High-temperature Electrolysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
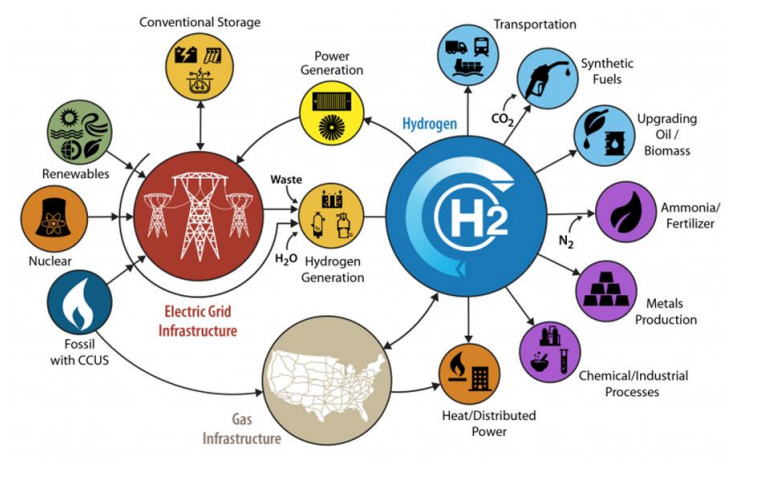 High-temperature electrolysis (also HTE or steam electrolysis, or HTSE) is a technology for producing
High-temperature electrolysis (also HTE or steam electrolysis, or HTSE) is a technology for producing
Overall: 2H2O -> 2H2 + O2
:Cathode: 2H2O ->2H + 2OH^
:Anode: 2OH^ -> H2O + (1/2)O2
 High temperature electrolysis is more efficient economically than traditional room-temperature
High temperature electrolysis is more efficient economically than traditional room-temperature
PDF. Presentation: MARS 2020 Mission and Instruments". November 6, 2014.
U.S. DOE high-temperature electrolysis
 High-temperature electrolysis (also HTE or steam electrolysis, or HTSE) is a technology for producing
High-temperature electrolysis (also HTE or steam electrolysis, or HTSE) is a technology for producing hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
from water at high temperatures or other products, such as iron or carbon nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
, as higher energy lowers needed electricity to split molecules and opens up new, potentially better electrolytes like molten salts or hydroxides. Unlike electrolysis at room temperature, HTE operates at elevated temperature ranges depending on the thermal capacity of the material. Because of the detrimental effects of burning fossil fuels on humans and the environment, HTE has become a necessary alternative and efficient method by which hydrogen can be prepared on a large scale and used as fuel. The vision of HTE is to move towards decarbonization in all economic sectors. The material requirements for this process are: the heat source, the electrodes, the electrolyte, the electrolyzer membrane, and the source of electricity. Principle
The process utilizes energy (in the form of heat) from sources to convert water into steam, which is then passed into an electrolytic system (made up of two electrodes connected to the source of current, an electrolyte, and a membrane). At high temperatures (over 650 °C in most topologies), the materials used to construct the cells become conductive. Therefore, electrochemical reactions begin to occur, and the cell begins to function once it has reached the proper temperature and electricity is supplied while it is being fed with steam. The steam will eventually split into hydrogen (cathode) and oxygen (anode) according to the equations below: :Efficiency
 High temperature electrolysis is more efficient economically than traditional room-temperature
High temperature electrolysis is more efficient economically than traditional room-temperature electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
because some of the energy is supplied as heat, which is cheaper than electricity, and also because the electrolysis reaction is more efficient at higher temperatures. In fact, at 2500 °C, electrical input is unnecessary because water breaks down to hydrogen and oxygen through thermolysis. Such temperatures are impractical; proposed HTE systems operate between 100 °C and 850 °C.
If one assumes that the electricity used comes from a heat engine
A heat engine is a system that transfers thermal energy to do mechanical or electrical work. While originally conceived in the context of mechanical energy, the concept of the heat engine has been applied to various other kinds of energy, pa ...
, it takes 141.86 megajoules (MJ) of heat energy to produce one kg of hydrogen, for the HTE process itself and for the electricity required. At 100 °C, 350 MJ of thermal energy are required (41% efficient). At 850 °C, 225 MJ are required (64% efficient). Above 850 °C, one begins to exceed the capacity of standard chromium steels to resist corrosion, and it's already no easy matter to design and implement an industrial scale chemical process to operate at such a high temperature point.
Materials
Solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs) are electrochemical devices that function at high temperatures and are used for high-temperature electrolysis. These cells' ingredients ensure that the device will function well both physically and electrochemically at high temperatures. Therefore, the selection of materials for the electrodes and electrolyte in a solid oxide electrolyser cell is essential. One option being investigated for the process usedyttria-stabilized zirconia
Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) is a ceramic in which the cubic crystal structure of zirconium dioxide is made stable at room temperature by an addition of yttrium oxide. These oxides are commonly called "zirconia" ( Zr O2) and "yttria" ( Y2 O3 ...
(YSZ) electrolytes, Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
(Ni)- cermet steam/Hydrogen electrodes, and d Oxide of Lanthanum oxide (La2O3), Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
and Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
oxygen electrodes.
Economic potential
Even with HTE, electrolysis is a fairly inefficient way to store energy. Significant conversion losses of energy occur both in the electrolysis process, and in the conversion of the resulting hydrogen back into power. At current hydrocarbon prices, HTE can not compete withpyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of hydrocarbons as an economical source of hydrogen, which produces carbon dioxide as a by-product.
HTE is of interest as a more efficient route to the production "green" hydrogen, to be used as a carbon neutral
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and Greenhouse gas removal, removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon diox ...
fuel and general energy storage. It may become economical if cheap non-fossil fuel sources of heat (concentrating solar, nuclear, geothermal, waste heat) can be used in conjunction with non-fossil fuel sources of electricity (such as solar, wind, ocean, nuclear).
Possible supplies of cheap high-temperature heat for HTE are all nonchemical, including nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s, concentrating solar thermal collectors, and geothermal sources. HTE has been demonstrated in a laboratory at 108 kilojoules (electric) per gram of hydrogen produced,
but not at a commercial scale.
Advantages and Challenges
Obviously, the most notable advantage of HTE is that it provides an opportunity for which green hydrogen is prepared on a large scale, because it has the potential for zero emissions. The process provides an improved reaction kinetics for the splitting of water molecule. Part of the electricity requirement is replaced with heat, which makes it a bit cheaper because electricity is more expensive than heat.
However, HTE technology suffered limitations due to:
# Above 100 °C, the electrolysis of liquid water requires pressurization, and is therefore limited by the working pressures that can be reasonably attained.
# creating materials that are both chemically and physically stable in conditions of intense oxidation and reduction, as well as high working temperatures.
# chemical and physical stability at low electrical conductivities, high working temperatures, and/or ionic concentrations.
Alternatives
There are hundreds ofthermochemical cycle
In chemistry, thermochemical cycles combine solely heat sources (''thermo'') with ''chemical'' reactions to split water into its hydrogen and oxygen components. The term ''cycle'' is used because aside of water, hydrogen and oxygen, the chemical c ...
s known to use heat to extract hydrogen from water. For instance, the thermochemical sulfur-iodine cycle. Since the electricity generation step has a fairly low efficiency and is eliminated, thermochemical production might reach higher efficiencies than HTE. However, large-scale thermochemical production will require significant advances in materials that can withstand high-temperature, high-pressure, highly corrosive environments.
United States Department of Energy
The DOEOffice of Nuclear Energy
The Office of Nuclear Energy (NE) is an agency of the United States Department of Energy which promotes nuclear power as a resource capable of meeting the energy, environmental, and national security needs of the United States by resolving techni ...
has demonstration projects to test 3 nuclear facilities with high-temperature electrolysis in the United States at:
* Nine Mile Point Nuclear Generating Station
Nine Mile Point Nuclear Station is a nuclear power plant with two nuclear reactors located in the town of Scriba, approximately five miles northeast of Oswego, New York, on the shore of Lake Ontario. The site is also occupied by the James A. ...
in Oswego, NY
* Davis–Besse Nuclear Power Station in Oak Harbor, Ohio
* Prairie Island Nuclear Power Plant in Red Wing, Minnesota
Red Wing is a city in and the county seat of Goodhue County, Minnesota, United States, along the upper Mississippi River. The population was 16,547 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is part of the Minneapolis–Saint Paul metropo ...
Mars ISRU
High temperature electrolysis with solid oxide electrolyser cells was used to produce 5.37 grams of oxygen per hour onMars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
from atmospheric carbon dioxide for the Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment in the NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
Mars 2020
Mars 2020 is a NASA mission that includes the rover ''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'', the now-retired small robotic helicopter ''Ingenuity (helicopter), Ingenuity'', and associated delivery systems, as part of the Mars Exploration Progra ...
Perseverance rover, using zirconia electrolysis devices.The Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE)PDF. Presentation: MARS 2020 Mission and Instruments". November 6, 2014.
See also
*Office of Nuclear Energy
The Office of Nuclear Energy (NE) is an agency of the United States Department of Energy which promotes nuclear power as a resource capable of meeting the energy, environmental, and national security needs of the United States by resolving techni ...
* High-pressure electrolysis
References
U.S. DOE high-temperature electrolysis
Footnotes
{{DEFAULTSORT:High-Temperature Electrolysis Electrolysis Hydrogen production