|
Hessdalen Light
The Hessdalen lights are unidentified lights which have been observed in a stretch of the Hessdalen valley in rural central Norway periodically since at least the 1930s. Background The Hessdalen lights appear both by day and by night, and seem to float through and above the valley. They are usually bright white, yellow or red and can appear above and below the horizon. The duration of the phenomenon may be a few seconds to well over an hour. Sometimes the lights move with enormous speed; at other times they seem to sway slowly back and forth. On yet other occasions, they hover in mid‑air. Unusual lights have been reported in the region since at least the 1930s. Especially high activity occurred between December 1981 and mid-1984, during which the lights were observed 15–20 times per week, attracting many overnight tourists. , the number of observations had dwindled, with only 10 to 20 sightings yearly. Since 1983, "Project Hessdalen" initiated by UFO-Norge and UFO-Sverige h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hessdalen
Hessdalen is a village in Holtålen Municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. Hessdalen also refers to the long valley that surrounds the village. Hessdalen is located in the central part of the valley, approximately south of the city of Trondheim, approximately north of the mining town of Røros, and about southwest of the village of Renbygda. About 150 people live in the village and surrounding valley. Hessdalen Church is located in the village of Hessdalen and the lake Øyungen lies about southwest of the village. The Hessdalen area is known for the occurrence of unexplained aerial luminous phenomena called the Hessdalen lights. The phenomenon is monitored by the Hessdalen AMS. Name The first element is the name of the local river ''Hesja'' and the last element is the definite form of ''dal'', which means " dale" or "valley A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Element
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Coefficient
In chemical kinetics, a reaction rate constant or reaction rate coefficient () is a proportionality constant which quantifies the rate and direction of a chemical reaction by relating it with the concentration of reactants. For a reaction between reactants A and B to form a product C, where :A and B are reactants :C is a product :''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are stoichiometric coefficients, the reaction rate is often found to have the form: r = k mathrmm mathrm Here is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature, and and are the molar concentrations of substances A and B in moles per unit volume of solution, assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution. (For a reaction taking place at a boundary, one would use moles of A or B per unit area instead.) The exponents ''m'' and ''n'' are called partial orders of reaction and are ''not'' generally equal to the stoichiometric coefficients ''a'' and ''b''. Instead they depend on the reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronic Transition
In theoretical chemistry, molecular electronic transitions take place when electrons in a molecule are excited from one energy level to a higher energy level. The energy change associated with this transition provides information on the structure of the molecule and determines many of its properties, such as colour. The relationship between the energy involved in the electronic transition and the frequency of radiation is given by Planck's relation. Organic molecules and other molecules The electronic transitions in organic compounds and some other compounds can be determined by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, provided that transitions in the ultraviolet (UV) or visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum exist for the compound. Electrons occupying a HOMO (highest-occupied molecular orbital) of a sigma bond (σ) can get excited to the LUMO (lowest-unoccupied molecular orbital) of that bond. This process is denoted as a transition. Likewise, promotion of an electron from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion-acoustic Waves
In plasma physics, an ion acoustic wave is one type of longitudinal oscillation of the ions and electrons in a plasma, much like acoustic waves traveling in neutral gas. However, because the waves propagate through positively charged ions, ion acoustic waves can interact with their electromagnetic fields, as well as simple collisions. In plasmas, ion acoustic waves are frequently referred to as acoustic waves or even just sound waves. They commonly govern the evolution of mass density, for instance due to pressure gradients, on time scales longer than the frequency corresponding to the relevant length scale. Ion acoustic waves can occur in an unmagnetized plasma or in a magnetized plasma parallel to the magnetic field. For a single ion species plasma and in the long wavelength limit, the waves are dispersionless (\omega=v_sk) with a speed given by (see derivation below) :v_s = \sqrt where k_\text is the Boltzmann constant, M is the mass of the ion, Z is its charge, T_e is the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Low Frequency
Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters (an obsolete metric unit equal to 10 kilometers). Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low- data-rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations (broadcasting time signals to set radio clocks) and secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines. Propagation characteristics Because of their long wavelengths, VLF radio waves can diffract around large obstacles and so are not blocked by mountain ranges, and they can propagate as ground wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
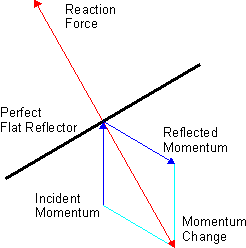
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, Reflection (physics), reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Acoustic Wave
In plasma physics, an ion acoustic wave is one type of longitudinal oscillation of the ions and electrons in a plasma, much like acoustic waves traveling in neutral gas. However, because the waves propagate through positively charged ions, ion acoustic waves can interact with their electromagnetic fields, as well as simple collisions. In plasmas, ion acoustic waves are frequently referred to as acoustic waves or even just sound waves. They commonly govern the evolution of mass density, for instance due to pressure gradients, on time scales longer than the frequency corresponding to the relevant length scale. Ion acoustic waves can occur in an unmagnetized plasma or in a magnetized plasma parallel to the magnetic field. For a single ion species plasma and in the long wavelength limit, the waves are dispersionless (\omega=v_sk) with a speed given by (see derivation below) :v_s = \sqrt where k_\text is the Boltzmann constant, M is the mass of the ion, Z is its charge, T_e is the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Density
In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Volume charge density (symbolized by the Greek letter ρ) is the quantity of charge per unit volume, measured in the SI system in coulombs per cubic meter (C⋅m−3), at any point in a volume. Surface charge density (σ) is the quantity of charge per unit area, measured in coulombs per square meter (C⋅m−2), at any point on a surface charge distribution on a two dimensional surface. Linear charge density (λ) is the quantity of charge per unit length, measured in coulombs per meter (C⋅m−1), at any point on a line charge distribution. Charge density can be either positive or negative, since electric charge can be either positive or negative. Like mass density, charge density can vary with position. In classical electromagnetic theory charge density is idealized as a '' continuous'' scalar function of position \boldsymbol, like a fluid, and \rho(\boldsymbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of Silicon dioxide, SiO2. Quartz is, therefore, classified structurally as a Silicate mineral#Tectosilicates, framework silicate mineral and compositionally as an oxide mineral. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Journal Of Applied Physics
The ''Japanese Journal of Applied Physics'' (JJAP) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1962 and is published by the Japan Society of Applied Physics. From 1982 until 2008, the journal was published in two editions, Part 1 and Part 2: * Part 1 was published monthly and was for regular papers, short notes and review papers. * Part 2 was published semi-monthly and was for letters and express letters. In 2008, Part 2 was separated as an independent journal and renamed ''Applied Physics Express''. Part 1 continues to be published as the ''Japanese Journal of Applied Physics''. In June 2013, the Japan Society of Applied Physics signed an agreement with IOP Publishing for its journals to be published by IOP Publishing. inpublishing.co.uk. 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process: materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an applied electric field. For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measurable piezoelectricity when their static structure is deformed by about 0.1% of the original dimension. Conversely, those same crystals will change about 0.1% of their static dimension when an external electric field is applied. The inverse piezoelectric effect is used in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |