League after the battle of Mycale (479 BC), it paid a tribute of twelve talents, a testimony to its wealth; it had a gold co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeantides
Aeantides () is the name of several people in Classical antiquity: * Aeantides, the tyrant of Lampsacus, to whom Hippias gave his daughter Archedice in marriage. * Aeantides, a tragic poet of Alexandria, mentioned as one of the seven poets who formed the Alexandrian Pleiad. He lived in the time of Ptolemy II Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G .... References Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Aeantides People from Lampsacus Ancient Greek tragic poets Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown 3rd-century BC Greek poets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcmaeonidae
The Alcmaeonidae (; , ; Attic: , ) or Alcmaeonids () were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens, a branch of the Neleides who claimed descent from the mythological Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ... Alcmaeon, the great-grandson of Nestor (mythology), Nestor. In the 7th to late 5th centuries BC, the Alcmaeonidae played a significant role in the developments and events that occurred in Athens. Such developments included overthrowing an Athenian tyrant, helping to lay the foundations of Athenian democracy, and having generals for Athens during the Peloponnesian War. The Alcmaeonidae were mentioned frequently throughout Herodotus' ''Histories (Herodotus), The Histories'', and many played a key role in shaping Athens. The first prominent Alcmaeonid was M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panathenaic Games
The Panathenaic Games () were held every four years in Athens in Ancient Greece from 566 BC to the 3rd century AD. These Games incorporated religious festival, ceremony (including prize-giving), athletic competitions, and cultural events hosted within a stadium. History The Panathenaic festival was formed in order to honor the goddess Athena who had become the patron of Athens after having a competition with the god Poseidon where they were to win the favor of the Athenian people by offering the people gifts. The festival would also bring unity among the people of Athens. The attempted assassination of the tyrants Hippias and Hipparchus during the Panathenaea in 514 BC by Harmodius and Aristogeiton was often regarded as the birth of Athenian democracy. As the birthplace of Athena is Lake Tritonis in North Africa, Athenians did not contest North Africans to also participate in the Panathenaic games since they considered them to have a similar culture of that of Hellenists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannicide
Tyrannicide is the killing or assassination of a tyrant or unjust ruler, purportedly for the common good, and usually by one of the tyrant's subjects. Tyrannicide was legally permitted and encouraged in Classical Athens. Often, the term "tyrant" was a justification for political murders by rivals, but in some exceptional cases students of Platonic philosophy risked their lives against tyrants. The killing of Clearchus of Heraclea in 353 BC by a cohort led by his own court philosopher is considered a sincere tyrannicide. A person who carries out a tyrannicide is also called a "tyrannicide". The term originally denoted the action of Harmodius and Aristogeiton, who are often called the Tyrannicides, in killing Hipparchus (brother of Hippias), Hipparchus of Athens in 514 BC. Political theory Tyrannicide can also be a political theory and, as an allegedly Justification (jurisprudence), justified form of the crime of murder, a dilemmatic case in the philosophy of law, and as such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmodius And Aristogeiton
Harmodius (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἁρμόδιος, ''Harmódios'') and Aristogeiton (Ἀριστογείτων, ''Aristogeíton''; both died 514 BC) were two lovers in Classical Athens who became known as the Tyrannicides (τυραννόκτονοι, ''tyrannoktonoi'') for their assassination of Hipparchus (brother of Hippias), Hipparchus, the brother of the tyrant Hippias (tyrant), Hippias, for which they were executed. A few years later, in 510 BC, the Sparta, Spartan king Cleomenes I forced Hippias to go into exile, thereby opening the way to the subsequent democratic reforms of Cleisthenes. The Athenian democrats later celebrated Harmodius and Aristogeiton as national heroes, partially to conceal the role played by Sparta in the removal of the Athenian tyranny. Cleisthenes notably commissioned the Harmodius and Aristogeiton (sculpture), famous statues of the Tyrannicides. Background The two principal historical sources covering Harmodius and Aristogeiton are the ''History of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamnos With Death Of The Tyrant Hipparchus, Syriskos Painter, Athens, 475-470 BC, L 515 - Martin Von Wagner Museum - Würzburg, Germany - DSC05785
A (; plural ) is a type of Pottery of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek vase used to serve and store liquids. have a wide mouth, a foot, and two handles, and were usually made with a lid. The earliest known examples come from archaic Greece, archaic Laconia and Etruria, and they began to be manufactured in Athens in the middle of the fifth century BCE. Attic , often finely decorated, were mostly made for export to Etruria. They are often found in funerary contexts, and may have been purchased specifically for this use; in vase-paintings, they are often shown being used to mix or serve wine, sometimes with a Ladle (spoon), ladle. They were painted in Red-figure pottery, red-figure, in Black-figure pottery, black-figure and using Six's technique, by artists including Oltos, Euphronios, Smikros, Polygnotos (vase painter), Polygnotos, the Berlin Painter and the Kleophrades Painter. Their manufacture ceased around 420 BCE, possibly due to the reduction in trade between Athens an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megacles
Megacles or Megakles () was the name of several notable men of ancient Athens, as well as an officer of Pyrrhus of Epirus. First archon The first Megacles was possibly a legendary archon of Athens from 922 BC to 892 BC. Archon eponymous The second Megacles was a member of the Alcmaeonidae family, and the archon eponymous in 632 BC when Cylon made his unsuccessful attempt to take over Athens. Megacles was convicted of killing Cylon's supporters (who had taken refuge on the Acropolis as suppliants of Athena) and was exiled from the city, along with all the other members of his genos, the Alcmaeonidae. The Alcmaeonidae inherited a '' miasma'' ("stain") that lasted for generations among Megacles' descendants. Alcmaeonidae The third Megacles, the grandson of the above eponymous archon, son of Alcmaeon and member of the Alcmaeonidae family, was an opponent of Pisistratus in the 6th century BC. He drove out Pisistratus during the latter's first reign as tyrant in 560 BC, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
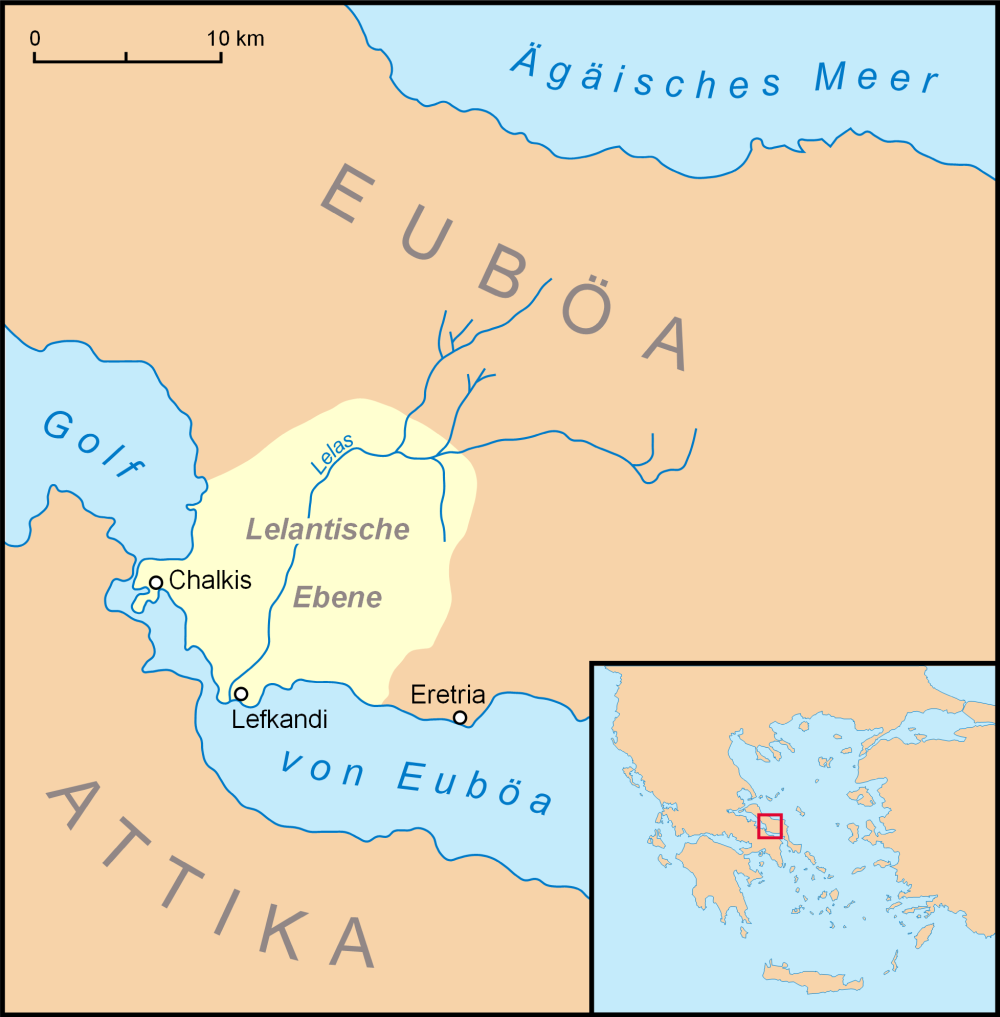
Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain. A granary and several other buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |