|
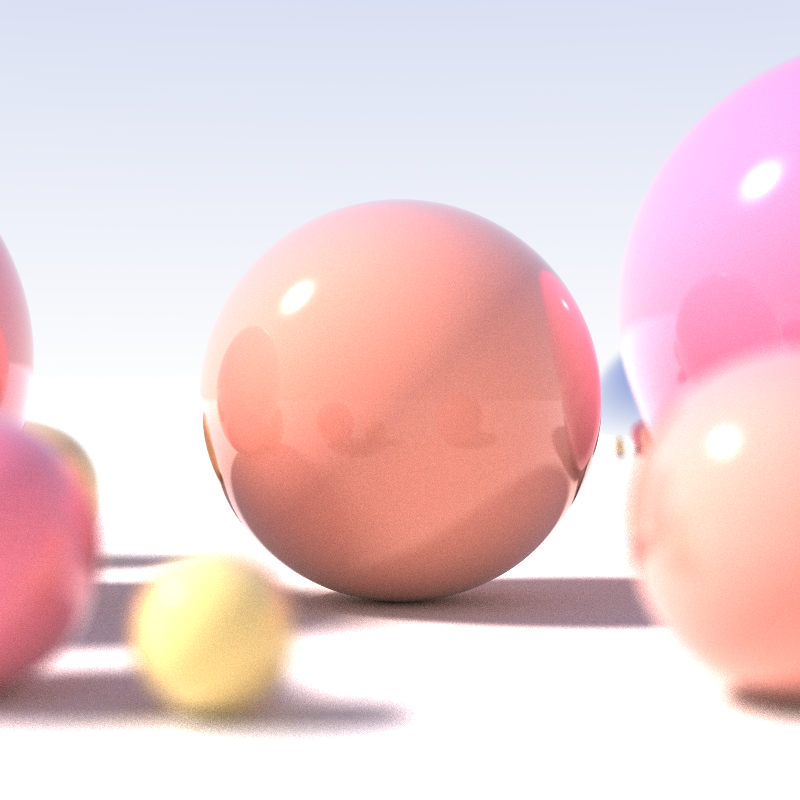
Hidden Surface Determination
In 3D computer graphics, hidden-surface determination (also known as shown-surface determination, hidden-surface removal (HSR), occlusion culling (OC) or visible-surface determination (VSD)) is the process of identifying what surfaces and parts of surfaces can be seen from a particular viewing angle. A hidden-surface determination algorithm is a solution to the visibility problem, which was one of the first major problems in the field of 3D computer graphics. The process of hidden-surface determination is sometimes called hiding, and such an algorithm is sometimes called a hider. When referring to line rendering it is known as hidden-line removal. Hidden-surface determination is necessary to render a scene correctly, so that one may not view features hidden behind the model itself, allowing only the naturally viewable portion of the graphic to be visible. Background Hidden-surface determination is a process that identifies which surfaces are not visible to the user (for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Computer Graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coordinate system#Cartesian coordinates in three dimensions, Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later (possibly as an Computer animation, animation) or displayed in Real-time computer graphics, real time. 3D computer graphics, contrary to what the name suggests, are most often displayed on two-dimensional displays. Unlike 3D film and similar techniques, the result is two-dimensional, without visual depth perception, depth. More often, 3D graphics are being displayed on 3D displays, like in virtual reality systems. 3D graphics stand in contrast to 2D computer graphics which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanline Rendering
Scanline rendering (also scan line rendering and scan-line rendering) is an algorithm for visible surface determination, in 3D computer graphics, that works on a row-by-row basis rather than a polygon-by-polygon or pixel-by-pixel basis. All of the polygons to be rendered are first sorted by the top y coordinate at which they first appear, then each row or scan line of the image is computed using the intersection of a scanline with the polygons on the front of the sorted list, while the sorted list is updated to discard no-longer-visible polygons as the active scan line is advanced down the picture. The main advantage of this method is that sorting vertices along the normal of the scanning plane reduces the number of comparisons between edges. Another advantage is that it is not necessary to translate the coordinates of all vertices from the main memory into the working memory—only vertices defining edges that intersect the current scan line need to be in active memory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Tracing
Beam tracing is an algorithm to simulate wave propagation. It was developed in the context of computer graphics to render 3D scenes, but it has been also used in other similar areas such as acoustics and electromagnetism simulations. Beam tracing is a derivative of the ray tracing algorithm that replaces rays, which have no thickness, with beams. Beams are shaped like unbounded pyramids, with (possibly complex) polygonal cross sections. Beam tracing was first proposed by Paul Heckbert and Pat Hanrahan. In beam tracing, a pyramidal beam is initially cast through the entire viewing frustum. This initial viewing beam is intersected with each polygon in the environment, typically from nearest to farthest. Each polygon that intersects with the beam must be visible, and is removed from the shape of the beam and added to a render queue. When a beam intersects with a reflective or refractive polygon, a new beam is created in a similar fashion to ray-tracing. A variant of beam tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Rendering
In computer-generated imagery and real-time 3D computer graphics, portal rendering is an algorithm for visibility determination. For example, consider a 3D computer game environment, which may contain many polygons, only a few of which may be visible on screen at a given time. By determining which polygons are currently not visible, and not rendering those objects, significant performance improvements can be achieved. A portal system is based on using the partitioning of space to form generalizations about the visibility of objects within those spaces. Regions of map space are divided into polygonal, generally convex, areas called ''zones'', or sometimes ''sectors''. Adjacent zones are linked to one another via shared dividing polygons termed ''portals''. Approaches that precompute visibility for zones are referred to as potentially visible set or ''PVS'' methods. For example, in a computer game such as '' Descent'', the game area might be divided into several zones. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potentially Visible Set
In 3D computer graphics, Potentially Visible Sets are used to accelerate the rendering of 3D environments. They are a form of occlusion culling, whereby a candidate set of ''potentially visible'' polygons are pre-computed, then indexed at run-time in order to quickly obtain an estimate of the visible geometry. The term ''PVS'' is sometimes used to refer to any occlusion culling algorithm (since in effect, this is what all occlusion algorithms compute), although in almost all the literature, it is used to refer specifically to occlusion culling algorithms that pre-compute visible sets and associate these sets with regions in space. In order to make this association, the camera's view-space (the set of points from which the camera can render an image) is typically subdivided into (usually convex) regions and a PVS is computed for each region. Benefits vs. Cost The benefit of offloading visibility as a pre-process are: * The application just has to look up the pre-computed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Complexity
Depth(s) may refer to: Science and mathematics * Depth (ring theory), an important invariant of rings and modules in commutative and homological algebra * Depth in a well, the measurement between two points in an oil well * Color depth (or "number of bits" or "bit depth"), in computer graphics * Market depth, in financial markets, the size of an order needed to move the market a given amount * Moulded depth, a nautical measurement * Sequence depth, or coverage, in genetic sequencing * Depth (coordinate), a type of vertical distance * Tree depth Art and entertainment * ''Depth'' (video game), an asymmetrical multiplayer video game for Microsoft Windows * ''Depths'' (novel), a 2004 novel by Henning Mankell * ''Depths'' (Oceano album), 2009 * ''Depths'' (Windy & Carl album), 1998 * ''Depth'' (EP), a 2024 EP by Yuta * "Depths" (''Law & Order: Criminal Intent''), an episode of ''Law & Order: Criminal Intent'' * ''Depth'', the Japanese title for the PlayStation game relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Projection
A 3D projection (or graphical projection) is a Design, design technique used to display a three-dimensional (3D) object on a two-dimensional (2D) surface. These projections rely on perspective (graphical), visual perspective and aspect analysis to Projection mapping, project a complex object for viewing capability on a simpler plane. 3D projections use the Primary Qualities, primary qualities of an object's basic shape to create a map of points, that are then connected to one another to create a visual element. The result is a graphic that contains conceptual properties to interpret the figure or image as not actually flat (2D), but rather, as a solid object (3D) being viewed on a 2D display. 3D objects are largely displayed on two-dimensional mediums (such as paper and computer monitors). As such, graphical projections are a commonly used design element; notably, in engineering drawing, technical drawing, drafting, and computer graphics. Projections can be calculated through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Camera
In 3D computer graphics, 3D video games, a virtual camera system aims at controlling a camera or a set of cameras to display a view of a 3D virtual world. Camera systems are used in video games where their purpose is to show the action at the best possible angle; more generally, they are used in 3D virtual worlds when a third-person view is required. As opposed to filmmakers, virtual camera system creators have to deal with a world that is interactive and unpredictable. It is not possible to know where the player character is going to be in the next few seconds; therefore, it is not possible to plan the shot (filming), shots as a filmmaker would do. To solve this issue, the system relies on certain rules or artificial intelligence to select the most appropriate shots. There are mainly three types of camera systems. In ''fixed camera systems'', the camera does not move at all, and the system displays the player's character in a succession of still shots. ''Tracking cameras'', on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viewing Frustum
In 3D computer graphics, a viewing frustum or view frustum is the region of space in the modeled world that may appear on the screen; it is the field of view of a perspective virtual camera system. The view frustum is typically obtained by taking a geometrical frustum—that is a truncation with parallel planes—of the pyramid of vision, which is the adaptation of (idealized) '' cone of vision'' that a camera or eye would have to the rectangular viewports typically used in computer graphics. Some authors use ''pyramid of vision'' as a synonym for view frustum itself, i.e. consider it truncated. The exact shape of this region varies depending on what kind of camera lens is being simulated, but typically it is a frustum of a rectangular pyramid (hence the name). The planes that cut the frustum perpendicular to the viewing direction are called the ''near plane'' and the ''far plane''. Objects closer to the camera than the near plane or beyond the far plane are not drawn. Somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warnock Algorithm
The Warnock algorithm is a hidden surface algorithm invented by John Warnock that is typically used in the field of computer graphics. It solves the problem of rendering a complicated image by recursive subdivision of a scene until areas are obtained that are trivial to compute. In other words, if the scene is simple enough to compute efficiently then it is rendered; otherwise it is divided into smaller parts which are likewise tested for simplicity., 608 pages This is a divide and conquer algorithm In computer science, divide and conquer is an algorithm design paradigm. A divide-and-conquer algorithm recursively breaks down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same or related type, until these become simple enough to be solved dir ... with run-time of O(np), where ''n'' is the number of polygons and ''p'' is the number of pixels in the viewport. The inputs are a list of polygons and a viewport. The best case is that if the list of polygons is simple, then draw th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Tracing (graphics)
In 3D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling Light transport theory, light transport for use in a wide variety of Rendering (computer graphics), rendering algorithms for generating digital image, digital images. On a spectrum of Computation time, computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as ray casting, #Recursive ray tracing algorithm, recursive ray tracing, Distributed ray tracing, distribution ray tracing, photon mapping and path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as still computer-generated imagery, CGI images, and film and television visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to real-time computer graphics, real-time applications such as video games, where Frame rate, speed is critical in rendering each Film frame, frame. Since 2018, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Space Partitioning
In computer science, binary space partitioning (BSP) is a method for space partitioning which recursively subdivides a Euclidean space into two convex sets by using hyperplanes as partitions. This process of subdividing gives rise to a representation of objects within the space in the form of a Tree (data structure), tree data structure known as a BSP tree. Binary space partitioning was developed in the context of 3D computer graphics in 1969. The structure of a BSP tree is useful in rendering (computer graphics), rendering because it can efficiently give spatial information about the objects in a scene, such as objects being ordered from front-to-back with respect to a viewer at a given location. Other applications of BSP include: performing geometrical operations with shapes (constructive solid geometry) in Computer-aided design, CAD, collision detection in robotics and 3D video games, ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing, virtual landscape simulation, and other applications tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |