|
Heterodimeric Amino Acid Transporter
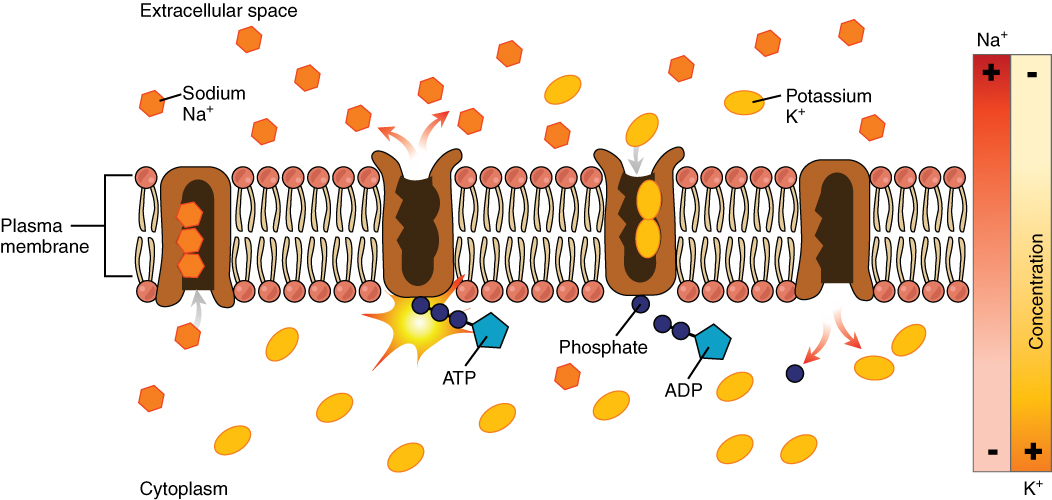
Heterodimeric amino-acid transporters are a family of transport proteins that facilitate the transport of certain amino acids across cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...s. Each comprises a light and a heavy protein subunit. Transport activity happens in the light. The following table lists the members of this family: References Transport proteins Protein families Solute carrier family {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Protein
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A6
Y+L amino acid transporter 2, also known as cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A6'' gene. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter Heterodimeric amino-acid transporters are a family of transport proteins that facilitate the transport of certain amino acids across cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically r ... References Further reading * * * * * Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Proteins
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystinuria
Cystinuria is an inherited autosomal recessive disease characterized by high concentrations of the amino acid cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of cystine stones in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It is a type of aminoaciduria. "Cystine", not "cysteine," is implicated in this disease; the former is a dimer of the latter. Presentation Cystinuria is a cause of recurrent kidney stones. It is a disease involving the defective transepithelial transport of cystine and dibasic amino acids in the kidney and intestine and is one of many causes of kidney stones. If not treated properly, the disease could cause serious damage to the kidneys and surrounding organs, and in some rare cases death. The stones may be identified by a positive nitroprusside cyanide test. The crystals are usually hexagonal, translucent, and white. Upon removal, the stones may be pink or yellow, but later they turn greenish due to exposure to air. Cystinuria is usually asymptomatic when no stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC3A1
Neutral and basic amino acid transport protein rBAT is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC3A1'' gene. Mutations in the SLC3A1 gene are associated with cystinuria. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter * Solute carrier family The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A9
b(0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1, also known as b(0,+)AT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A9'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that belongs to a family of light subunits of amino acid transporters. This protein plays a role in the high-affinity and sodium-independent transport of cystine and neutral and dibasic amino acids, and appears to function in the reabsorption of cystine in the kidney tubule. The protein associates with the protein coded for by SLC3A1. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene cause non-type I cystinuria, a disease that leads to cystine stones in the urinary system due to impaired transport of cystine and dibasic amino acids. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter * Solute carrier family The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A10
Asc-type amino acid transporter 1 (Asc-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A10'' gene. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter Heterodimeric amino-acid transporters are a family of transport proteins that facilitate the transport of certain amino acids across cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically r ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A11
Cystine/glutamate transporter is an antiporter that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A11'' gene. The ''SLC7A11'' gene encodes a sodium-independent cystine-Glutamate (neurotransmitter), glutamate antiporter that is chloride dependent, also known as xCT. Along with a heavy chain subunit from ''SLC3A2'', the SLC7A11 light chain comprises system Xc-, which is the functional cystine-glutamate antiporter. While the SLC3A2 heavy chain is a chaperone for many other light chains that participate in amino acid transport, the SLC7A11 light chain is specific for system Xc-, and the terms xCT/SLC7A11 and system Xc- are used interchangeably in much of the literature. SLC7A11 plays an important role in glutathione production throughout nervous and non-nervous tissues. In the nervous system, SLC7A11 regulates synaptic activity by stimulating extrasynaptic receptors and performs nonvesicular glutamate release. This gene is highly expressed by astrocytes and couples the uptake of one molecule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysinuric Protein Intolerance
Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting amino acid transport. It is characterised by the body's inability to properly digest and use certain proteins. This condition leads to various metabolic complications and is typically diagnosed in infancy or early childhood. About 140 patients have been reported, almost half of them of Finnish origin. Individuals from Japan, Italy, Morocco and North Africa have also been reported plus one in Bixby, Oklahoma. Signs and symptoms Infants with LPI are usually symptom-free when breastfed because of the low protein concentration in human milk, but develop vomiting and diarrhea after weaning. The patients show failure to thrive, poor appetite, growth retardation, enlarged liver and spleen, prominent osteoporosis and osteopenia, delayed bone age and spontaneous protein aversion. Forced feeding of protein may lead to convulsions and coma. Mental development is normal if prolonged episode of hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A7
Y+L amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A7'' gene. Interactions SLC7A7 has been shown to interact with SLC3A2. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter * Solute carrier family * Lysinuric protein intolerance Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting amino acid transport. It is characterised by the body's inability to properly digest and use certain proteins. This condition leads to various metabolic ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Lysinuric Protein Intolerance Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A8
Large neutral amino acids transporter small subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A8'' gene. See also * Heterodimeric amino acid transporter * Solute carrier family The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family Thyroid hormone transporters {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |