|
High Pressure Electrolysis
High-pressure electrolysis (HPE) is the electrolysis of water by decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to the passing of an electric current through the water. The difference with a standard proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzer is the compressed hydrogen output around at 70 °C. By pressurising the hydrogen in the electrolyser the need for an external hydrogen compressor is eliminated, the average energy consumption for internal differential pressure compression is around 3%. Approaches As the required compression power for water is less than that for hydrogen-gas the water is pumped up to a high-pressure, in the other approach differential pressure is used. There is also an importance for the electrolyser stacks to be able to accept a fluctuating electrical input, such as that found with renewable energy. This then enables the ability to help with grid balancing and energy storage. Ultrahigh-pressure electrolysis Ultrahigh-pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-pressure PEM Electrolyser Stacks
In science and engineering the study of high pressure examines its effects on materials and the design and construction of devices, such as a diamond anvil cell, which can create high pressure. ''High pressure'' usually means pressures of thousands (kiloBar (unit), bars) or millions (megabars) of times atmospheric pressure (about 1 bar or 100,000 Pa). History and overview Percy Williams Bridgman received a Nobel Prize in 1946 for advancing this area of physics by two magnitudes of pressure (400 MPa to 40 GPa). The list of founding fathers of this field includes also the names of Harry George Drickamer, Tracy Hall, Francis P. Bundy, , and . It was by applying high pressure as well as high temperature to carbon that synthetic synthetic diamond, diamonds were first produced alongside many other interesting discoveries. Almost any material when subjected to high pressure will compact itself into a denser form, for example, quartz (also called silica or silicon dioxide) will first adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Purity
Hydrogen purification is any technology used to purify hydrogen. The impurities in hydrogen gas depend on the source of the H2, e.g., petroleum, coal, electrolysis, etc. The required purity is determined by the application of the hydrogen gas. For example, ultra-high purified hydrogen is needed for applications like proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Purification technologies Low temperature methods The default large-scale purification of H2 produced in oil refineries exploits its very low boiling point of −253 °C. Most impurities have boiling points well above this temperature. Low temperature methods can be complemented by scrubbing to remove particular impurities. Palladium membrane hydrogen purifiers Hydrogen can be purified by passing through a membrane composed of palladium and silver. Permeability of the former to hydrogen was discovered back in the 1860s. An alloy with a ca. 3:1 ratio for Pd:Ag is more structural robust than pure Pd, which is the active compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
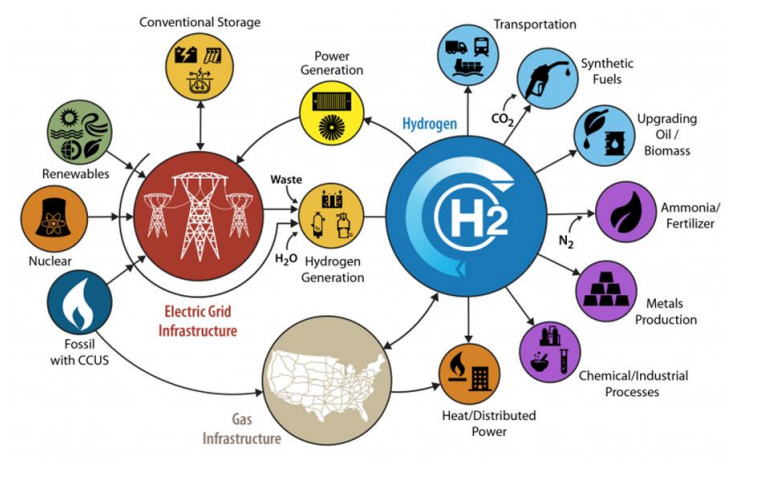
Hydrogen Technologies
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses. Some hydrogen technologies are carbon neutral and could have a role in preventing climate change and a possible future hydrogen economy. Hydrogen is a chemical widely used in various applications including ammonia production, oil refining and energy. The most common methods for producing hydrogen on an industrial scale are: Steam reforming, oil reforming, coal gasification, water electrolysis. Hydrogen is not a primary energy source, because it is not naturally occurring as a fuel. It is, however, widely regarded as an ideal energy storage medium, due to the ease with which electricity can convert water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis and can be converted back to electrical power using a fuel cell or hydrogen turbine. There are a wide number of different types of fuel and electrolysis ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Electrolysis
High-temperature electrolysis (also HTE or steam electrolysis, or HTSE) is a technology for producing hydrogen from water at high temperatures or other products, such as iron or carbon nanomaterials, as higher energy lowers needed electricity to split molecules and opens up new, potentially better electrolytes like molten salts or hydroxides. Unlike electrolysis at room temperature, HTE operates at elevated temperature ranges depending on the thermal capacity of the material. Because of the detrimental effects of burning fossil fuels on humans and the environment, HTE has become a necessary alternative and efficient method by which hydrogen can be prepared on a large scale and used as fuel. The vision of HTE is to move towards decarbonization in all economic sectors. The material requirements for this process are: the heat source, the electrodes, the electrolyte, the electrolyzer membrane, and the source of electricity. Principle The process utilizes energy (in the form of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Engineering
Electrochemical engineering is the branch of chemical engineering dealing with the technological applications of electrochemical phenomena, such as electrosynthesis of chemicals, electrowinning and refining of metals, flow batteries and fuel cells, surface modification by electrodeposition, electrochemical separations and corrosion. According to the IUPAC, the term ''electrochemical engineering'' is reserved for electricity-intensive processes for industrial or energy storage applications and should not be confused with ''applied electrochemistry'', which comprises small batteries, amperometric sensors, microfluidic devices, microelectrodes, solid-state devices, voltammetry at disc electrodes, etc. More than 6% of the electricity is consumed by large-scale electrochemical operations in the US. Scope Electrochemical engineering combines the study of heterogeneous charge transfer at electrode/electrolyte interphases with the development of practical materials and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Fuel Cell
A regenerative fuel cell or reverse fuel cell (RFC) is a fuel cell A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ... run in reverse mode, which consumes electricity and chemical B to produce chemical A. By definition, the process of any fuel cell could be reversed. However, a given device is usually optimized for operating in one mode and may not be built in such a way that it can be operated backwards. Standard fuel cells operated backwards generally do not make very efficient systems unless they are purpose-built to do so as with high-pressure electrolysers, regenerative fuel cells, solid-oxide electrolyser cells and unitized regenerative fuel cells. Process description A hydrogen fueled proton-exchange membrane fuel cell, for example, uses hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen (O2) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEM Electrolysis
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis is the electrolysis of water in a cell equipped with a solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) that is responsible for the conduction of protons, separation of product gases, and electrical insulation of the electrodes. The PEM electrolyzer was introduced to overcome the issues of partial load, low current density, and low pressure operation currently plaguing the alkaline electrolyzer. It involves a proton-exchange membrane. Electrolysis of water is an important technology for the production of hydrogen to be used as an energy carrier. With fast dynamic response times, large operational ranges, and high efficiencies, water electrolysis is a promising technology for energy storage coupled with renewable energy sources. In terms of sustainability and environmental impact, PEM electrolysis is considered as a promising technique for high purity and efficient hydrogen production since it emits only oxygen as a by-product without any carbon emissions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-pressure Hydrogen Energy Generator
In science and engineering the study of high pressure examines its effects on materials and the design and construction of devices, such as a diamond anvil cell, which can create high pressure. ''High pressure'' usually means pressures of thousands (kilobars) or millions (megabars) of times atmospheric pressure (about 1 bar or 100,000 Pa). History and overview Percy Williams Bridgman received a Nobel Prize in 1946 for advancing this area of physics by two magnitudes of pressure (400 MPa to 40 GPa). The list of founding fathers of this field includes also the names of Harry George Drickamer, Tracy Hall, Francis P. Bundy, , and . It was by applying high pressure as well as high temperature to carbon that synthetic diamonds were first produced alongside many other interesting discoveries. Almost any material when subjected to high pressure will compact itself into a denser form, for example, quartz (also called silica or silicon dioxide) will first adopt a denser form known as coesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline Gallon Equivalent
Gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) or gasoline-equivalent gallon (GEG) is the amount of an alternative fuel it takes to equal the energy content of one liquid gallon of gasoline. GGE allows consumers to compare the energy content of competing fuels against a commonly known fuel, namely gasoline. It is difficult to compare the cost of gasoline with other fuels if they are sold in different units and physical forms. GGE attempts to solve this. One GGE of CNG and one GGE of electricity have exactly the same energy content as one gallon of gasoline. In this way, GGE provides a direct comparison of gasoline with alternative fuels, including those sold as a gas (natural gas, propane, hydrogen) and as metered electricity. Definition In 1994, the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defined "gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) s5.660 pounds of natural gas." Compressed natural gas (CNG), for example, is a gas rather than a liquid. It can be measured by its volume in sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and energy production, the research and development of nuclear power, the military's nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the secretary of energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current secretary of energy is Chris Wright, who has served in the position since February 2025. The department's headquarters are in sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Safety
Hydrogen safety covers the safe production, handling and use of hydrogen, particularly hydrogen gas fuel and liquid hydrogen. Hydrogen possesses the NFPA 704's highest rating of four on the flammability scale because it is flammable when mixed even in small amounts with ordinary air. Ignition can occur at a volumetric ratio of hydrogen to air as low as 4% due to the oxygen in the air and the simplicity and chemical properties of the reaction. However, hydrogen has no rating for innate hazard for reactivity or toxicity. The storage and use of hydrogen poses unique challenges due to its ease of leaking as a gaseous fuel, low-energy ignition, wide range of combustible fuel-air mixtures, buoyancy, and its ability to embrittle metals that must be accounted for to ensure safe operation. Liquid hydrogen poses additional challenges due to its increased density and the extremely low temperatures needed to keep it in liquid form. Moreover, its demand and use in industry—as rocket fuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Battery (electricity), battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical energy, chemical, gravitational potential energy, gravitational potential, Electric potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic energy, kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide short-term energy storage, while others can endure for much longer. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped. Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Common e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |