|
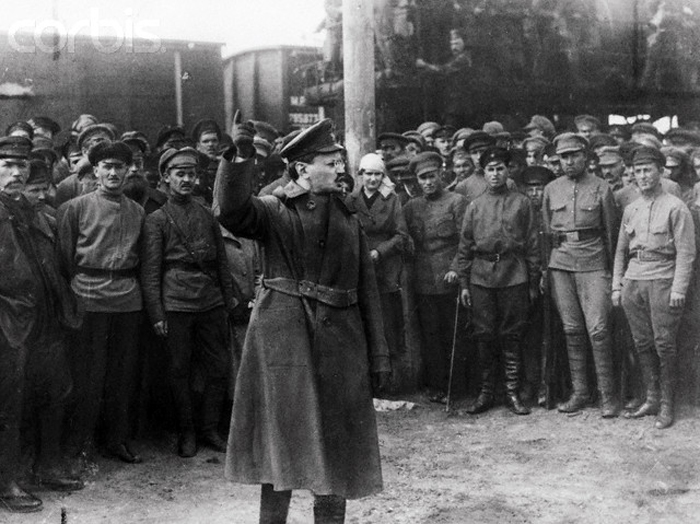
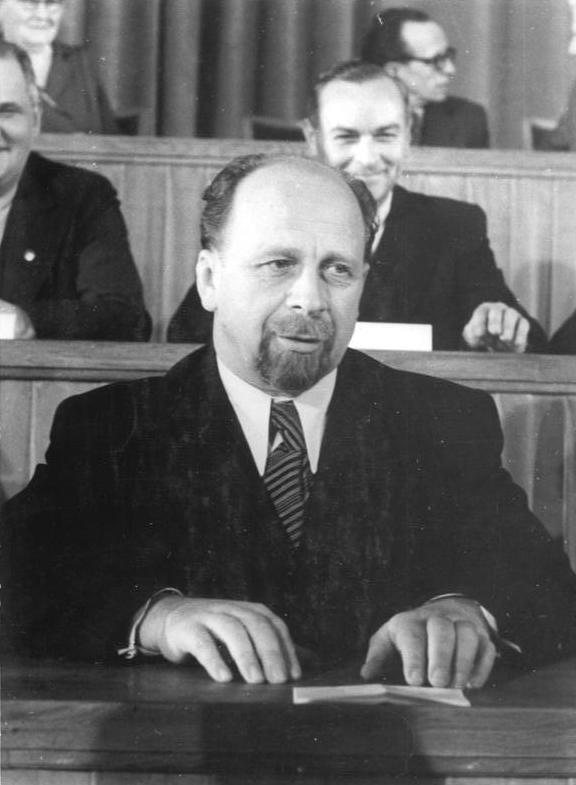
Hermann Matern
Hermann Matern (June 17, 1893 in Burg bei Magdeburg – January 24, 1971 in Berlin) was a German communist politician ( KPD) and high ranking functionary of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany and statesman in the German Democratic Republic. Life and early career Early political activities Matern was the son of a social democratic worker and himself worked as a tanner. He joined the Socialist Youth Workers and later the Social Democratic Party of Germany in 1911. He later resigned from the SPD when the party accepted war loans. During the first World War he served as a soldier in France. In 1918, he joined the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD) and was a participant in the November Revolution and a member of the Workers' and Soldiers' Council Here he was elected commander of the guard regiment in Magdeburg. From 1919 to 1926 he worked as a tanner in Burg, became a member of the KPD and became KPD chairman in Burg, works council chairman, honorary city council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Unity Party Of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (german: Sozialistische Einheitspartei Deutschlands, ; SED, ), often known in English as the East German Communist Party, was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany) from the country's foundation in October 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989. It was a Marxist–Leninist communist party, established in April 1946 as a merger between the East German branches of the Communist Party of Germany and Social Democratic Party of Germany. Although the GDR was a one-party state, some other institutional popular front parties were permitted to exist in alliance with the SED; these parties included the Christian Democratic Union, the Liberal Democratic Party, the Democratic Farmers' Party, and the National Democratic Party. In the 1980s, the SED rejected the liberalisation policies of Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, such as '' perestroika'' and '' glasnost'', which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Masurians and Lithuanians formed minorities. From the 13th century, East Prussia was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Defense Council Of East Germany
The National Defense Council of the German Democratic Republic (German: ''Nationaler Verteidigungsrat der DDR'' - NVR) was created in 1960 as the supreme state body of the German Democratic Republic (also known as East Germany or the GDR) in charge of national defense matters, including mobilization planning. The NVR held the supreme command of the GDR's armed forces (including the internal security forces), and the NVR's chairman was considered the GDR's commander-in-chief. Background The predecessor of the NVR, the ''Security Commission'' of the Politbüro of the Central Committee of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), met for the first time on 6 July 1954. With the enactment of the "Law on the Formation of the National Defense Council of the GDR" on 13 February 1960, the Security Commission was transformed into the NVR. When the State Council was created on 12 September 1960 to replace the office of President, the law creating the State Council (which amended the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkskammer
__NOTOC__ The Volkskammer (, ''People's Chamber'') was the unicameral legislature of the German Democratic Republic (colloquially known as East Germany). The Volkskammer was initially the lower house of a bicameral legislature. The upper house was the Chamber of States, or ''Länderkammer'', but in 1952 the states of East Germany were dissolved, and the Chamber was abolished in 1958. Constitutionally, the Volkskammer was the highest organ of state power in the GDR, and both constitutions vested it with great lawmaking powers. All other branches of government, including the judiciary, were responsible to it. By 1960, the chamber appointed the Council of the State, the Council of Ministers, and the National Defence Council. In practice, however, it was a pseudo-parliament that did little more than rubber-stamp decisions already made by the SED — always by unanimous consent — and listen to the General Secretary's speeches. Membership In October 1949 the ''Volksrat'' cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a List of communist ideologies, communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its Soviet satellite states, satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and various countries in the Non-Aligned Movement and Third World during the Cold War, as well as the Communist International after Bolshevisation. Today, Marxism–Leninism is the ideology of the ruling parties of Chinese Communist Party, China, Communist Party of Cuba, Cuba, Lao People's Revolutionary Party, Laos and Communist Party of Vietnam, Vietnam (all One-party state, one-party 'socialist republics'), as well as many List of communist parties, other communist parties, while Juche, the state ideology of North Korea is derived from Marxism–Leninism. Marxist–Leninist states are commonly referred to as "communist states" by Western academics. Marxism–Leninism holds that a Two-stage theory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Communist Party
The German Communist Party (german: Deutsche Kommunistische Partei, ) is a communist party in Germany. The DKP supports left positions and was an observer member of the European Left. At the end of February 2016 it left the European party. History The DKP considered itself a reconstitution of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD), which had been banned by the Federal Constitutional Court in 1956 for its aggressively militant opposition to the West German constitution. The new party was formed in 1969 by former KPD functionaries in close cooperation with East Germany's ruling party, the Socialist Unity Party (SED), from which the DKP received both political directives and – through covert transfers – most of its funds. The foundation was preceded by talks between former KPD functionaries and Gustav Heinemann, the West German minister of justice, who explained to them that while a refounding of a banned party was not legally possible, Communists were free to form an entirel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the executive committee for communist parties. It is present in most former and existing communist states. Names The term "politburo" in English comes from the Russian ''Politbyuro'' (), itself a contraction of ''Politicheskoye byuro'' (, "Political Bureau"). The Spanish term ''Politburó'' is directly loaned from Russian, as is the German ''Politbüro''. Chinese uses a calque (), from which the Vietnamese (), and Korean ( ''Jeongchiguk'') terms derive. History The first politburo was created in Russia by the Bolshevik Party in 1917 during the Russian Revolution that occurred during that year. The first Politburo had seven members: Lenin, Zinoviev, Kamenev, Trotsky, Stalin, Sokolnikov, and Bubnov. During the 20th century, politburos were established in most Communist states. They included the politburos of the USSR, East Germany, Afghanistan, and Czechoslovakia. Several countries still have a politburo system in operation: Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Litke
Karl may refer to: People * Karl (given name), including a list of people and characters with the name * Karl der Große, commonly known in English as Charlemagne * Karl Marx, German philosopher and political writer * Karl of Austria, last Austrian Emperor * Karl (footballer) (born 1993), Karl Cachoeira Della Vedova Júnior, Brazilian footballer In myth * Karl (mythology), in Norse mythology, a son of Rig and considered the progenitor of peasants (churl) * ''Karl'', giant in Icelandic myth, associated with Drangey island Vehicles * Opel Karl, a car * ST ''Karl'', Swedish tugboat requisitioned during the Second World War as ST ''Empire Henchman'' Other uses * Karl, Germany, municipality in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany * '' Karl-Gerät'', AKA Mörser Karl, 600mm German mortar used in the Second World War * KARL project, an open source knowledge management system * Korean Amateur Radio League, a national non-profit organization for amateur radio enthusiasts in South Korea * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Occupation Zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 1 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly referred to in English as East Germany, was established in the Soviet Occupation Zone. The SBZ was one of the four Allied occupation zones of Germany created at the end of World War II with the Allied victory. According to the Potsdam Agreement, the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (German initials: SMAD) was assigned responsibility for the middle portion of Germany. Eastern Germany beyond the Oder-Neisse line, equal in territory to the SBZ, was to be annexed by Poland and its population expelled, pending a final peace conference with Germany. By the time forces of the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merger Of The KPD And SPD Into The Socialist Unity Party Of Germany
The Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) merged to form the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) on 21 April 1946 in the territory of the Soviet occupation zone. It is considered a forced merger. In the course of the merger, about 5,000 Social Democrats who opposed it were detained and sent to labour camps and jails. Although nominally a merger of equals, the merged party quickly fell under Communist domination. The SED became the ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in 1949; by then, it had become a full-fledged Communist Party–for all intents and purposes, the KPD under a new name. It developed along lines similar to other Communist Parties in what became the Soviet Bloc. The SED would be the only ruling party of the GDR until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in December 1989. Background Among circles of the workers' parties KPD and SPD there were different interpretations of the reasons for the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulbricht Group
The Ulbricht Group was a group of exiled members of the Communist Party of Germany (''Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands'', or KPD), led by Walter Ulbricht, who flew from the Soviet Union back to Germany on April 30, 1945. Composed of functionaries from the KPD and ten anti-fascist prisoners of war, their job was to seek out anti-fascist individuals and prepare the groundwork for the re-establishment of communist organizations and unions in postwar Berlin. There were two additional regional groups, the Ackermann Group in Saxony and the Sobottka Group in Mecklenburg. Many of the group's members later became high-level officials in the government of the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Political operation The tasks for the Ulbricht Group and the other communist cadre who were to return to Germany were defined at a meeting between Wilhelm Pieck and Georgi Dimitrov held in Moscow on April 25, 1945. Dimitrov was then a high-level functionary of the Central Committee of the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Committee For A Free Germany
The National Committee for a Free Germany (german: Nationalkomitee Freies Deutschland, or NKFD) was a German anti-Nazi organization that operated in the Soviet Union during World War II.The Russians in Germany: A History of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, By Norman M. Naimark Published 1995 Harvard University Press Communism and culture/ Germany (East) 586 pages History The rise of the Nazi Party to power in Germany in 1933 led to the outlawing of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and persecutions of its members, many of whom fled to the Soviet Union. With the German invasion of the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa, German prisoners of war began to fall into Soviet hands. Attempts to establish an anti-Nazi organization from these POWs met with little success, since most of them still believed in the final victory of the Wehrmacht. With the German defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad, the number of German POWs increased and their belief in a victorious Germany weakened, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |