|
Hieronymus Emser
Jerome (or Hieronymus) Emser (March 20, 1477 – November 8, 1527), was a German theologian and antagonist of Martin Luther, was born of a good family at Ulm. He studied Greek at Tübingen and jurisprudence at Basel, and after acting for three years as chaplain and secretary to Raymond Peraudi, cardinal of Gurk, he began lecturing on classics in 1504 at Erfurt, where Luther may have been among his audience. In the same year he became secretary to Duke George of Albertine Saxony, who, unlike his cousin Frederick the Wise, the elector of Ernestine Saxony, remained the stanchest defender of Roman Catholicism among the princes of northern Germany. Duke George at this time was bent on securing the canonization of Bishop Benno of Meissen, and at his instance Emser travelled through Saxony and Bohemia in search of materials for a life of Benno, which he subsequently published in German and Latin. In pursuit of the same object he made an unsuccessful visit to Rome in 1510. Meanwhile, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitaphium Emseri (cropped)
{{dab ...
An epitaphium is a Latin epitaph. ''Epitaphium'' may refer to the following works: Music * ''Epitaphium'' (Stravinsky) * ''Epitaphium'' (Waterhouse) *''Epitaphium Carpentarij'', by Marc-Antoine Charpentier *''Epitaphium Joannis Hunyadi'', by Kodály *''Epitaphium temporum pereunti'', by Bronius Kutavicius *''Epitaphium Stanisław Wiechowicz in memoriam'', Symphony No. 2 for choir and orchestra Krzysztof Meyer *''Epitaphium – Children of the Sun'', by Jeffrey Lewis Poetry *Epitaphium Citharistriae, by Victor Plarr *Epitaphium Ansae reginae, to Ansa, Queen of the Lombards Ansa (died after 774) was a noblewoman who became the Queen of the Lombards in 756 and reigned until their fall to the Franks in 774 AD. She, like other Medieval Queens at the time, played a significant role in the stability and preservation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prebend
A prebendary is a member of the Catholic or Anglican clergy, a form of canon with a role in the administration of a cathedral or collegiate church. When attending services, prebendaries sit in particular seats, usually at the back of the choir stalls, known as prebendal stalls. History At the time of the Domesday Book in 1086, the canons and dignitaries of the cathedrals of England were supported by the produce and other profits from the cathedral estates.. In the early 12th century, the endowed prebend was developed as an institution, in possession of which a cathedral official had a fixed and independent income. This made the cathedral canons independent of the bishop, and created posts that attracted the younger sons of the nobility. Part of the endowment was retained in a common fund, known in Latin as ''communia'', which was used to provide bread and money to a canon in residence in addition to the income from his prebend. Most prebends disappeared in 1547, when nearl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New International Encyclopedia
''The New International Encyclopedia'' was an American encyclopedia first published in 1902 by Dodd, Mead & Co. It descended from the ''International Cyclopaedia'' (1884) and was updated in 1906, 1914 and 1926. History ''The New International Encyclopedia'' was the successor of the ''International Cyclopaedia'' (1884). Initially, ''The International Cyclopaedia'' was largely a reprint of Alden's ''Library of Universal Knowledge'', which itself was a reprint of the British '' Chambers's Encyclopaedia''. The title was changed to ''The New International Encyclopedia'' in 1902, with editors Harry Thurston Peck, Daniel Coit Gilman and Frank Moore Colby. The encyclopedia was popular and reprints were made in 1904, 1905, 1907 (corrected and expanded to 20 volumes), 1909 and 1911. The 2nd edition appeared from 1914 to 1917 in 24 volumes. With Peck and Gilman deceased, Colby was joined by a new editor, Talcott Williams. This edition was set up from new type and thoroughly revise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgate
The Vulgate () is a late-4th-century Bible translations into Latin, Latin translation of the Bible. It is largely the work of Saint Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels used by the Diocese of Rome, Roman Church. Later, of his own initiative, Jerome extended this work of revision and translation to include most of the books of the Bible. The Vulgate became progressively adopted as the Bible text within the Western Church. Over succeeding centuries, it eventually eclipsed the texts. By the 13th century it had taken over from the former version the designation (the "version commonly used") or for short. The Vulgate also contains some ''Vetus Latina'' translations that Jerome did not work on. The Catholic Church affirmed the Vulgate as its official Latin Bible at the Council of Trent (1545–1563), though there was no single authoritative edition of the book at that time in any language. The Vulgate did eventually receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
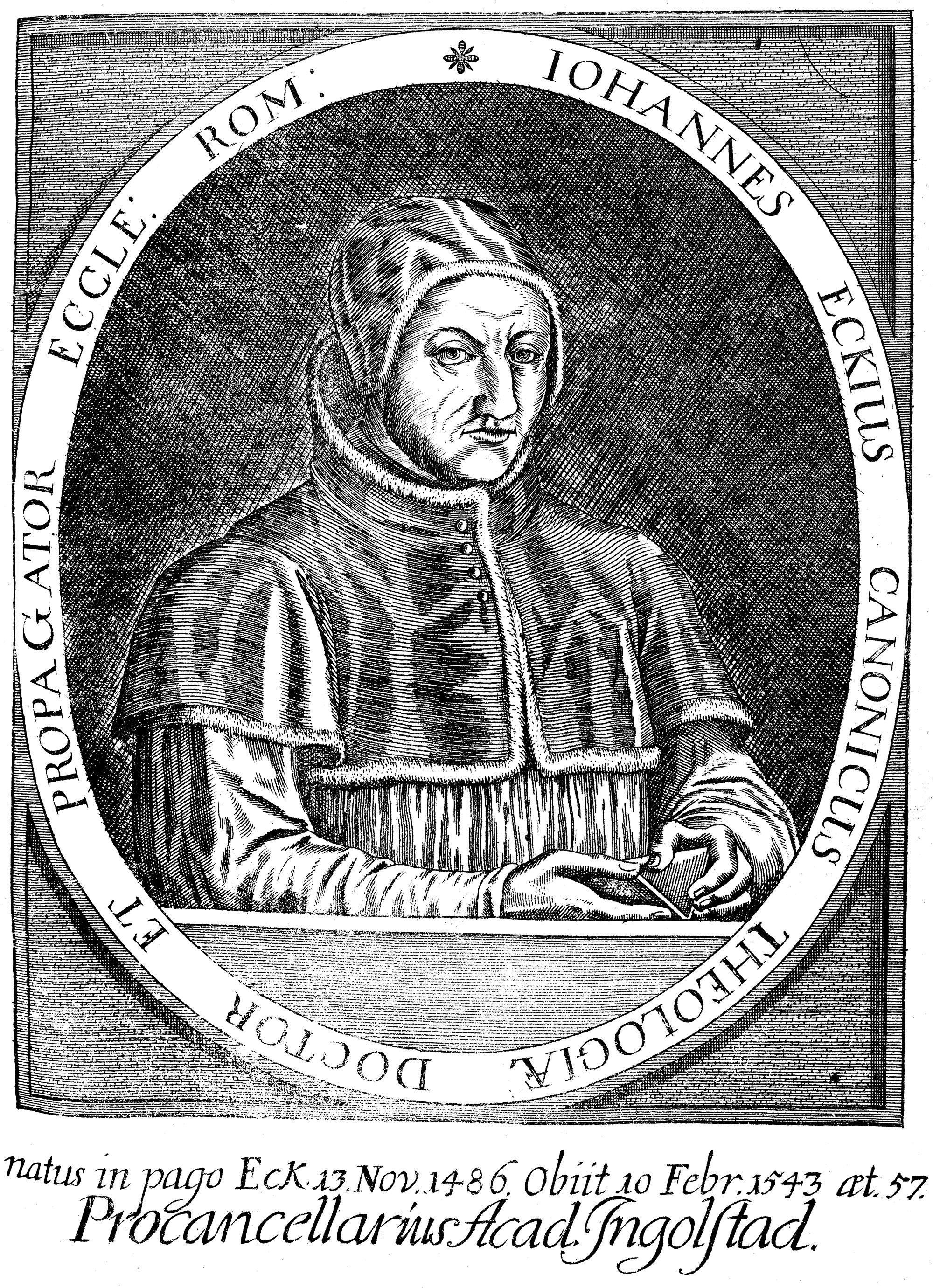
Johann Maier Eck
Johann Maier von Eck (13 November 1486 – 13 February 1543), often anglicized as John Eck, was a German Catholic theologian, Scholasticism, scholastic, prelate, and opponent of Martin Luther. Life Johann Eck was born Johann Maier at Eck (later Egg, near Memmingen, Memmingen, Swabia) and derived his additional surname from his birthplace, which he himself, after 1523, always modified into Eckius or Eccius, i.e. "of Eck". His father, Michael Maier, was a peasant and bailiff, or ''Amtmann'', of the village. The boy's education was undertaken by his uncle, Martin Maier, parish priest at Rottenburg (Neckar), Rottenburg on the river Neckar. At the age of 12 he entered the University of Heidelberg, which he left in the following year for university of Tübingen, Tübingen. After taking his master's degree in 1501, he began the study of theology under Johann Jakob Lempp, and studied the elements of Hebrew and political economy with . Johann Eck left Tübingen in 1501 on account of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenaries, Swiss mercenary system, he attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus. During his tenures at Basel and Einsiedeln, Zwingli began to familiarize himself with many criticisms Christian institutions were facing regarding their reform guidance and garnered scripture which aimed to address such criticisms. IIn 1519, Zwingli became the (people's priest) of the Grossmünster in Zurich where he began to preach ideas on reform of the Catholic Church. In his first public controversy in 1522, he attacked the Fasting and abstinence in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as Sacred Scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of 27 Christianity, Christian texts written in Koine Greek by various authors, forming the second major division of the Christian Bible. It includes four Gospel, gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, epistles attributed to Paul the Apostle, Paul and other authors, and the Book of Revelation. The Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed gradually over the first few centuries of Christianity through a complex process of debate, rejection of Heresy, heretical texts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VIII Of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolution of the monasteries, dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was List of people excommunicated by the Catholic Church, excommunicated by the pope. Born in Greenwich, Henry brought radical changes to the Constitution of England, expanding royal power and ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings in opposition to papal supremacy. He frequently used charges of treason and heresy to quell dissent, and those accused were often executed without a formal trial using bills of attainder. He achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members of the congregation, and of receiving the sacraments. It is practiced by all of the ancient churches (such as the Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches and the Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox churches) as well as by other Christian denominations; however, it is also used more generally to refer to similar types of institutional religious exclusionary practices and shunning among other religious groups. The Amish have also been known to excommunicate members that were either seen or known for breaking rules, or questioning the church, a practice known as shunning. Jehovah's Witnesses use the term disfellowship to refer to their form of excommunication. The word ''excommunication'' means putting a specific indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Bull
A papal bull is a type of public decree, letters patent, or charter issued by the pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the leaden Seal (emblem), seal (''bulla (seal), bulla'') traditionally appended to authenticate it. History Papal bulls have been in use at least since the 6th century, but the phrase was not used until around the end of the 13th century, and then only internally for unofficial administrative purposes. However, it had become official by the 15th century, when one of the offices of the Apostolic Chancery was named the "register of bulls" ("''registrum bullarum''"). By the accession of Pope Leo IX in 1048, a clear distinction developed between two classes of bulls of greater and less solemnity. The majority of the "great bulls" now in existence are in the nature of confirmations of property or charters of protection accorded to monasteries and religious institutions. In an era when there was much fabrication of such documents, those who procured bulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X (; born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, 11 December 14751 December 1521) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 March 1513 to his death in December 1521. Born into the prominent political and banking Medici family of Florence, Giovanni was the second son of Lorenzo de' Medici, ruler of the Florentine Republic, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1489. Following the death of Pope Julius II, Giovanni was elected pope after securing the backing of the younger members of the College of Cardinals. Early on in his rule he oversaw the closing sessions of the Fifth Council of the Lateran, but struggled to implement the reforms agreed. In 1517 he led a costly war that succeeded in securing his nephew Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici as Duke of Urbino, but reduced papal finances. In Protestant circles, Leo is associated with granting indulgences for those who donated to reconstruct St. Peter's Basilica, a practice that was soon challenged by M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig Debate
The Leipzig Debate () was a theological disputation originally between Andreas Karlstadt, Martin Luther and Johann Eck. Karlstadt, the dean of the Wittenberg theological faculty, felt that he had to defend Luther against Eck's critical commentary on the 95 Theses and so challenged Johann Eck, a professor of theology at the University of Ingolstadt, to a public debate concerning the doctrines of free will and grace. The Leipzig Debate took place in June and July 1519 at Pleissenburg Castle in Leipzig, Germany. Its purpose was to discuss Martin Luther's teachings and was initiated and conducted in the presence of George, Duke of Saxony, an opponent of Luther. Eck, considered the master debater in the Holy Roman Empire, was concerned about clerical abuses, but his life's work had been dedicated to the defence of Catholic teachings and combating heresy. Eck invited Luther to join the debate, and when Luther arrived in July, he and Eck expanded the terms of the debate to include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |