|
High Cup
High Cup Gill (or High Cup Nick or just High Cup), almost a geometrically perfect U-shaped chasm, is a valley deeply incised into the Pennines, Pennine scarp to the northeast of Appleby-in-Westmorland in Cumbria and within the North Pennines AONB in northern England. It is considered to be U-shaped valley, glacial in origin, ice having over-ridden the area during successive ice ages. To its southeast is Murton, Cumbria, Murton Fell and Dufton Fell is to the north. Toponym The Ordnance Survey name the valley as High Cup Gill but it is often referred to by the name High Cup Nick, a name which properly refers in a more limited sense to the point at its northeastern limit where the headwaters of Highcup Gill Beck pass from the relatively flat terrain of High Cup Plain over the lip of High Cup Scar into the valley. 'Gill (ravine) , Gill' is a word of Norse origin meaning narrow valley or ravine whilst 'beck' signifies a stream; both occur widely in the hills of northern England. As see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Permian Period, Ma. It is the fifth and penultimate period of the Paleozoic era and the fifth period of the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon. In North America, the Carboniferous is often treated as two separate geological periods, the earlier Mississippian (geology), Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin ("coal") and ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern "system" names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare (geologist), William Conybeare and William Phillips (geologist), William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. Carboniferous is the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiddaw Group
The Skiddaw Group is a group (stratigraphy), group of sedimentary rock formations named after the mountain Skiddaw in the England, English Lake District. The rocks are almost wholly Ordovician in age (Tremadocian, Tremadoc through Arenig to Ordovician#Subdivisions, Llanvirn epoch (geology), epochs) though the lowermost beds are possibly of Cambrian age. This rock sequence has previously been known as the Skiddaw Slates, the Skiddaw Slates Group and the Skiddavian Series. Its base is not exposed but in its main outcrop area, it is considered to be in excess of thick though less elsewhere. It consists largely of mudstones and siltstones with subordinate wacke-type sandstones. Their main occurrence is within the northern and central fells of the Lake District, either side of the major ENE-WSW aligned Causey Pike Fault, but inliers and outliers (geology), inliers are found at Black Combe in the south of the Lake District and at Cross Fell in the North Pennines. Stratigraphy In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic rock. Foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering, but instead is in planes perpendicular to the direction of metamorphic compression. The foliation in slate, called " slaty cleavage", is caused by strong compression in which fine-grained clay forms flakes to regrow in planes perpendicular to the compression. When expertly "cut" by striking parallel to the foliation with a specialized tool in the quarry, many slates display a property called fissility, forming smooth, flat sheets of stone which have long been used for roofing, floor tiles, and other purposes. Slate is frequently grey in color, especially when seen ''en masse'' covering roofs. However, slate occurs in a variety of colors even from a single locality; for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenstonedale Group
The Ravenstonedale Group is a Carboniferous lithostratigraphic group (a sequence of rock strata) in the Pennines of northern England. The name is derived from the locality of Ravenstonedale in southeast Cumbria. The rocks of the Ravenstonedale Group have also previously been referred to as the Ravenstonedale Limestone. The group comprises limestones and oolites and some sandstones and shales which reach a maximum thickness of 380m in the Brough area. It is divided into a lower Raydale Dolomite Formation which is overlain by the Marsett Formation and then by an upper Penny Farm Gill Formation.Its base is everywhere an unconformity with Ordovician and Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ... rocks beneath. References * {{Refend Carboniferous System of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be distinguished without a micros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility. Although its permeability and porosity is relatively low, siltstone is sometimes a tight gas reservoir rock, an unconventional reservoir for natural gas that requires hydraulic fracturing for economic gas production. Siltstone was prized in ancient Egypt for manufacturing statuary and cosmetic palettes. The siltstone quarried at Wadi Hammamat was a hard, fine-grained siltstone that resisted flaking and was almost ideal for such uses. Description There is not complete agreement on the definition of siltstone. One definition is that siltstone is mudrock (clastic sedimentary rock containing at least 50% clay and silt) in which at least 2/3 of the clay and silt fraction is composed of silt-sized particles. Silt is defined as grains 2–62 μm in diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoredale Series
The Yoredale Series, in geology, is a now obsolete term for a local phase of the Carboniferous rocks of the north of England, ranging in age from the Asbian Substage to the Yeadonian Substage. The term Yoredale Group is nowadays applied to the same broad suite of rocks. The name was introduced by J. Phillips on account of the typical development of the phase in Yoredale (now generally known as Wensleydale), Yorkshire. Properties and condition In the Yorkshire Dales the Carboniferous rocks assume an aspect very different from that which obtains in the South. Beds of detrital sediment, sandstones, shales and occasional ironstones and thin coals separate the limestones into well-defined beds. These limestone beds have received various names of local significance ( Hardraw Scar, Simonstone, Middle, Underset, Main and many others), and owing to the country being little disturbed by faulting and being much cut up by the streams, they stand out as escarpments on either side of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
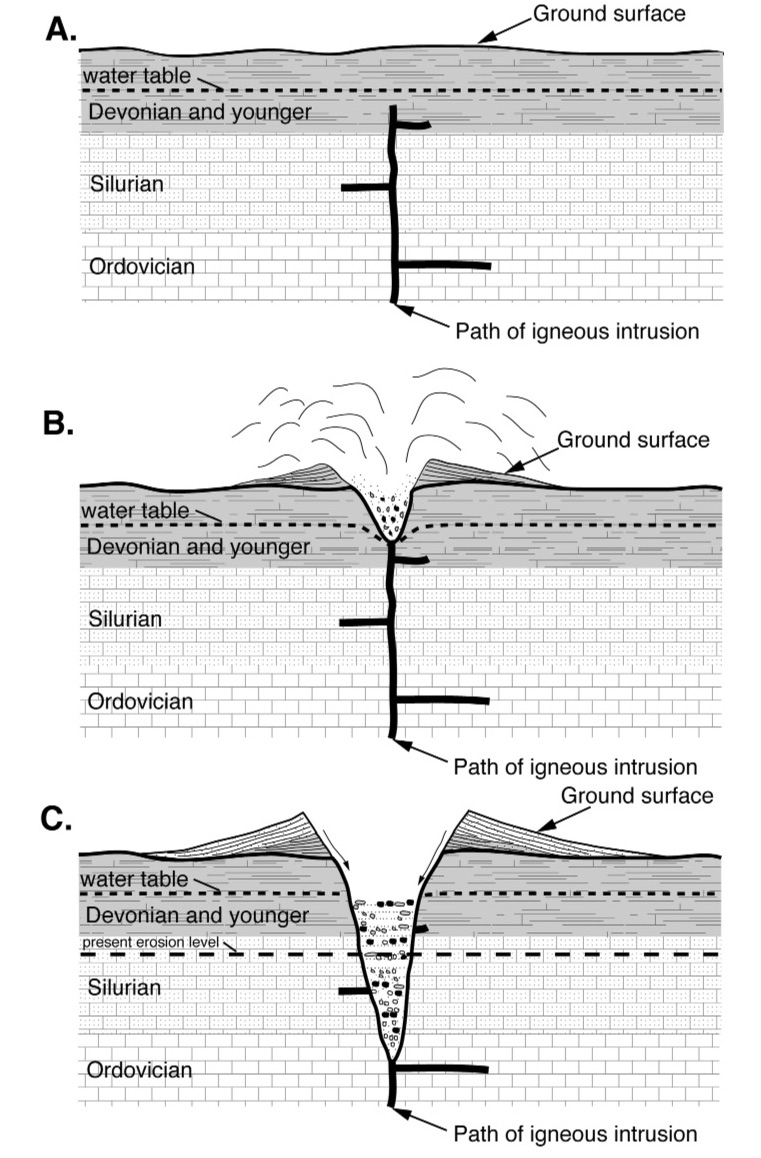
Country Rock (geology)
In geology, country rock is the rock native to an area, in contrast to any intrusion of viscous geologic material, commonly magma, or perhaps rock salt (in salt domes) or unconsolidated sediments. Magma is typically less dense than the rock it intrudes, widening and filling existing cracks, sometimes melting the already-existing country rock. The term "country rock" is similar to, and in many cases interchangeable with, the terms basement and wall rocks. Country rock can denote the widespread lithology of a region in relation to the rock which is being discussed or observed. Geologic settings Settings in geology when the term ''country rock'' is used include: Igneous intrusions When describing a pluton or dike, the igneous rock can be described as intruding the surrounding ''country rock'', the rock into which the pluton has intruded.Newfoundland and LabradorGlossary of Geological Terms Accessed June 2018. When country rock is intruded by a dike, perpendicular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |