|
Himchari National Park
Himchari National Park ( bn, হিমছড়ি জাতীয় উদ্যান) is a major national park and nature reserve in Bangladesh. The park is located at Ramu and Cox's Bazar Sadar Upazila, Cox's Bazar District, in the southeast region of the country. It is located mainly on the hills and is adjoining to Bay of Bengal to the west. Himchari National Park covers approximately of mixed evergreen forests Biome. It was declared a protected area in 1980. Location It is located 13 km East of Cox's Bazar town. The overall appearance of the forest is various patches of dense forest and grass lands. The climate is generally humid and warm. The park has Tropical monsoon climate, tropical monsoons from June to September every year. The soil is loamy, clay and sandy loam at various places. Administration The entire forest area is managed and is under the jurisdiction of Cox's Bazar South Forest Division. There are four forest beats in the parks namely Kolatoli, Chainda, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cox's Bazar District
Cox's Bazar ( bn, কক্সবাজার জেলা , ''Cox's Bazar Jela'' also ''Cox's Bazar Zila'') is a district in the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh. It is named after Cox's Bazar town. It is located south of Chittagong. Cox's Bazar is also known by the name ''Panowa'' ("yellow flower"). Another old name was ''Palongkee''. The modern Cox's Bazar derives its name from Captain Hiram Cox (died 1799), an army officer who served in British India. It is one of the fishing ports of Bangladesh. At Cox's Bazar is one of the world's longest natural sea beaches ( long including mud flats). Geography Often termed as the world's longest beach, Cox's Bazar is a major tourist destination within Bangladesh. Cox's Bazar District has an area of . It is bounded by Chittagong District on the north, Bay of Bengal in the south, Bandarban District on the east, and the Bay of Bengal on the west. Major rivers include Matamuhuri, Bakkhali, Reju Khal, Naf River, Maheshkhali chann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acronychia Pedunculata
''Acronychia pedunculata'' is a large shrub or small tree of the understory, gaps and fringes of low country and lower hill tropical forests of tropical Asia. Description Leaves: elliptic to suboblong, often with tapered base. Twigs more or less angular, glabrous. Flowers: greenish white; I-acillary, corymbose panicles, about across in inflorescences of wide. Flowering: February–April, July–August. The fruits are cream to brownish yellow drupes, slightly angled, in diameter with a short apiculate tip. Leaves and fruits, and other parts of the plant, contain aromatic oils with a resinous scent. In Sri Lanka, the flowering time is February–April and July–August. Distribution South and Southeast Asia from India & Sri Lanka to South China & Taiwan, Indochina, Malesia & Papua New Guinea. Local names * * * Nepali: Paolay * Assamese: Laojan * Tamil & Malayalam: Mutta-nari Uses Extracts of its leaves, bark, stems and fruits are widely used in herbal medicinal ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
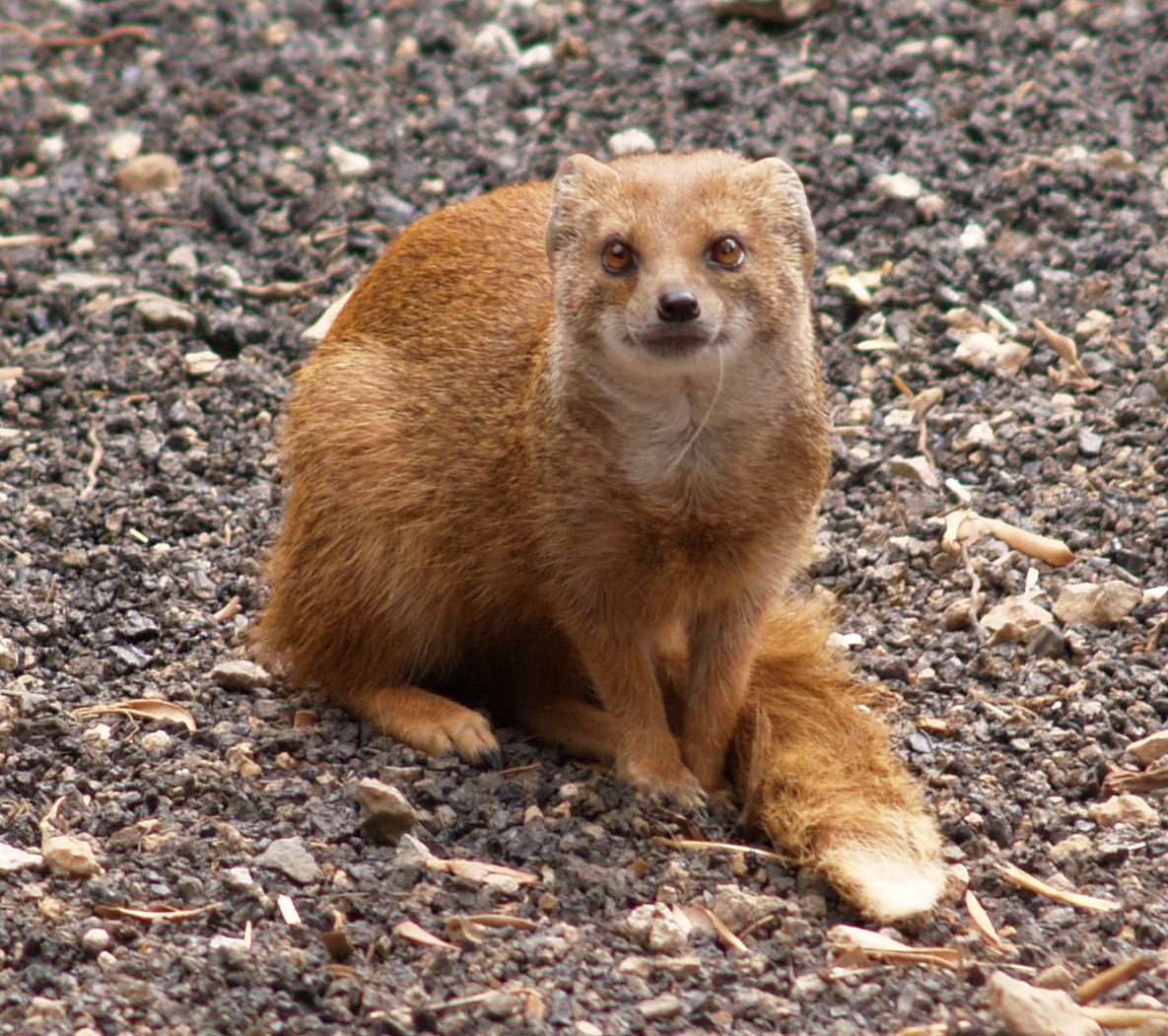
Mongoose
A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to southern Europe, Africa and Asia, whereas the Mungotinae comprises 11 species native to Africa. The Herpestidae originated about in the Early Miocene and genetically diverged into two main genetic lineages between 19.1 and . Etymology The English word "mongoose" used to be spelled "mungoose" in the 18th and 19th centuries. The name is derived from names used in India for ''Herpestes'' species: or in classical Hindi; in Marathi; in Telugu; , and in Kannada. The form of the English name (since 1698) was altered to its "-goose" ending by folk etymology. The plural form is "mongooses". Characteristics Mongooses have long faces and bodies, small, rounded ears, short legs, and long, tapering tails. Most are brindled or grizzly; a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhesus Macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or grey in colour, it is in length with a tail and weighs . It is native to South, Central, and Southeast Asia and has the widest geographic range of all non-human primates, occupying a great diversity of altitudes and a great variety of habitats, from grasslands to arid and forested areas, but also close to human settlements. Feral colonies are found in the United States, thought to be either released by humans or escapees after hurricanes destroyed zoo and wildlife park facilities. The rhesus macaque is diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrial. It is mostly herbivorous, mainly eating fruit, but will also consume seeds, roots, buds, bark, and cereals. Studies show almost 100 different plant species in its diet. Rhesus macaques are gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is now one of the widest-ranging mammals in the world, as well as the most widespread suiform. It has been assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide range, high numbers, and adaptability to a diversity of habitats. It has become an invasive species in part of its introduced range. Wild boars probably originated in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene and outcompeted other suid species as they spread throughout the Old World. , up to 16 subspecies are recognized, which are divided into four regional groupings based on skull height and lacrimal bone length. The species lives in matriarchal societies consisting of interrelated females and their young (both male and female). Fully grown males are usually solita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
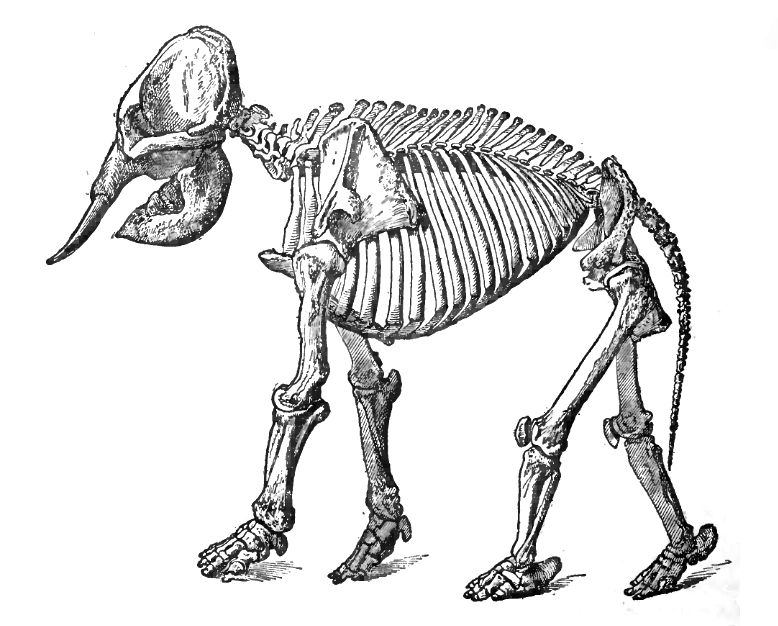
Asian Elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the north, Sumatra in the south, and to Borneo in the east. Three subspecies are recognised—'' E. m. maximus'' from Sri Lanka, ''E. m. indicus'' from mainland Asia and '' E. m. sumatranus'' from the island of Sumatra. Formerly, there was also the Syrian elephant or Western Asiatic elephant (''Elephas maximus asurus'') which was the westernmost population of the Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''). This subspecies became extinct in ancient times. Skeletal remains of ''E. m. asurus'' have been recorded from the Middle East: Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey from periods dating between at least 1800 BC and likely 700 BC. It is one of only three living species of elephants or elephantids anywhere in the world, the others being the Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloth Bear
The sloth bear (''Melursus ursinus'') is a myrmecophagous bear species native to the Indian subcontinent. It feeds on fruits, ants and termites. It is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, mainly because of habitat loss and degradation. It is the only species in the genus ''Melursus''. It has also been called "labiated bear" because of its long lower lip and palate used for sucking up insects. It has a long, shaggy fur, a mane around the face, and long, sickle-shaped claws. It is lankier than brown and Asian black bears. It shares features of insectivorous mammals and evolved during the Pleistocene from the ancestral brown bear through divergent evolution. Sloth bears breed during spring and early summer and give birth near the beginning of winter. When their territories are encroached upon by humans, they sometimes attack them. Historically, humans have drastically reduced these bears' habitat and diminished their population by hunting them for food and products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Black Bear
The Asian black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), also known as the Asiatic black bear, moon bear and white-chested bear, is a medium-sized bear species native to Asia that is largely adapted to an arboreal lifestyle. It lives in the Himalayas, southeastern Iran, the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent, the Korean Peninsula, China, the Russian Far East, the islands of Honshū and Shikoku in Japan, and Taiwan. It is listed as Vulnerable species, vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and is threatened by deforestation and poaching for its body parts, which are used in traditional medicine. Characteristics The Asian black bear has black fur, a light brown muzzle, and a distinct whitish or creamy patch on the chest, which is sometimes V-shaped. Its ears are bell shaped, proportionately longer than those of other bears, and stick out sideways from the head. Its tail is short, around long.#Brown, Brown, ''Bear Anatomy and Physiology'' Adults measure at the shoulder, and in length. Adu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus '' Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. It is territorial and generally a solitary but social predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat to support its requirements for prey and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then become independent, leaving their mother's home range to establish their own. The tiger was first scientifically described in 1758. It once ranged widely from the Eastern Anatolia Region in the west to the Amur River basin in the east, and in the south from the foothills of the Himalayas to Bali in the Sunda Islands. Since the early 20th century, tiger populations have lost at least 93% of their historic range and have been extirpated from Western and Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Cat
The fishing cat (''Prionailurus viverrinus'') is a medium-sized wild cat of South and Southeast Asia. Since 2016, it is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Fishing cat populations are threatened by destruction of wetlands and have declined severely over the last decade. The fishing cat lives foremost in the vicinity of wetlands, along rivers, streams, oxbow lakes, in swamps, and mangroves. The fishing cat is the state animal of West Bengal. Taxonomy ''Felis viverrinus'' was proposed by Edward Turner Bennett in 1833 who described a fishing cat skin from India. '' Prionailurus'' was proposed by Nikolai Severtzov in 1858 as generic name for spotted wild cats native to Asia. ''Felis viverrinus rhizophoreus'' was proposed by Henri Jacob Victor Sody in 1936 who described a specimen from the north coast of West Java that had a slightly shorter skull than fishing cat specimens from Thailand. There is evidence that the nominate taxon and the Javan fishing cat are distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopard Cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely distributed although threatened by habitat loss and hunting in parts of its range. Historically, the leopard cat of continental Asia was considered the same species as the Sunda leopard cat. As of 2017, the latter is recognised as a distinct species, with the taxonomic name ''Prionailurus javanensis''. Leopard cat subspecies differ widely in fur colour, tail length, skull shape and size of carnassials. Archaeological evidence indicates that the leopard cat was the first cat species domesticated in Neolithic China about 5,000 years ago in Shaanxi and Henan Provinces. Characteristics A leopard cat is about the size of a domestic cat, but more slender, with longer legs and well-defined webs between its toes. Its small head is marked with two prominent dark stripes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoolock Gibbon
The hoolock gibbons are three primate species of genus ''Hoolock'' in the gibbon family, Hylobatidae, native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China. Description Hoolocks are the second-largest of the gibbons, after the siamang. They reach a size of 60 to 90 cm and weigh 6 to 9 kg. The sexes are about the same size, but they differ considerably in coloration; males are black-colored with remarkable white brows, while females have a grey-brown fur, which is darker at the chest and neck. White rings around their eyes and mouths give their faces a mask-like appearance. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' says that the name "hoolock" is from "a language of Assam." Distribution In northeast India, the hoolock is found south of Brahmaputra and the North Bank areas and east of the Dibang Rivers. Its range extends into seven states covering Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura (The seven northeastern states of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |