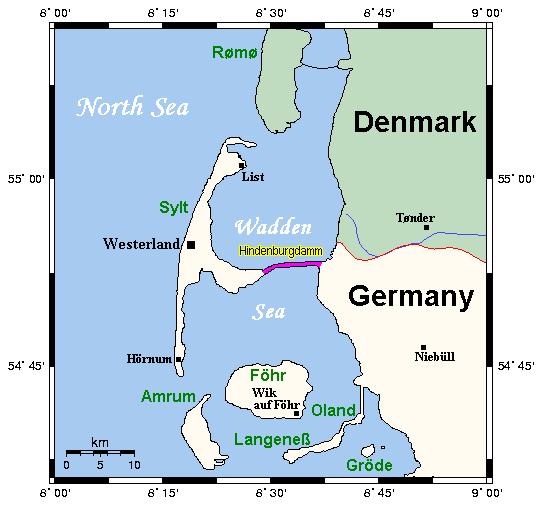
|
Hindenburg Causeway
The Hindenburgdamm or Hindenburg Dam is an 11 km (7 mile) long causeway joining the North Frisian island of Sylt Sylt (; ; Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, with a distinctively shaped shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian Islands and is the largest island in North Fris ... to mainland Schleswig-Holstein. Its coordinates are . It was opened on 1 June 1927 and is exclusively a railway corridor. The companies that built the Hindenburgdamm, a job that took four years, were Philipp Holzmann AG of Frankfurt, working from the mainland, and Peter Fix Söhne of Duisburg working from Sylt. A train trip along the causeway takes about 10 minutes, and the time between the auto terminals at Niebüll on the mainland and Westerland (Schleswig), Westerland on Sylt is about 30 minutes. The Hindenburgdamm is part of the railway line known as the ''Marschbahn'' ("Marsh Railway"), which is Double track ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itzehoe
Itzehoe (; ) is a town in Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. As the capital of the district Steinburg, Itzehoe is located on the Stör, a navigable tributary of the Elbe, 51 km (31.7 mi) northwest of Hamburg and 24 km (14.9 mi) north of Glückstadt. The population is about 32,530. History Itzehoe is one of the oldest towns in Holstein. As early as 810 AD, Charlemagne built the Esesfeld castle in the Oldenburgskuhle, 2 kilometres from the later town, as protection against the Denmark, Danes marauding from the north, but this has no direct connection with the development of Itzehoe. Under its protection, Archbishop Ebbo of Reims built a small monastery or prayer house, the ‘Cella Lila’, in the summer of 823 in what is now Münsterdorf as a base for the Christian mission he initiated in Denmark. The larger Echeho Castle, built around 1000 in the nearby meander of the Stör , River Stör, became the nucleus of a settlement that developed into a trading t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tønder
Tønder (; ) is a town in the Region of Southern Denmark. With a population of 7,477 (as of 1 January 2025), it is the main town and the administrative seat of the Tønder Municipality. History The first mention of Tønder might have been in the mid-12th century, when the Arab geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi mentioned the landmark ''Tu(r)ndira'', which might have been a reference to either Tønder, or the nearby town of Møgeltønder. Tønder was granted port privileges by the Hanseatic League in 1243, making it Denmark's oldest privileged market town. In 1532 it was hit by severe floods, with water levels reaching 1.8 m in St Laurent's church. In the 1550s, Tønder's port lost direct access to the sea due to Levee, dykes being built to the west of town at the direction of Duke John II, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Haderslev, Hans the Elder of Schleswig-Holstein-Haderslev, the son of Frederick I of Denmark. The town centre is dominated by houses from the late 17th and early 18th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husum
Husum (, ) is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of the annual international piano festival ''Raritäten der Klaviermusik'' (Rarities of Piano Music) founded in 1986. History Husum was first mentioned as ''Husembro'' in 1252, when king Abel was murdered. Like most towns on the North Sea, Husum was strongly influenced by storm tides. In 1362 a disastrous storm tide, the " Grote Mandrenke" flooded the town and carved out the inland harbour. Before this date Husum was not situated directly on the coast. The people of the city took advantage of this opportunity and built a marketplace, which led to a great economic upturn. Between 1372 and 1398 the population of Husum grew rapidly, and two villages, ''Oster-Husum'' (East-Husum) and ''Wester-Husum'' (West-Husum), were founded. The name ''Husum'' is first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altona, Hamburg
Altona (), also called Hamburg-Altona, is the westernmost Boroughs and quarters of Hamburg#Boroughs, urban borough (''Bezirk'') of the Germany, German States of Germany, city state of Hamburg. Located on the right bank of the Elbe river, Altona had a population of 270,263 in 2016. From 1640 to 1864, Altona was under the administration of the Denmark, Danish monarchy. Altona was an independent borough until 1937. History Danish period Altona was founded in 1535 as a village of fishermen in what was then Holstein-Pinneberg. In 1640, Altona came under Denmark-Norway, Danish rule as part of Holstein-Glückstadt, and in 1664 was granted town rights, municipal rights by the Danish King Frederik III of Denmark, Frederik III, who then ruled in personal union as Duke of Holstein. Altona was one of the Danish monarchy's most important harbor towns. The railway from Altona to Kiel, the Hamburg-Altona–Kiel railway (), was opened in 1844. Imperial period The wars between Denmark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the north Atlantic Ocean.* * * Metropolitan Denmark, also called "continental Denmark" or "Denmark proper", consists of the northern Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying southwest of Sweden, south of Norway, and north of Germany, with which it shares a short border. Denmark proper is situated between the North Sea to the west and the Baltic Sea to the east.The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. The Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has roughly List of islands of Denmark, 1,400 islands greater than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English. Unlike Holstein and Lauenburg, Schleswig was never a part of the German Confederation. Schleswig was instead a fief of Denmark, and its inhabitants spoke Danish, German, and North Frisian. Both Danish and German National Liberals wanted Schleswig to be part of a Danish or German national state in the 19th century. A German uprising in March 1848 caused the First Schleswig War which ended in 1852. The Second Schleswig War (1864) ended with the three duchies being governed jointly by Austria and Prussia. In 1866, they became a part of Prussia. Name and naming dispute In the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. Prussia formed the German Empire when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by 1932 Prussian coup d'état, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians who were conquered by the Teutonic Knightsan organized Catholic medieval Military order (religious society), military order of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second War Of Schleswig
The Second Schleswig War (; or German Danish War), also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War, was the second military conflict over the Schleswig–Holstein question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 February 1864, when Prussian and Austrian forces crossed the border into the Danish fief Schleswig. Denmark fought troops of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire representing the German Confederation. Like the First Schleswig War (1848–1852), it was fought for control of the duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg. Succession disputes concerning the duchies arose when the Danish king died without an heir acceptable to the German Confederation. The war started after the passing of the History of Schleswig-Holstein#The November Constitution, November Constitution of 1863, which tied the Duchy of Schleswig more closely to the Denmark, Danish kingdom, which was viewed by the German side as a violation of the London Protocol (1852), L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Flats
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal flat ecosystems are as extensive globally as mangroves, covering at least of the Earth's surface. / They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries; they are also seen in freshwater lakes and salty lakes (or inland seas) alike, wherein many rivers and creeks end. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of estuarine silts, clays and aquatic animal detritus. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily. A recent global remote sensing analysis estimated that approximately 50% of the global extent of tidal flats occurs within eight countries (Indonesia, China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudflat Hiking
Mudflat hiking (, , West Frisian: ''Waadrinnen'', ) is a recreation enjoyed in the Netherlands, northwest Germany, Denmark, England and France. Mudflat hikers are people who, with the aid of a tide table, use a period of low water to walk and wade on the watershed of the mudflats, especially from the Frisian mainland coast to the Frisian islands. The Wadden Sea, a belt of the North Sea, is well suited to this traditional practice. Belts of this shallow sea lie off the mainland of the Netherlands, between Friesland and the Frisian Islands; off the coast of northwestern Germany; and off the coast of southwest Jutland in Denmark. In the Netherlands, mudflat hikers can walk from the mainland to Terschelling, Ameland, Engelsmanplaat, Schiermonnikoog, Simonszand, and Rottumeroog. Other mudflat hiking routes are known but are not recommended, either because of their inherent dangers (the correct path is difficult to follow and/or there are insufficient margins of error in timing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadden Sea National Parks
The Wadden Sea National Parks in Denmark, Germany and the Netherlands are located along the German Bight of the North Sea. In Germany and Denmark they also mark the area of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of the Wadden Sea. Divided from each other by administrative borders, they form a single ecological entity. The purpose of the national parks is the protection of the Wadden Sea ecoregion. Denmark * Wadden Sea National Park (Nationalpark Vadehavet), from Blåvandshuk to Rudbøl in Denmark Germany * Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park, comprising the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein and the North Frisian Islands * Hamburg Wadden Sea National Park, extending from the mouth of the Elbe to the tiny islands of Neuwerk and Scharhörn, part of Hamburg * Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park, comprising the northern coast of Lower Saxony and including the East Frisian Islands Netherlands * Lauwersmeer National Park consists of the southern and eastern parts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |