|
Hexafluoroisobutylene
Hexafluoroisobutylene is an organofluorine compound with the formula (CF3)2C=CH2. This colorless gas is structurally similar to isobutylene. It is used as a comonomer in the production of modified polyvinylidene fluoride. It is produced in a multistep process starting with the reaction of acetic anhydride with hexafluoroacetone. It is oxidized by sodium hypochlorite to hexafluoroisobutylene oxide. As expected, it is a potent dienophile.{{cite journal, title=The chemistry and utility of hexafluoroisobutylene (HFIB) and hexafluoroisobutylene oxide (HFIBO), author= Murphy, Peter M., journal=Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, year=2013, volume=156, pages=345–362, doi=10.1016/j.jfluchem.2013.07.015 See also *Perfluoroisobutene Perfluoroisobutene (PFIB) is the perfluorocarbon counterpart of the hydrocarbon isobutene and has the formula (CF3)2C=CF2. An alkene, it is a colorless gas that is notable as a highly toxic perfluoroalkene. Few simple alkenes are as toxic. Safet ... Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluoroacetone
Hexafluoroacetone (HFA) is a chemical compound with the formula (CF3)2CO. It is structurally similar to acetone; however, its reactivity is markedly different. It a colourless, hygroscopic, nonflammable, highly reactive gas characterized by a musty odour. The most common form of this substance is hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate (1.5 H2O), which is a hemihydrate of hexafluoropropane-2,2-diol , a geminal diol. Synthesis The industrial route to HFA involves treatment of hexachloroacetone with HF: :(CCl3)2CO + 6 HF → (CF3)2CO + 6 HCl Hexafluoropropylene oxide rearranges to give HFA. In the laboratory, HFA can be prepared in a two step process from perfluoropropene. In the first step KF catalyzes the reaction of the alkene with elemental sulfur to give the 1,3-dithietane CF3)2CSsub>2. This species is then oxidized by iodate to give (CF3)2CO. Uses Hexafluoroacetone is used in the production of hexafluoroisopropanol: :(CF3)2CO + H2 → (CF3)2CHOH It is also used as a pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorine Compound
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch, Peer ''Modern flu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
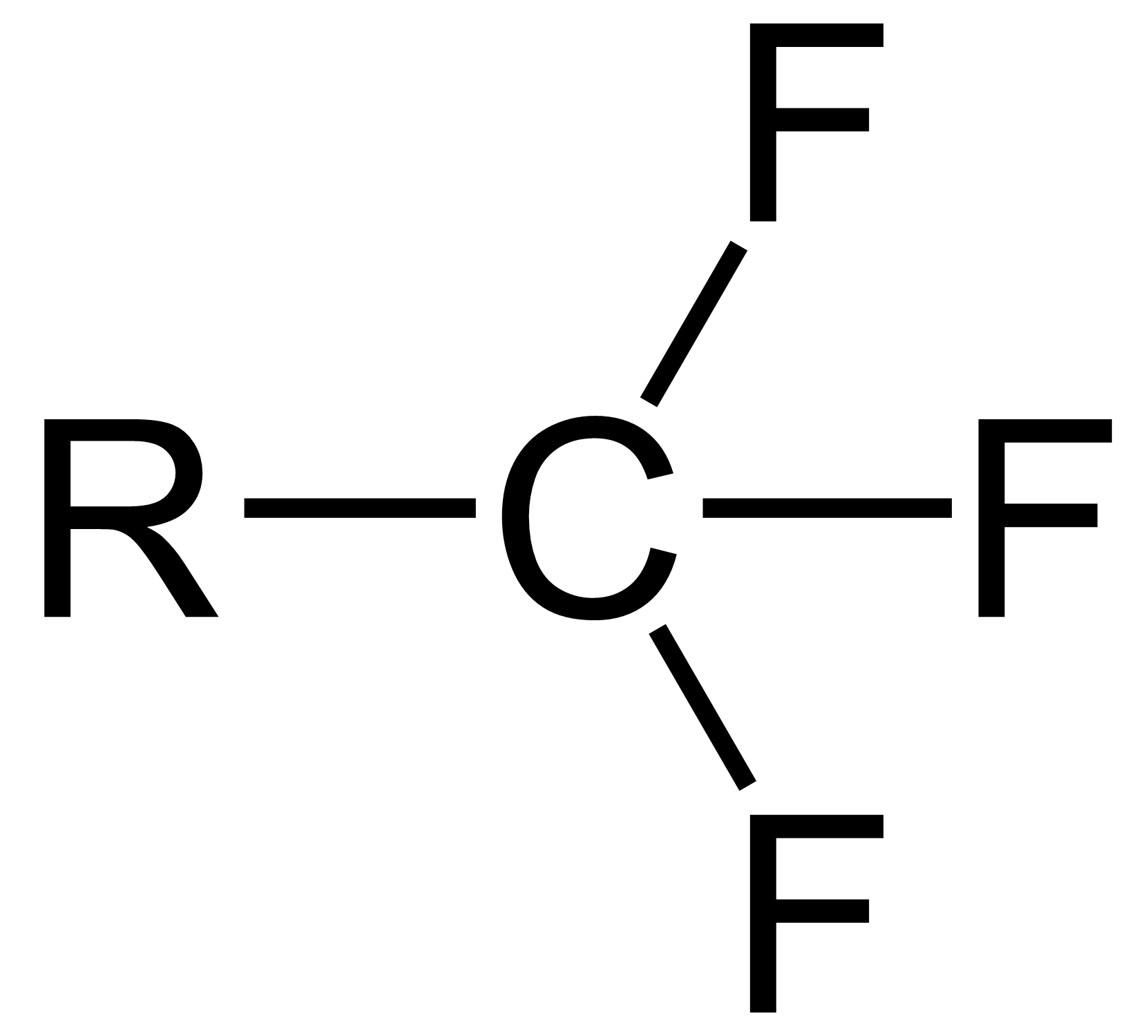
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comonomer
In polymer chemistry, a comonomer refers to a polymerizable precursor to a copolymer aside from the principal monomer. In some cases, only small amounts of a comonomer are employed, in other cases substantial amounts of comonomers are used. Furthermore, in some cases, the comonomers are statistically incorporated within the polymer chain, whereas in other cases, they aggregate. The distribution of comonomers is referred to as the " blockiness" of a copolymer. 1-Octene, 1-hexene, and 1-butene are used comonomers in the manufacture of polyethylenes. The advantages to such copolymers has led to a focus on catalysts that facilitate the incorporation of these comonomers, e.g., constrained geometry complexes. Comonomers are often employed to improve the plastification of polymeric materials, i.e. the flexibility of the polymer. Unlike traditional plasticizers, comonomers are not leachable. In other cases, comonomers are used to introduce crosslinking. Divinylbenzene, for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinylidene Fluoride
1,1-Difluoroethylene, also known as vinylidene fluoride, is a hydrofluoroolefin. It is a flammable gas. Global production in 1999 was approximately 33,000 metric tons. It is primarily used in the production of fluoropolymers such as polyvinylidene fluoride. Preparation 1,1-Difluoroethylene can be prepared by elimination reaction from a 1,1,1-trihaloethane compound, for example, loss of hydrogen chloride from 1-chloro-1,1-difluoroethane:. : or loss of hydrogen fluoride from 1,1,1-trifluoroethane 1,1,1-Trifluoroethane, or R-143a or simply trifluoroethane, is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) compound that is a colorless gas. It should not be confused with the much more commonly used HFC gas R-134a, nor confused with the isomeric compound 1,1,2-tr ...: : See also * 1,2-Difluoroethylene * Perfluoroisobutene References {{DEFAULTSORT:Difluoroethylene, 1, 1- Organofluorides Vinylidene compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air. Structure and properties Acetic anhydride, like most acid anhydrides, is a flexible molecule with a nonplanar structure. The pi system linkage through the central oxygen offers very weak resonance stabilization compared to the dipole-dipole repulsion between the two carbonyl oxygens. The energy barriers to bond rotation between each of the optimal aplanar conformations are quite low. Like most acid anhydrides, the carbonyl carbon atom of acetic anhydride has electrophilic character, as the leaving group is carboxylate. The internal asymmetry may contribute to acetic anhydride's potent electrophilicity as the asymmetric geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite (commonly known in a dilute solution as bleach) is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaOCl (or NaClO), comprising a sodium cation () and a hypochlorite anion (or ). It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid. The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate ·5, a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated. Sodium hypochlorite is most often encountered as a pale greenish-yellow dilute solution referred to as liquid bleach, which is a household chemical widely used (since the 18th century) as a disinfectant or a bleaching agent. In solution, the compound is unstable and easily decomposes, liberating chlorine, which is the active principle of such products. Sodium hypochlorite is the oldest and still most important chlorine-based bleach. Its corrosive properties, common availability, and reaction products make it a signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfluoroisobutene
Perfluoroisobutene (PFIB) is the perfluorocarbon counterpart of the hydrocarbon isobutene and has the formula (CF3)2C=CF2. An alkene, it is a colorless gas that is notable as a highly toxic perfluoroalkene. Few simple alkenes are as toxic. Safety Perfluoroisobutene is quite toxic with an LCt = 880 mg⋅min⋅m−3 (mice). It is a Schedule 2 substance of the Chemical Weapons Convention. Perfluoroisobutene is highly reactive toward nucleophiles. It hydrolyzes readily to give the relatively innocuous (CF3)2CHCO2H, which readily decarboxylates to give hexafluoropropane. It forms addition compounds with thiols, and it is this reactivity that may be related to its toxicity. PFIB is a product of pyrolysis of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), one of the substances invoked to explain polymer fume fever. External links International Chemical Safety Card 1216 See also *Phosgene *Bis(trifluoromethyl) disulfide Bis(trifluoromethyl) disulfide (TFD) is a fluorinated organosulfur c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |