|
Hiberno-Norman
Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans (; ) is a modern term for the descendants of Norman settlers who arrived during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. Most came from England and Wales. They are distinguished from the native Gaelic Irish; although some Normans eventually became Gaelicised. The Hiberno-Normans were a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy who controlled the Lordship of Ireland. The Hiberno-Normans were associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland and contributed to the emergence of a Hiberno-English dialect. Some of the most prominent Hiberno-Norman families were the Burkes (de Burghs), Butlers, and FitzGeralds. One of the most common Irish surnames, Walsh, derives from Welsh Normans who arrived in Ireland as part of this group. Some Norman families were said to have become " more Irish than the Irish themselves" by merging culturally and intermarrying with the Gaels. The dominance of the Catholic Hibern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FitzGerald Dynasty
The FitzGerald dynasty is a Hiberno-Norman noble and aristocratic dynasty, originally of Cambro-Normans, Cambro-Norman and Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman origin. They have been Peerage of Ireland, peers of Ireland since at least the 13th century, and are described in the Annals of the Four Masters as having become "more Irish than the Irish themselves" or Gaels, due to assimilation with the native Gaelic aristocratic and popular culture. The dynasty has also been referred to as the Geraldines and Ireland's largest landowners. They achieved power through colonisation and the conquest of large swathes of Irish territory by the sons and grandsons of Gerald de Windsor (c. 1075 – 1135). Gerald de Windsor (Gerald de Windsor, Gerald FitzWalter) was the first Castellan of Pembroke Castle in Wales, and became the male progenitor of the FitzMaurice and FitzGerald Dynasty ("fitz", from the Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ''fils'' indicating "sons of" Gerald). His father, English feuda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Gaelic warfare, Warfare between List of Irish kingdoms, these territories was common. Traditionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of Irish clans, clans and, like the rest of History of Europe, Europe, was structured hierarchically according to Social class, class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly Pastoralism, pastoral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish People
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the State religion, established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English Dissenters, English Dissenting churches, such as the Methodism, Methodist Church, though some were Catholic Church, Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior Irish military diaspora#Britain, army and naval officers since the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland for over a century, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterianism, Presbyteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelicised
Gaelicisation, or Gaelicization, is the act or process of making something Gaels, Gaelic or gaining characteristics of the ''Gaels'', a sub-branch of Celticisation. The Gaels are an ethno-linguistic group, traditionally viewed as having spread from Ireland to Scotland and the Isle of Man. ''Gaelic'', as a linguistic term, refers to the Goidelic languages, Gaelic languages but can also refer to the transmission of any other Gaelic cultural feature such as social norms and customary law, customs, music and sport. It is often referred to as a part of Celts (modern), Celtic identity since Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man are all considered Celtic nations, and the Gaelic languages are considered a sub-group of the Celtic languages. Early history Examples of ethnic groups that have gone through a period of Gaelicisation in history include the Norse-Gaels, the Picts, the Kingdom of Strathclyde, Britons of south-western Scotland, the Scoto-Normans, and the Hiberno-Normans, Modern e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
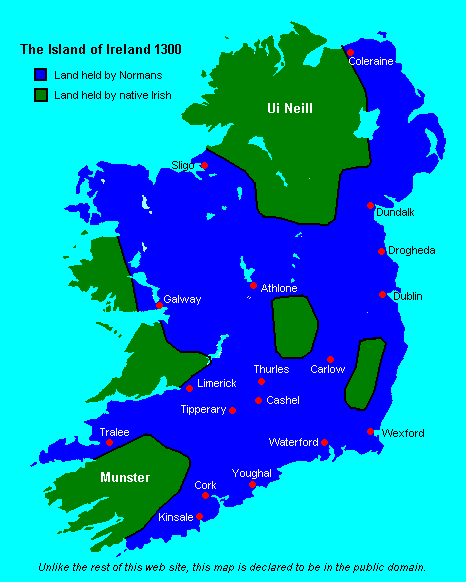
Ireland 1300
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambro-Normans
Cambro-Normans (; "Wales", ; ) were Normans who settled in southern Wales and the Welsh Marches after the Norman invasion of Wales. Cambro-Norman knights were also the leading force in the Cambro-Norman invasion of Ireland, led by Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke in 1170. In Wales Following the Norman conquest of England, Norman forces would invade South Wales, where William FitzOsbern, 1st Earl of Hereford overran the Kingdom of Gwent and the Earl of Shrewsbury invaded the Kingdom of Deheubarth. Despite a number of Welsh revolts against Norman rule, these areas (along with the Gower), would become the main focus of Norman settlement in Wales. Although Welsh forces would retake much of the Norman territories following their crushing victory at the Battle of Crug Mawr in 1136, the Norman King of England would control much of the Welsh borders and southern agricultural land by the 12th century. This led to Wales being split in two, with one area becoming the Marcher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Surnames
A formal Irish name consists of a given name and a surname. In the Irish language, most surnames are patronymic surnames (distinct from patronyms, which are seen in Icelandic names for example). The form of a surname varies according to whether its bearer is a man, a woman, or a woman married to a man, who adopts his surname. An alternative traditional naming convention consists of the first name followed by a double patronym, usually with the father and grandfather's names. This convention is not used for official purposes but is generalized in (Irish-speaking areas) and also survives in some rural non- areas. Sometimes the name of the mother or grandmother may be used instead of the father or grandfather. Epithets A first name may be modified by an adjective to distinguish its bearer from other people with the same name. ("big") and ("young") are used to distinguish parent and child, like " senior" and " junior" are used in English, but are placed between the given name a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland (), sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman Lords between 1177 and 1542. The lordship was created following the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169–1171. It was a papal fief, granted to the Plantagenet kings of England by the Holy See, via . As the Lord of Ireland was also the King of England, he was represented locally by a governor, variously known as the Justiciar, Lieutenant, Lord Lieutenant or Lord Deputy. The kings of England claimed lordship over the whole island, but in reality the king's rule only ever extended to parts of the island. The rest of the island – referred to subsequently as Gaelic Ireland – remained under the control of various Gaelic Irish kingdoms or chiefdoms, who were often at war with the Anglo-Normans. The area under English rule and law grew and shrank over time, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Irish Than The Irish Themselves
"More Irish than the Irish themselves" (; ) is a phrase used in Irish historiography to describe a phenomenon of cultural assimilation in late medieval Norman Ireland. History The descendants of Anglo-Norman lords who had settled in Ireland in the 12th century had been significantly Gaelicised by the end of the Middle Ages, forming septs and clans after the indigenous Gaelic pattern, and became known as the Gall or "Old English" (contrasting with the "New English" arriving with the Tudor conquest of Ireland). The Statutes of Kilkenny, 1366, complained that " ... now many English of the said land, forsaking the English language, manners, mode of riding, laws and usages, live and govern themselves according to the manners, fashion, and language of the Irish enemies". In 1596 the Elizabethan poet Edmund Spenser (c. 1552–13 January 1599) whilst employed as part of the English administration in Ireland, paraphrased the saying in his controversial treatise, '' A View of the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster Scots People
The Ulster Scots people or Scots-Irish are an ethnic group descended largely from Lowland Scottish people, Scottish and Northern English people, English settlers who moved to the northern province of Ulster in Ireland mainly during the 17th century. There is an Ulster Scots dialect of the Scots language. Historically, there have been considerable population exchanges between Ireland and Scotland over the millennia. This group are found mostly in the province of Ulster; their ancestors were Protestant settlers who migrated from the Scottish Lowlands and Northern England during the Plantation of Ulster, which was a Plantation (settlement or colony), planned process of colonisation following the Tudor conquest of Ireland. The largest numbers came from Ayrshire, Cumbria, Dumfries and Galloway, county Durham, Durham, Lanarkshire, Northumberland, Renfrewshire, Scottish Borders, Yorkshire and, to a lesser extent, from the Scottish Highlands. Ulster Scots people, displaced throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Protestant
Protestantism is a Christianity, Christian community on the island of Ireland. In the 2011 census of Northern Ireland, 48% (883,768) described themselves as Protestant, which was a decline of approximately 5% from the 2001 census. In the 2011 census of the Republic of Ireland, 4.27% of the population described themselves as Protestant. In the Republic, Protestantism was the second largest religious grouping until the 2002 census in which they were exceeded by those who chose "No Religion". Some forms of Protestantism existed in Ireland in the early 16th century before the English Reformation, but demographically speaking, these were very insignificant and the real influx of Protestantism began only with the spread of the English Reformation to Ireland. The Church of Ireland was established church, established by King Henry VIII of England, who had himself proclaimed as King of Ireland. History Reformation in Ireland During the English Reformation in the 1530s, the Parliament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particularly in contexts of national identity, political history, and diaspora, from other Catholic populations globally. They constitute the majority population in the Republic of Ireland, where approximately 3.9 million people identified as Catholic in the 2022 census, and a significant minority in Northern Ireland, with around 820,000 adherents. The Irish diaspora has established Irish Catholic communities worldwide, particularly in the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom, where they have played a major role in shaping cultural, religious, and political landscapes. Historically, Irish Catholics experienced systemic discrimination, especially under British rule, through the imposition of Penal Laws in the 17th and 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |