|
Herasmius
''Herasmius'' is an extinct genus of heterosteid placoderm from the Devonian period. Fossils have been discovered freshwater deposits in Norway and Canada. Description The type species ''Herasmius granulatus'' was discovered in early Eifelian-aged freshwater deposits from the Wood Bay Group on the island of Spitsbergen in the Svalbard archipelago of Norway, and was described in 1966 by Orvig based on an incomplete skull. It was placed in the family Heterostiidae along with the genus '' Heterosteus''. ''Herasmius'' is smaller than ''Heterosteus'', and also differs by having a comparatively broader, shorter skull. A second species, ''Herasmius dayi'', was described in 2017 by Schultze & Cumbaa, found in Lower Devonian marine deposits of the Bear Rock Formation along the Anderson River of Northwest Territories, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
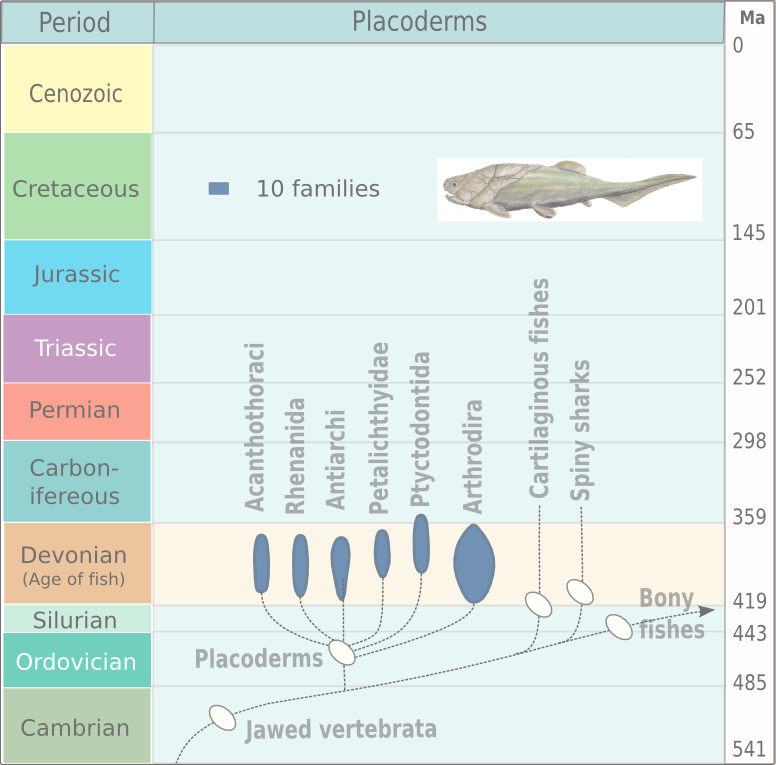
Heterosteidae
Heterosteidae (also known as Heterostiidae) is an extinct family of moderately large to giant, flattened, benthic arthrodire placoderms with distinctive, flattened, triangular skulls that are extremely broad posteriorly, but become very narrow anteriorly. Heterosteidae belongs to the superfamily SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ... Dunkleosteoidea, a relative of the giant '' Dunkleosteus'', as shown in the cladogram below: Genera '' Herasmius'' Orvig, 1969 '' Heterosteus'' Asmuss, 1856 '' Yinostius'' J. Wang & N. Wang, 1984 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q15259423 Arthrodires Placoderm families Early Devonian first appearances Middle Devonian extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosteus
''Heterosteus'' (also known as ''Heterostius'') is an extinct genus of heterosteid placoderm of the Middle Devonian known from remains discovered in Europe and Greenland. Name ''Heterosteus'' was originally described in 1837 as species of '' Trionyx'', a softshelled turtle. Also in later studies it was often misidentified and given names like ''Ichthyosauroides'', '' Asterolepis asmussi'' and ''Chelonichthys asmusii''. Even in recent studies, it is controversial as to whether to use genus name ''Heterosteus'' or ''Heterostius''. According to International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, suffix ‘-ostius’ in scientific name should not be corrected as ‘-osteus’, so some study uses genus name ''Heterostius''. Description This genus includes the largest species in the family, and are among the largest arthrodires, as well, with the type species, ''H. asmussi'', having an estimated body length of up to . The genus differs from ''Herasmius'' by having the orbits on slight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodires
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, '' Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Rolfosteus'' measured j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Journal Of Earth Sciences
The ''Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1963, which reports current research on all aspects of the Earth sciences. It is published by NRC Research Press. The journal also publishes special issues that focus on information and studies limited in scope to a specific segment of the Earth sciences. The editor-in-chief is Dr. Brendan Murphy (St. Francis Xavier University) and Sally Pehrsson (University of Saskatchewan). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 1.369. References External links * {{Authority control Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1963 Canadian Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson River (Northwest Territories)
The Anderson River (Inuvialuktun: ''Kuuk'', river) is in the Northwest Territories in northern Canada. It originates in lakes northwest of Great Bear Lake; its headwaters are possibly on the north side of Colville Lake in the vicinity of the hamlet of Colville Lake.spectacularnwt.com Anderson River Region at Inuvialuit Living History It flows north and west in the area between the Mackenzie and Coppermine Rivers. Its mouth is on the |
Bear Rock Formation
Bear Rock (Dene: Kweteniɂaá) is a geologic formation in the Sahtu Region of the Northwest Territories located across the mouth of the Great Bear River from Tulita. Geology Bear Rock is a lithostratigraphic sedimentary outcropping composed primarily of gypsum, dolomite, limestone, and breccia laid down in the Late Silurian to Middle Devonian (422.9 - 385.3 ma) periods. It is a site of karst features including caves and sinkholes, including one that was featured on Fodor's "15 of Canada's Most Stunning Natural Wonders" list. Marine fossils including acanthodians, brachiopods and corals have been found here. Folklore Bear Rock is said to be the rock over which a mythical hero, known to various Dene groups as either Yamoria, Yamozah, or Zhamba Dezha, stretched the skins of giant beavers after he had slain them to stop them from terrorizing the people. It has been a traditional place of prayer and reflection for these indigenous people for generations. 2019 landslide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Devonian
The Early Devonian is the first of three epochs comprising the Devonian period, corresponding to the Lower Devonian series. It lasted from and began with the Lochkovian Stage , which was followed by the Pragian from and then by the Emsian, which lasted until the Middle Devonian began, . During this time, the first ammonoids appeared, descending from bactritoid nautiloids. Ammonoids during this time period were simple and differed little from their nautiloid counterparts. These ammonoids belong to the order Agoniatitida, which in later epochs evolved to new ammonoid orders, for example Goniatitida and Clymeniida. This class of cephalopod molluscs would dominate the marine fauna until the beginning of the Mesozoic The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Creta ... Era. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |