|
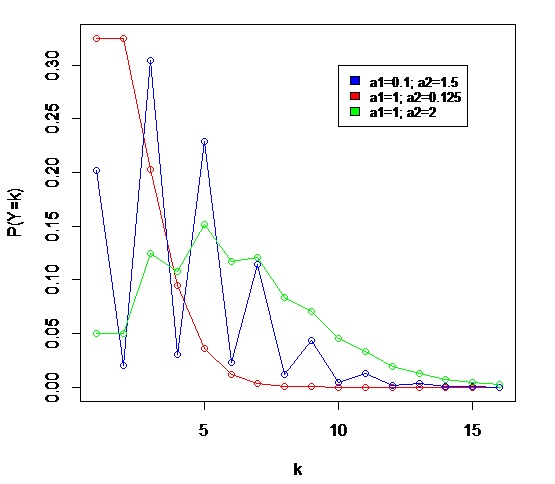
Hermite Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Hermite distribution, named after Charles Hermite, is a discrete probability distribution used to model ''count data'' with more than one parameter. This distribution is flexible in terms of its ability to allow a moderate over-dispersion in the data. The authors Kemp and Kemp have called it "Hermite distribution" from the fact its probability function and the moment generating function can be expressed in terms of the coefficients of (modified) Hermite polynomials. History The distribution first appeared in the paper ''Applications of Mathematics to Medical Problems'', by Anderson Gray McKendrick in 1926. In this work the author explains several mathematical methods that can be applied to medical research. In one of this methods he considered the bivariate Poisson distribution and showed that the distribution of the sum of two correlated Poisson variables follow a distribution that later would be known as Hermite distribution. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMF Hermite
PMF may stand for: * Danish Union of Educators (Danish: ''Pædagogisk Medhjælper Forbund''), a former Danish trade union * Pacific Music Festival, an international classical music festival held annually in Sapporo, Japan * Paramilitary forces, a semi-militarized force * Private military firm, a private company providing armed combat or security services for financial gain. * Parma Airport, Italy (IATA airport code) * Peptide mass fingerprinting, an analytical technique for protein identification * Pierre Mendès France (1907–1982), Prime Minister of France * Polarization-maintaining optical fiber, a type of optical fiber * Polycarbon monofluoride, a graphite compound with fluorine; also known as carbon monofluoride * Popular Mobilization Forces, an Iraqi state-sponsored umbrella organization * Potential of mean force, in chemistry, potential giving the average force on a particle from a set of molecules * Presidential Management Fellows Program, a US government fellowship * Prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when all observed outcomes are assumed to have Normal distributions with the same variance. From the perspective of Bayesian in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurtosis
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from el, κυρτός, ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") is a measure of the "tailedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. Like skewness, kurtosis describes a particular aspect of a probability distribution. There are different ways to quantify kurtosis for a theoretical distribution, and there are corresponding ways of estimating it using a sample from a population. Different measures of kurtosis may have different interpretations. The standard measure of a distribution's kurtosis, originating with Karl Pearson, is a scaled version of the fourth moment of the distribution. This number is related to the tails of the distribution, not its peak; hence, the sometimes-seen characterization of kurtosis as " peakedness" is incorrect. For this measure, higher kurtosis corresponds to greater extremity of deviations (or outliers), and not the configuration of data near the mean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined. For a unimodal distribution, negative skew commonly indicates that the ''tail'' is on the left side of the distribution, and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. In cases where one tail is long but the other tail is fat, skewness does not obey a simple rule. For example, a zero value means that the tails on both sides of the mean balance out overall; this is the case for a symmetric distribution, but can also be true for an asymmetric distribution where one tail is long and thin, and the other is short but fat. Introduction Consider the two distributions in the figure just below. Within each graph, the values on the right side of the distribution taper differently from the values on the left side. These tapering sides are called ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment (mathematics)
In mathematics, the moments of a function are certain quantitative measures related to the shape of the function's graph. If the function represents mass density, then the zeroth moment is the total mass, the first moment (normalized by total mass) is the center of mass, and the second moment is the moment of inertia. If the function is a probability distribution, then the first moment is the expected value, the second central moment is the variance, the third standardized moment is the skewness, and the fourth standardized moment is the kurtosis. The mathematical concept is closely related to the concept of moment in physics. For a distribution of mass or probability on a bounded interval, the collection of all the moments (of all orders, from to ) uniquely determines the distribution (Hausdorff moment problem). The same is not true on unbounded intervals ( Hamburger moment problem). In the mid-nineteenth century, Pafnuty Chebyshev became the first person to think sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the '' arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the '' population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulant Generating Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulants of a probability distribution are a set of quantities that provide an alternative to the '' moments'' of the distribution. Any two probability distributions whose moments are identical will have identical cumulants as well, and vice versa. The first cumulant is the mean, the second cumulant is the variance, and the third cumulant is the same as the third central moment. But fourth and higher-order cumulants are not equal to central moments. In some cases theoretical treatments of problems in terms of cumulants are simpler than those using moments. In particular, when two or more random variables are statistically independent, the -th-order cumulant of their sum is equal to the sum of their -th-order cumulants. As well, the third and higher-order cumulants of a normal distribution are zero, and it is the only distribution with this property. Just as for moments, where ''joint moments'' are used for collections of random var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book '' Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the exponential functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Mass Function
In probability and statistics, a probability mass function is a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. Sometimes it is also known as the discrete density function. The probability mass function is often the primary means of defining a discrete probability distribution, and such functions exist for either scalar or multivariate random variables whose domain is discrete. A probability mass function differs from a probability density function (PDF) in that the latter is associated with continuous rather than discrete random variables. A PDF must be integrated over an interval to yield a probability. The value of the random variable having the largest probability mass is called the mode. Formal definition Probability mass function is the probability distribution of a discrete random variable, and provides the possible values and their associated probabilities. It is the function p: \R \to ,1/math> defined by for - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the possible upper sides of a flipped coin such as heads H and tails T) in a sample space (e.g., the set \) to a measurable space, often the real numbers (e.g., \ in which 1 corresponding to H and -1 corresponding to T). Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup. In the formal mathematical language of measure theory, a rando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |