|
Hermann Rauschning
Hermann Adolf Reinhold Rauschning (7 August 1887 – 8 February 1982) was a German politician and author, adherent of the Conservative Revolution movement who briefly joined the Nazi movement before breaking with it. He was the President of the Senate of the Free City of Danzig, Senate (head of government and chief of state) of the Free City of Danzig from 1933 to 1934. In 1934, he renounced Nazi Party membership and in 1936 emigrated from Germany. He eventually settled in the United States and began openly denouncing Nazism. Rauschning is chiefly known for his book ''Conversations with Hitler, Gespräche mit Hitler'' ("Conversations with Hitler", American title: ''Voice of Destruction'', British title: ''Hitler Speaks'') in which he claimed to have had many meetings and conversations with Adolf Hitler. Early life Rauschning was born in Thorn in the province of West Prussia (then part of the German Empire; now Toruń, Poland) to a Prussian Army officer. He attended the Prussian C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of The Free City Of Danzig
The Senate of the Free City of Danzig was the government of the Free City of Danzig from 1920 to 1939, after the Allied administration of Reginald Tower and the Danzig Staatsrat. Constitutional Regulations The separation of Danzig from the German Reich as a "Free City" without a vote led to the need to draft a constitution. In the Constitution of the Free City of Danzig, articles 25 to 42 detailed and regulated the role of the Senate. The Senate consisted of 7 full-time senators (including the President of the Senate, who was the chairman, and the Deputy President, the Vice Chairman) and 13 honorary senators. The full-time senators were elected from the Volkstag, and served 4-year terms. The honorary senators could serve indefinite terms. Only by a vote of no confidence from the Volkstag could honorary senators be recalled. Even with a dissolution of the Volkstag, the Senate could remain in power. The Senate was the highest state authority. In particular, it had the tasks: * to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German National People's Party
The German National People's Party (, DNVP) was a national-conservative and German monarchy, monarchist political party in Germany during the Weimar Republic. Before the rise of the Nazi Party, it was the major nationalist party in Weimar Germany. It was an alliance of Conservatism in Germany, conservative, German nationalism, nationalist, monarchist, , and antisemitic elements supported by the Pan-German League. Ideologically, the party was described as subscribing to authoritarian conservatism, German nationalism, and monarchism. Until 1931, the party also advocated for National liberalism, national liberal and Protectionism, protectionist economic policies, embracing corporatism, corporatist economic policies from 1931 onwards. Some members like the populist media mogul Alfred Hugenberg embraced Economic nationalism, economic nationalism and Statism, statism. Under Hugenberg the party is seen by some as a ''German Tory conservatism, Tory conservative'' party. It held anti-commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Moeller Van Den Bruck
Arthur Wilhelm Ernst Victor Moeller van den Bruck (23 April 1876 – 30 May 1925) was a German cultural historian, philosopher, and key intellectual figure of the Conservative Revolution. As an author and political theorist, he remains best known for his controversial 1923 book '' Das Dritte Reich'' ("The Third Reich"), which promoted German nationalism and ended up strongly influencing the NSDAP; despite his open opposition and numerous criticisms of Adolf Hitler. From 1906 to 1922, he also published Elisabeth Kaerrick's first full German translation of Dostoyevsky's written works. Biography Moeller van den Bruck was born on 23 April 1876 in Solingen, Westphalia, as the only child of bourgeois parents. His father was Ottomar Victor Moeller, a German state architect, and his mother was Elise van den Bruck, the daughter of Dutch architect van den Broeck and (allegedly) a Spanish mother. Moeller van den Bruck's given name was "Arthur" in honour of Arthur Schopenhauer, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Żuławy Wiślane
Żuławy Wiślane (plural from "żuława", meaning fen), in English known as the Vistula Fens, is the alluvial delta area of the river Vistula, in the northern part of Poland. It is a flat and deforested region comprising wetlands and agricultural plains that cover approximately 1,700 squared kilometres, with much of the land being situated below sea level. Poland's lowest point (1.8 metres below sea level) is located at Raczki Elbląskie in the Żuławy region. The area was largely reclaimed artificially by means of dykes, pumps, channels and an extensive drainage system. Its shape is similar to a reversed triangle formed by branching of Vistula into two separate rivers, Leniwka and Nogat at its height, confined by rivers themselves, and closed by the Vistula Lagoon at its base. Żuławy Wiślane extend from Poland's Pomerania Province in the west to the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship in the east, roughly between the cities of Elbląg, Malbork, Tczew and Gdańsk. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference that ended the World War I, First World War. The main organisation ceased operations on 18 April 1946 when many of its components were relocated into the new United Nations (UN) which was created in the aftermath of the World War II, Second World War. As the template for modern global governance, the League profoundly shaped the modern world. The League's primary goals were stated in its Covenant of the League of Nations, eponymous Covenant. They included preventing wars through collective security and Arms control, disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Its other concerns included labour conditions, just treatment of native inhabitants, Human trafficking, human and Illegal drug tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free City Of Gdansk
The Free City of Danzig (; ) was a city-state under the protection and oversight of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland) and nearly 200 other small localities in the surrounding areas. The polity was created on 15 November 1920 in accordance with the terms of Article 100 (Section XI of Part III) of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles after the end of World War I. Although predominantly German-populated, the territory was bound by the imposed union with Poland covering foreign policy, defence, customs, railways and post, but remained distinct from both the post-war Weimar Republic and the newly independent Polish Republic. In addition, Poland was given certain rights pertaining to port facilities in the city. In the 1920 Constituent Assembly election, the Polish Party received over 6% of the vote, but its percentage of votes later declined to about 3%. A large number of Danzig Poles voted for the Catholic Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poznań Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Poznań Voivodeship () was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in the years 1919–1939, created after World War I from the Prussian-German province of Poznań (Province of Posen). The borders were changed in 1939: the city of Bydgoszcz passed to the Pomeranian Voivodeship, but some eastern areas were included (see Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938). During World War II, it was occupied by Nazi Germany and annexed as ''Reichsgau Wartheland'' "(Reich province of the Land of the Warta River)". Area and counties Between April 1, 1938 and September 1, 1939, the Voivodeship's area was 28 089 km2, and its population - 2 339 600 (according to the 1931 Polish census). It consisted of 29 powiats (the highest number in Poland, however, most of them were very small, both in area and population), 100 towns (the highest number in Poland) and 237 villages. Railroad density was high, with 10.1 km. per 100& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the Armistice with Germany (Compiègne), armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, and agreed certain principles and conditions including the payment of reparations, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. Germany was not allowed to participate in the negotiations before signing the treaty. The treaty German disarmament, required Germany to disarm, make territorial concessions, extradite alleged war criminals, agree to Kaiser Wilhelm being p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
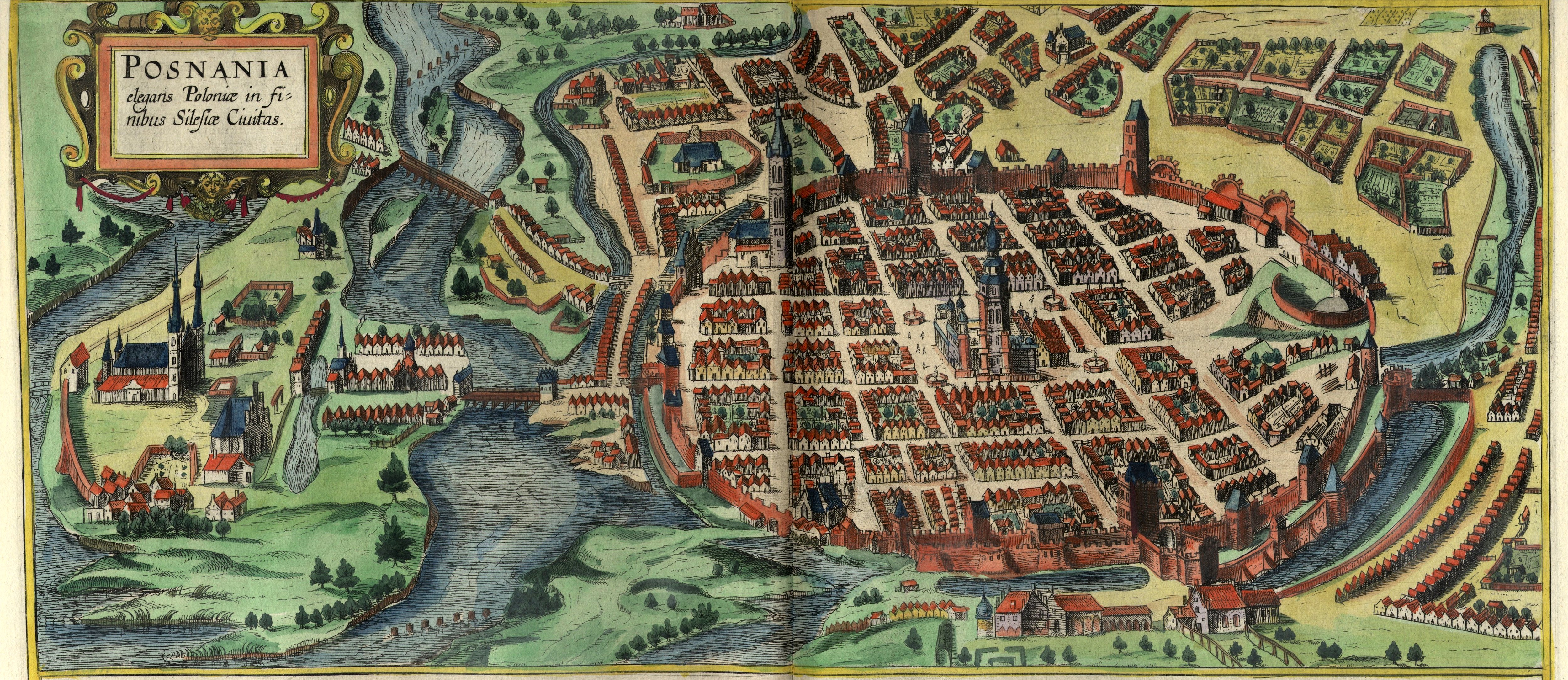
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin University
The Humboldt University of Berlin (, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin, Germany. The university was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named the (Royal) Friedrich Wilhelm University of Berlin (FWU Berlin; ). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around 35,000 students, and offers degree programs in some 171 disciplines from undergra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic languages, Slavic origin. Potsdam was a residence of the Prussian kings and the German Emperor until 1918. Its planning embodied ideas of the Age of Enlightenment: through a careful balance of architecture and landscape, Potsdam was intended as "a picturesque, pastoral dream" which would remind its residents of their relationship with nature and reason. The city, which is over 1,000 years old, is widely known for its palaces, its lakes, and its overall historical and cultural significance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |