|
High House Purfleet
High House is the collective name for a group of historic buildings in Purfleet, Thurrock, Essex, which was used as a farm for hundreds of years, with a Grade II listed house and barn, but with the addition of one of the best dovecotes (dove houses) in Southern England, which is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and notable for its nest box array. This property includes the house, coachman's cottage, chaise house, stable, granary, barn, workshop, cart sheds, dovecote, and inner and outer walled gardens. Known by many names in its past, the farm has been called Le Vineyards, because grape vines were grown on one of its south facing slopes. Its current name comes from the fact that it is a house high on the hill, which commands great views over the River Thames. History High House was originally built between 1552 and 1559 by Cecily Long to divide the Manor of West Thurrock, in Essex, equally between her two daughters. First built in timber and later replaced in brick in 1684, evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovecote HHPP Purfleet
A dovecote or dovecot , doocot ( Scots) or columbarium is a structure intended to house pigeons or doves. Dovecotes may be free-standing structures in a variety of shapes, or built into the end of a house or barn. They generally contain pigeonholes for the birds to nest. Pigeons and doves were an important food source historically in the Middle East and Europe and were kept for their eggs and dung. History and geography The oldest dovecotes are thought to have been the fortress-like dovecotes of Upper Egypt and the domed dovecotes of Iran. In these regions the droppings were used by farmers for fertilization. Pigeon droppings were also used for leather tanning and making gunpowder. In some cultures, particularly Medieval Europe, the possession of a dovecote was a symbol of status and power and was consequently regulated by law. Only nobles had this special privilege, known as ''droit de colombier''. Many ancient manors in France and the United Kingdom have a dovecote st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham Royal Ballet
Birmingham Royal Ballet (BRB) is one of the five major ballet companies of the United Kingdom, alongside The Royal Ballet, the English National Ballet, Northern Ballet and Scottish Ballet. Founded as the Sadler's Wells Theatre Ballet, the company was established in 1946 as a sister company to the earlier Sadler's Wells company, which moved to the Royal Opera House that same year, subsequently becoming known as The Royal Ballet. The new company was formed under the direction of John Field and remained at Sadler's Wells for many years, becoming known as the Sadler's Wells Royal Ballet in 1977. It also toured the UK and abroad, before relocating to Birmingham in 1990, where it uses the Birmingham Hippodrome stage when performing in the city. Birmingham Royal Ballet has extensive custom-built facilities, including a suite of dance studios, the ''Jerwood Centre for the Prevention and Treatment of Dance Injuries'' and a studio theatre known as the '' Patrick Centre''. In 1997, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artwork At High House Production Park
A work of art, artwork, art piece, piece of art or art object is an artistic creation of aesthetic value. Except for "work of art", which may be used of any work regarded as art in its widest sense, including works from literature and music, these terms apply principally to tangible, physical forms of visual art: *An example of fine art, such as a painting or sculpture. *Objects in the decorative arts or applied arts that have been designed for aesthetic appeal, as well as any functional purpose, such as a piece of jewellery, many ceramics and much folk art. *An object created for principally or entirely functional, religious or other non-aesthetic reasons which has come to be appreciated as art (often later, or by cultural outsiders). *A non-ephemeral photograph or film. *A work of installation art or conceptual art. Used more broadly, the term is less commonly applied to: *A fine work of architecture or landscape design *A production of live performance, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaign For Drawing
The Big Draw, formerly the Campaign for Drawing, is a British registered charity that promotes drawing and visual literacy. It was founded in 2000 by the Guild of St George, and is now an independent charity. The Big Draw believes that drawing is a universal language that can unite people across generations, backgrounds and borders. It is inspired by the Victorian artist and writer, John Ruskin, whose mission was not to teach people how to draw, but how to see. An arts educational charity, the Campaign demonstrates that drawing is a life skill: an essential tool for learning, expression and invention. Its publications for teachers and other educators provide comprehensive evidence that drawing supports formal and informal learning. The charity leads a programme of advocacy, empowerment and engagement, and is the driving force behind The Big Draw Festival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Barn At HHPP
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tony Hall, Baron Hall Of Birkenhead
Anthony William Hall, Baron Hall of Birkenhead, (born 3 March 1951) is a British life peer. He was Director-General of the BBC between April 2013 and August 2020, and chaired the board of trustees of the National Gallery from September 2020 Board of Trustees, National Gallery Retrieved 1 September 2020 to May 2021. Hall was Director of News at the between 1993 and 2001, and of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
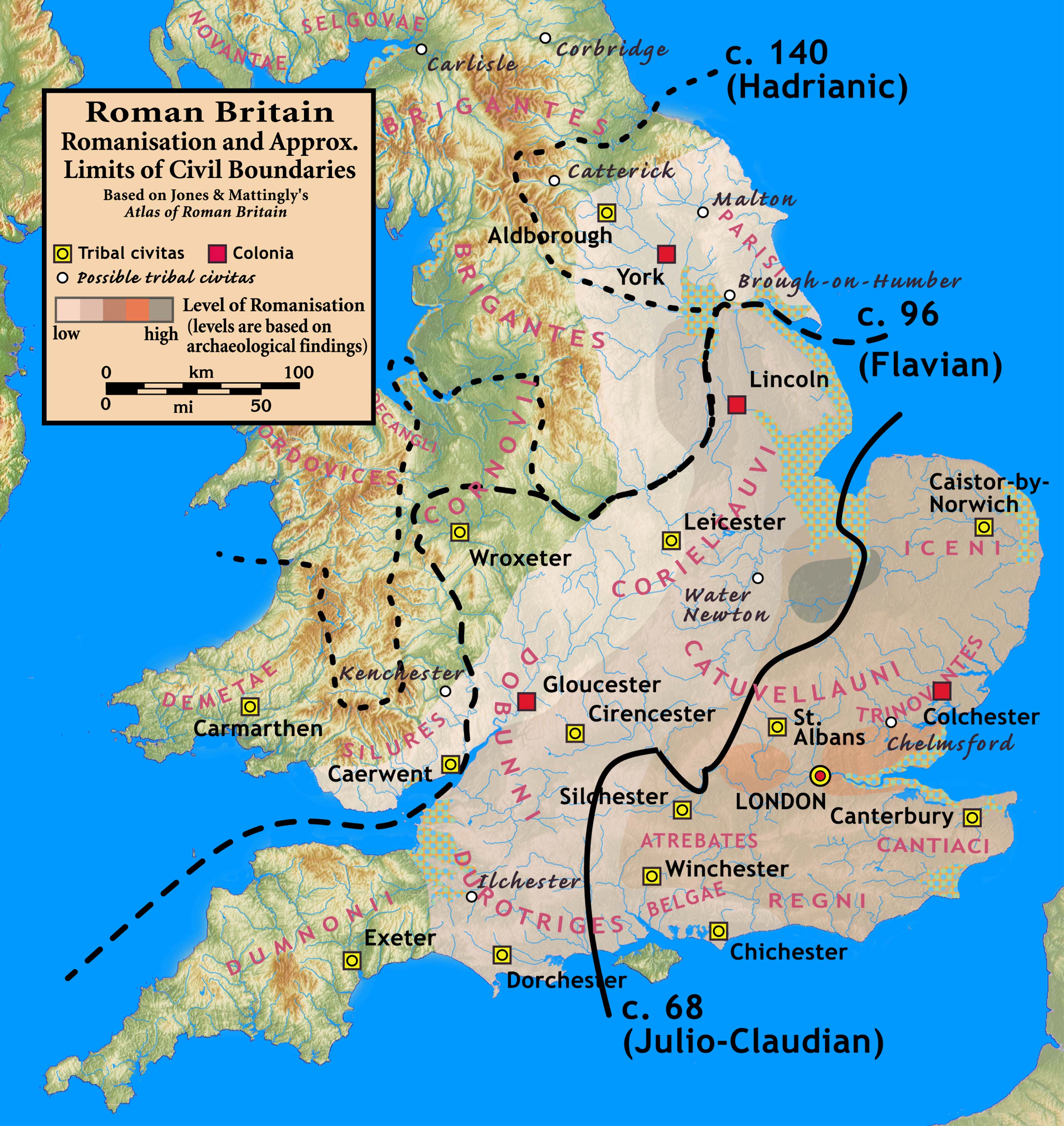
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RICS
The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) is a global professional body for those working in the Built Environment, Construction, Land, Property and Real Estate. The RICS was founded in London in 1868. It works at a cross-governmental level, and aims to promote and enforce the highest international standards in the valuation, management and development of land, real estate, construction and infrastructure. Founded as the Institution of Surveyors, it received a royal charter in 1881, and in 1947 became the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors. With a London HQ and regional offices across the United Kingdom, plus international offices, it serves a 113,000-strong membership distributed over nearly 150 countries. The RICS is linked to other national surveying institutions, collaborates with other professional bodies, and, in 2013, was a founder member of a coalition to develop the International Property Measurement Standards (IPMS). It also produces cost information a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Backstage Centre At High House Production Park, October 2012
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access To Music
Access Creative College, formerly Access to Music Ltd, is a UK-based independent training provider which specialises in industry-focused popular music and creative education. It operates across England with dedicated music colleges in Birmingham, Brighton, Bristol, Lincoln, London, Manchester, Norwich, and Plymouth. ACC's head office is in Manchester. Access Creative College was funded by the Education Funding Authority (EFA) and the Skills Funding Agency (SFA) and worked in partnership with other UK educational institutions, including Birmingham City University (BCU) and the Royal Northern College of Music (RNCM). History Access to Music was founded in 1992 by John Ridgeon to promote and improve popular music education in the UK. The first Access to Music head office was in Leicester. The music school formed a partnership with Leicester College followed by partnerships with regional colleges. The second Access to Music centre opened in Bristol in 1999 and the York and L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |