|
Hillel Lichtenstein
Rabbi Hillel Lichtenstein (1814–1891) was a Hungarian rabbi and the leader of hasidic Orthodoxy in Hungary. Life Hillel Lichtenstein was born at Vécs, Hungary (also called Vágvecse; today Veča, part of Šaľa, Slovakia) in 1814 to the dayan R. Baruch Bendit. After studying at the yeshiva of the Chassam Sofer, he married in 1837 the daughter of a well-to-do resident of Galanta, where he remained until 1850, when he was elected rabbi of Margarethen (Szent Margit). In 1854 he was elected rabbi of Klausenburg, but the opposition of the district rabbi, Avrohom Friedman, made it impossible for him to enter upon the duties of the office; finally he was expelled from Klausenburg by the authorities. Having lived for some time at Nagyvárad, he was recalled to Margarethen, where he remained until about 1865, when he was called to Szikszó. Thence he went, in 1867, to Kolomyia, where he remained until his death. He was a prominent leader of Haredi Judaism in Hungary: he not only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
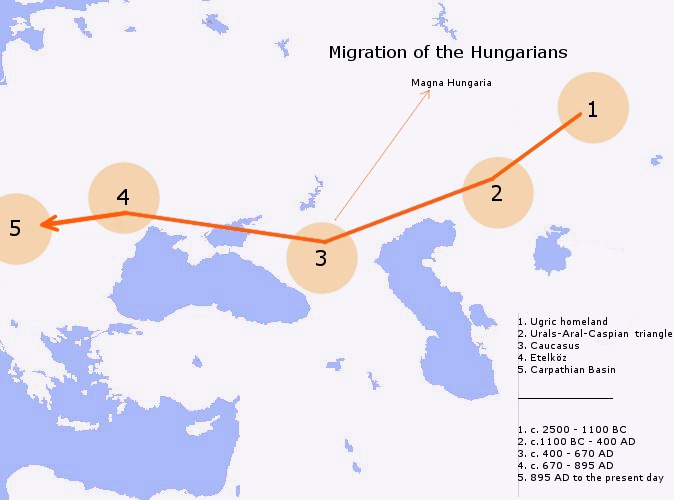
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty and Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. In addition, significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina, and therefore constitute the Hungarian diaspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolog Judaism
Neologs (, "Neolog faction") are one of the two large communal organizations among Hungarian Jewry. Socially, the liberal and modernist Neologs had been more inclined toward integration into Hungarian society since the Era of Emancipation in the 19th century. This was their main feature, and they were largely the representative body of urban, assimilated middle- and upper-class Jews. Religiously, the Neolog rabbinate was influenced primarily by Zecharias Frankel's Positive-Historical School, from which Conservative Judaism evolved as well, although the formal rabbinical leadership had little sway over the largely assimilationist communal establishment and congregants. Their rift with the traditionalist and conservative Orthodox Jews was institutionalized following the 1868–1869 Hungarian Jewish Congress, and they became a separate communal organization. The Neologs remained organizationally independent in those territories ceded under the terms of the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament. The book is an anthology of Hebrew religious hymns. In the Jewish and Western Christian traditions, there are 150 psalms, and several more in the Eastern Christian churches. The book is divided into five sections, each ending with a doxology, a hymn of praise. There are several types of psalms, including hymns or songs of praise, communal and individual laments, royal psalms, imprecation, and individual thanksgivings. The book also includes psalms of communal thanksgiving, wisdom, pilgrimage and other categories. Many of the psalms contain attributions to the name of King David and other Biblical figures including Asaph, the sons of Korah, Moses and Solomon. Davidic authorship of the Psalms is not accepted as historical fact by modern scholars, who view it as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the north; Poland and Slovakia to the west; Hungary, Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and List of cities in Ukraine, largest city, followed by Kharkiv, Odesa, and Dnipro. Ukraine's official language is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. Humans have inhabited Ukraine since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, it was the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion and later became a key centre of East Slavs, East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful realm in Europe in the 10th and 11th centuries, but gradually disintegrated into rival regional powers before being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicia (Central Europe)
Galicia may refer to: Geographic regions * Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain ** Gallaecia, a Roman province ** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia ** The medieval Kingdom of Galicia ** The Republic of Galicia, which only lasted for a few hours on 27 June 1931 * Galicia (Eastern Europe), a historical region in southeastern Poland and western Ukraine ** The Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia or Kingdom of Rus, a medieval kingdom ** The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, a crown land of the Austrian Empire and later the Austrian half (Cisleithania) of Austria-Hungary ** West Galicia or New Galicia, a short-lived administrative region of the Austrian Empire, eventually merged into the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria ** The District of Galicia, part of the Nazi General Government during the World War II occupation of Poland Named after Spanish Galicia * Galicia, Aklan, a barangay in Panay, Philippines * Nuev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolomyia
Kolomyia (, ), formerly known as Kolomea, is a city located on the Prut, Prut River in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast in the west of Ukraine. It serves as the administrative centre of Kolomyia Raion, hosting the administration of Kolomyia urban hromada. The population is The city rests approximately halfway between Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi, in the centre of the historical region of Pokuttia, with which it shares much of its history. Kolomyia is a notable railroad hub, as well as an industrial centre (textiles, shoes, metallurgical plant, machine works, wood and paper industry). It is a centre of Hutsul culture. Until 1925 the town was the most populous town in the region. Before the The Holocaust, Holocaust about half the town’s population was Jews, Jewish. Etymology The city has alternative names for it in other languages: * ; * ; * ; * . According to Ukrainian etymological dictionaries, the name ''Kolomyia'' is a compound word formed from the roots of the noun ''kolo'' ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaim Halberstam
Chaim Halberstam of Sanz (1793–1876) (), known as the ''Divrei Chaim'' after the title of his writings, was the rabbi of Sanz (), and the founding rebbe of the Sanz dynasty of Hasidic Judaism. Life Halberstam was a pupil of Rabbi Sholom Rokeach of Belz,'' Ami Living.'' No. 87. Sep/12/12. p. 44. Rabbi Moshe Yehoshua Heshl Orenstein and Rabbi Naftali Tzvi of Ropshitz. His first rabbinical position was in Rudnik. In 1830 he was appointed as the town rabbi of Sanz, where he founded a Hasidic dynasty. He attracted many followers and students, due to his piety and greatness. Sanz has been succeeded nowadays by the Sanz-Klausenberg, Sanz-Zmigrad, Tshakover (Chokover) Hasidic dynasties, and the Bobov Hasidic dynasties, among others. Family life Halberstam was born in 1793, in Tarnogród, today Poland. His first wife Rochel Feyga was the daughter of Rabbi Boruch Frenkl-Thumim (1760–1828), the rabbi of Lipník nad Bečvou ( ''Leipnik'') and author of the work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanz (Hasidic Dynasty)
Sanz (or Tsanz, ) is a Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic List of Hasidic dynasties, dynasty originating in the city of Sanz (Nowy Sącz) in Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia. The dynasty was founded by the rebbe Rabbi Chaim Halberstam (1793–1876) who was the rabbi of Nowy Sącz and the author of the work ''Divrei Chaim'' by which name he is known as well. Rabbi Chaim was a disciple of Rabbi Naftali Zvi of Ropshitz. He opened his court after the death of Rabbi Asher Yeshaya of Ropshitz (Hasidic dynasty), Ropshitz, son-in-law of Rabbi Naftali Tzvi. After his demise (25 Nisan 5636, 19 April 1876), his six sons and his seven sons-in-law built courtyards with new names in the cities where they served as rabbis, and their chassidim separated, but most of them went to his eldest son, Rabbi Yechezkel Shraga Halberstam of Sieniawa, Shinova. His fourth son, Rabbi Aharon, remained to serve as rabbi and rebbe in Sanz, but he was known as the 'Rav of Kreiz', that is, the rabbi of the province, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebbe
A Rebbe () or Admor () is the spiritual leader in the Hasidic movement, and the personalities of its dynasties.Heilman, Samuel"The Rebbe and the Resurgence of Orthodox Judaism."''Religion and Spirituality (Audio)''. UCTV, 20 Oct 2011. web. 31 Jul 2013. The titles of Rebbe and Admor, which used to be a general honorific even before the beginning of the movement, became, over time, almost exclusively identified with its Tzadikim. Usage Today, ''rebbe'' is used in the following ways: # Rabbi, a teacher of Torah: Yeshiva students or '' cheder'' (elementary school) students, when talking to their teacher, would address him with the honorific ''Rebbe'', as the Yiddish-German equivalent to the Hebrew word ''rabbi'' ( ' ). # Personal mentor and teacher: A person's main Rosh Yeshiva, Yeshiva teacher, or mentor, who teaches him or her Talmud and Torah and gives religious guidance, is referred to as ''rebbe'' (),''Oxford Dictionary of English'', ''Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism () or Hasidic Judaism is a religious movement within Judaism that arose in the 18th century as a Spirituality, spiritual revival movement in contemporary Western Ukraine before spreading rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most of those affiliated with the movement, known as ''hassidim'', reside in Israel and in the United States (mostly Brooklyn and the Hudson Valley). Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members aim to adhere closely both to Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the prewar lifestyle of Eastern European Jews. Many elements of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitzit
''Tzitzit'' ( ''ṣīṣīṯ'', ; plural ''ṣīṣiyyōṯ'', Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazi: '; and Samaritan Hebrew, Samaritan: ') are specially knotted ritual Fringe (trim), fringes, or tassels, worn in antiquity by Israelites and today by observant Jews and Samaritans. are usually attached to the four corners of the ''tallit gadol'' (prayer shawl), usually referred to simply as a or ; and ''tallit katan'' (everyday undershirt). Through synecdoche, a may be referred to as . Etymology The word may derive from the semitic root, Hebrew root [n-ts-h]. shares this root with the Hebrew for 'lock of hair'. For example, in the Book of Ezekiel an angel grabs the prophet "by the of [his] head;" he could be said to be "dragged by his hair." A popular etymological interpretation of derives from another word which shares this root. ( 'budding flower') may once have referred to floral ornamentation on clothing. One can hear distinct similarities with contemporaneous Akkadian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen
Kohen (, ; , ، Arabic كاهن , Kahen) is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic Priest#Judaism, priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. They are traditionally believed, and halakha, halakhically required, to be of direct Patrilineality, patrilineal descent from the biblical Aaron (also ''Aharon''), brother of Moses, and thus belong to the Tribe of Levi. During the existence of the Temple in Jerusalem (and previously the Tabernacle), ''kohanim'' performed the Temple korban, sacrificial offerings, which were only permitted to be offered by them. Following Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), its destruction, it seems that most of them joined the Synagogal Judaism, Synagogal Jewish movement before adopting gradually Rabbinic Judaism, other types of Judaism, List of converts to Christianity from Judaism, Christianity or List of converts to Islam from Judaism, Islam. Today, ''kohanim'' retain a lesser though distinct status within Rabbinic Judaism, Rabbinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |