|
Herbert Lindlar
Herbert Lindlar-Wilson (15 March 1909 – 27 June 2009), better known as Herbert Lindlar, was a British-Swiss chemist. He is known in particular through the development of his catalyst for hydrogenation, as the Lindlar catalyst bears his name. Biography Lindlar was born in Sheffield, England in March 1909 and moved to Switzerland with his family in 1909. He studied chemistry at the ETH Zurich and the University of Bern and graduated in 1939 with a thesis "about the behavior of dicarboxylic acids in the formation of ureides". He then joined the pharmaceutical company Hoffmann-La Roche F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche (), is a Swiss multinational holding healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on .... With the exception of one four-year hiatus, he worked for Hoffmann-La Roche until retirement in 1974. During these four years in Zurich and Basel, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces Double bond, double and Triple bond, triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The redox, reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
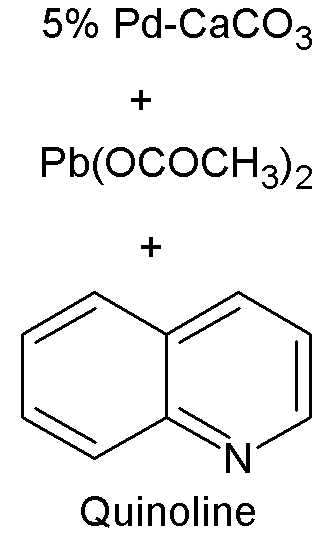
Lindlar Catalyst
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst consisting of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulfate then poisoned with various forms of lead or sulfur. It is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes). It is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar, who discovered it in 1952. Synthesis Lindlar catalyst is commercially available but can also be created by reducing palladium chloride in a slurry of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and adding lead acetate. A variety of other "catalyst poisons" have been used, including lead oxide and quinoline. The palladium content of the supported catalyst is usually 5% by weight. Catalytic properties The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes). The lead serves to deactivate the palladium sites, and further deactivation of the catalyst with quinoline or 3,6-dithia-1,8-octanediol enhances its selectivity, preventin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich (; ) is a public university in Zurich, Switzerland. Founded in 1854 with the stated mission to educate engineers and scientists, the university focuses primarily on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. ETH Zurich ranks among Europe's best universities. Like its sister institution École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL, ETH Zurich is part of the ETH Domain, Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology Domain, a consortium of universities and research institutes under the Swiss Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research. , ETH Zurich enrolled 25,380 students from over 120 countries, of which 4,425 were pursuing doctoral degrees. Students, faculty, and researchers affiliated with ETH Zurich include 22 Nobel Prize, Nobel laureates, two Fields Medalists, three Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize winners, and one Turing Award, Turing Award recipient, including Albert Einstein and John von Neumann. It is a founding member o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bern
The University of Bern (, , ) is a public university, public research university in the Switzerland, Swiss capital of Bern. It was founded in 1834. It is regulated and financed by the canton of Bern. It is a comprehensive university offering a broad choice of courses and programs in eight faculty (division), faculties and some 150 institutes. With around 19,000 students, the University of Bern is the third largest university in Switzerland. Organization The University of Bern operates at three levels: university, faculties and institutes. Other organizational units include interfaculty and general university units. The university's highest governing body is the Senate, which is responsible for issuing statutes, rules and regulations. Directly answerable to the Senate is the University Board of Directors, the governing body for university management and coordination. The board comprises the rector, the vice-rectors and the administrative director. The structures and functions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
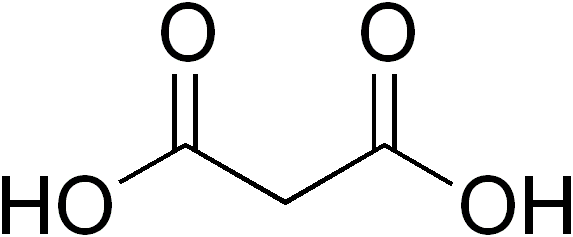
Dicarboxylic Acids
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or Aromatic compound, aromatic.Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to carboxylic acid, monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are usually colorless solids. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are used in industry. Adipic acid, for example, is a precursor to certain kinds of nylon. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are found in nature. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are two amino acids found in all life. Succinic and fumaric acids are essential for metabolism. A large inventory of derivatives are known including many mono- and diesters, amides, etc. Partial list of saturated dicarboxylic acids Some common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureides
Acylureas (also called ''N''-acylureas or ureides) are a class of chemical compounds formally derived from the acylation of urea. Uses Insecticides A subclass of acylureas known as benzoylureas are insecticides. They act as insect growth regulators by inhibiting the synthesis of chitin resulting in weakened cuticles and preventing molting. Members of this class include diflubenzuron, flufenoxuron, hexaflumuron, lufenuron, and teflubenzuron. Anticonvulsants and sedatives The acylurea functional group is also found in some pharmaceutical drugs such as the anticonvulsants phenacemide, pheneturide, chlorphenacemide, and acetylpheneturide (which are phenylureides), and the sedatives acecarbromal, bromisoval, and carbromal (which are bromoureides). Others include apronal (apronalide), capuride, and ectylurea. Barbiturates (a class of cyclic ureas) are structurally and mechanistically related to them. The phenylureides are also closely related to the hydantoins, such as phenyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoffmann-La Roche
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche (), is a Swiss multinational holding healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange. The company headquarters are located in Basel. Roche is the fifth-largest pharmaceutical company in the world by revenue and the leading provider of cancer treatments globally. In 2023, the company’s seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 76. The company owns the American biotechnology company Genentech, which is a wholly owned independent subsidiary, and the Japanese biotechnology company Chugai Pharmaceuticals, as well as the United States–based companies Ventana and Foundation Medicine. Roche's revenues during fiscal year 2020, were 58.32 billion Swiss francs. Descendants of the founding Hoffmann and Oeri families own slightly over half of the bearer shares with voting rights (a pool of family shareholders 45%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centenarian
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100. Because life expectancies at birth worldwide are well below 100, the term is invariably associated with longevity. The United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centenarians worldwide in 2012, and 573,000 in 2020, almost quadruple the 2000 estimate of 151,000. As world population and life expectancy continue to increase, the number of centenarians is expected to increase substantially in the 21st century. According to the Office of National Statistics in the United Kingdom, one-third of babies born in the country in 2013 are expected to live to 100. According to a 1998 United Nations demographic survey, Japan is expected to have 272,000 centenarians by 2050; other sources suggest that the number could be closer to 1 million. The incidence of centenarians in Japan was one per 3,522 people in 2008. In Japan, the population of centenarians is highly skewed towards females. Japan in fiscal year 2016 had 57,52 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1909 Births
Events January–February * January 4 – Explorer Aeneas Mackintosh of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition escapes death by fleeing across drift ice, ice floes. * January 7 – Colombia recognizes the independence of Panama. * January 9 – The British Nimrod Expedition, ''Nimrod'' Expedition to the South Pole, led by Ernest Shackleton, arrives at the Farthest South, farthest south reached by any prior expedition, at 88°23' S, prior to turning back due to diminishing supplies. * January 11 – The International Joint Commission on US-Canada boundary waters is established. * January 16 – Members of the ''Nimrod'' Expedition claim to have found the magnetic South Pole (but the location recorded may be incorrect). * January 24 – The White Star Liner RMS Republic (1903), RMS ''Republic'' sinks the day after a collision with ''SS Florida'' off Nantucket. Almost all of the 1,500 passengers are rescued. * January 28 – The last United States t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Men Centenarians
Swiss most commonly refers to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland *Swiss people Swiss may also refer to: Places * Swiss, Missouri * Swiss, North Carolina * Swiss, West Virginia * Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses * Swiss Café, an old café located in Baghdad, Iraq *Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports * Swiss International Air Lines **Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary *Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland * .swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also *Swiss made, label for Swiss products *Swiss cheese (other) *Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer Schweitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Albert Schweitzer (1875–1965), German theologian, musician, physician, and medical missionary, winner of the 1952 Nobel Peace Priz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |